Question: 8. Computing Fibonacci numbers. Consider the following recursive algorithm for computing the Fibonacci number F(n) on input n > 0: Fib(n): if n 1, define
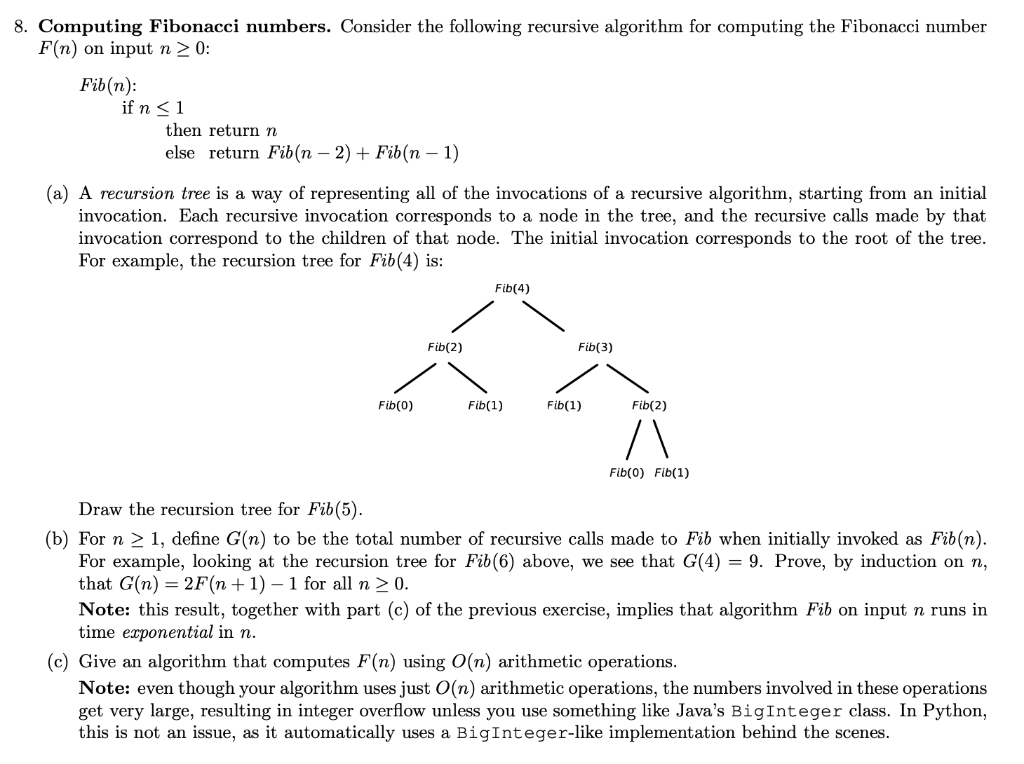
8. Computing Fibonacci numbers. Consider the following recursive algorithm for computing the Fibonacci number F(n) on input n > 0: Fib(n): if n 1, define G(n) to be the total number of recursive calls made to Fib when initially invoked as Fibn). For example, looking at the recursion tree for Fib(6) above, we see that G(4) = 9. Prove, by induction on n, that G(n) = 2F(n+1) - 1 for all n > 0. Note: this result, together with part (c) of the previous exercise, implies that algorithm Fib on input n runs in time exponential in n. (c) Give an algorithm that computes F(n) using O(n) arithmetic operations. Note: even though your algorithm uses just O(n) arithmetic operations, the numbers involved in these operations get very large, resulting in integer overflow unless you use something like Java's BigInteger class. In Python, this is not an issue, as it automatically uses a BigInteger-like implementation behind the scenes
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


