Question: 7-26. Lagrange multipliers Each function f has an absolute maximum value and absolute minimum value subject to the given constraint. Use Lagrange multipliers to


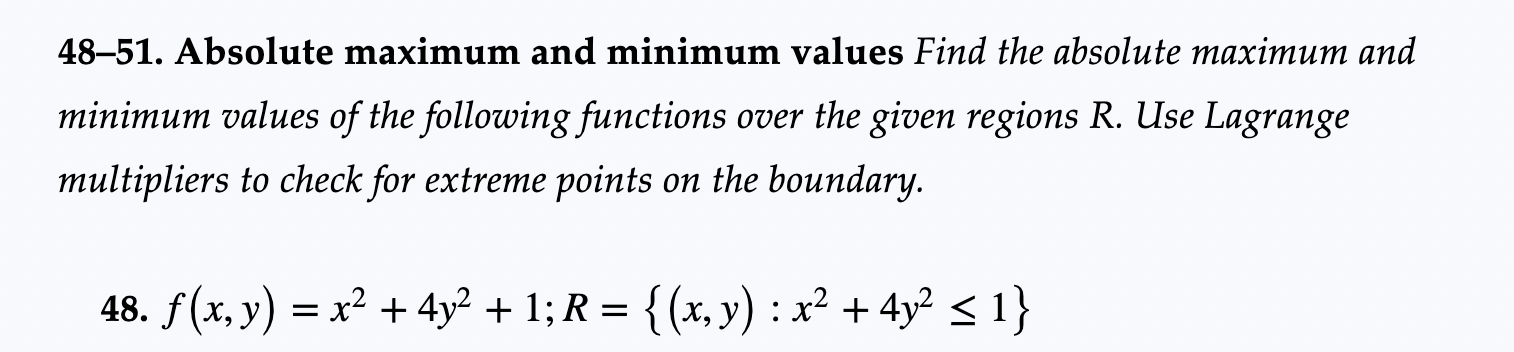

7-26. Lagrange multipliers Each function f has an absolute maximum value and absolute minimum value subject to the given constraint. Use Lagrange multipliers to find these values. 8. f(x, y) = xy subject to x + y = 1 48-51. Absolute maximum and minimum values Find the absolute maximum and minimum values of the following functions over the given regions R. Use Lagrange multipliers to check for extreme points on the boundary. 48. f(x, y) = x +4y + 1; R = {(x, y) : x+4y 1} 60. Geometric and arithmetic means Given positive numbers x1,...,xn, prove that the geometric mean (x1 x2 ... Xn) 1/n is no greater than in the following cases. the arithmetic mean x1+ . +xn n a. Find the maximum value of xyz, subject to x + y + z = k, where k is a positive real number and x > 0, y > 0, and z > 0. Use the result to prove that (xyz) 1/3 < x+y+z 3 b. Generalize part (a) and show that (x1x2 Xn)n ... x1+...+xn n
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


