Question: 9. Review Examine the following pseudcode. Inside the Add Numbers module, what is the scope of the variable new.sum? Module Add Numbers (numl, num2): new_sum
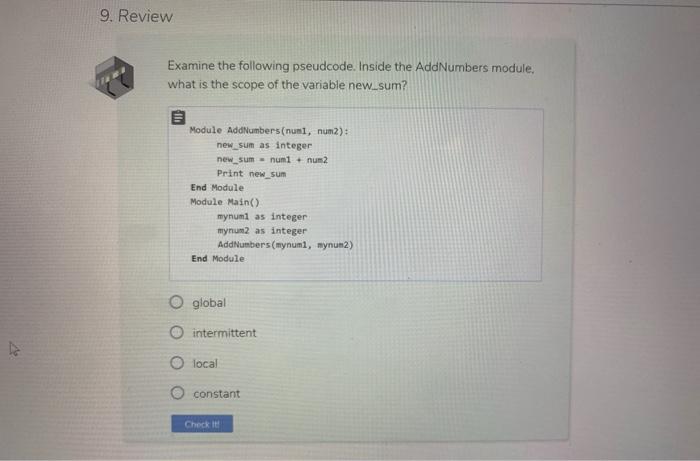
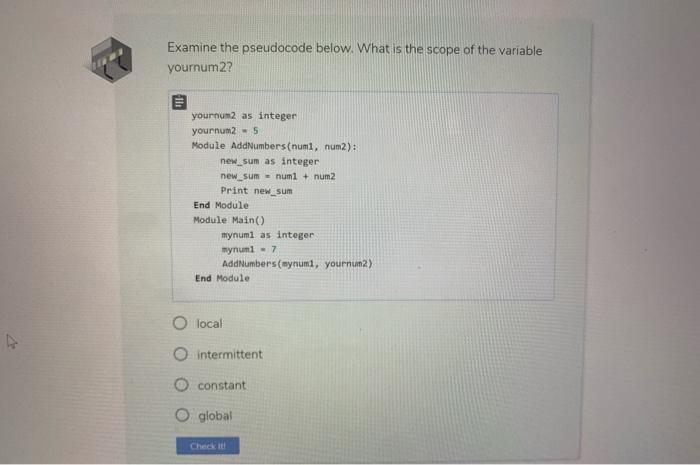
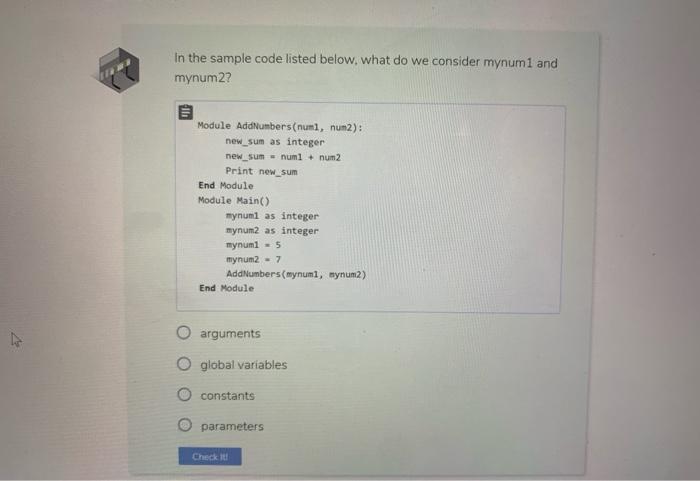
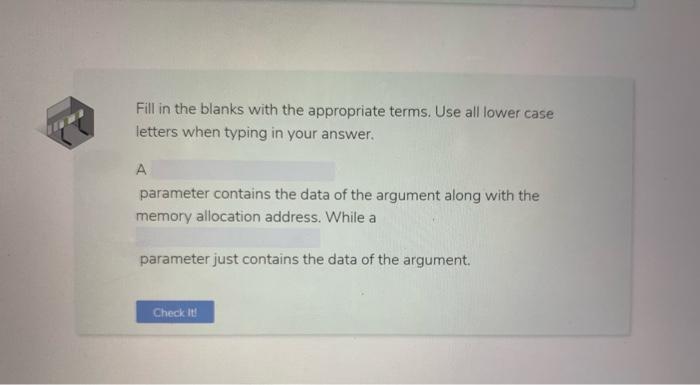
9. Review Examine the following pseudcode. Inside the Add Numbers module, what is the scope of the variable new.sum? Module Add Numbers (numl, num2): new_sum as integer new_sum = num1 + num2 Print new_sum End Module Module Main() mynuml as integer mynum2 as integer Add Numbers (mynumi, mynum2) End Module O global intermittent o local O constant Check it Examine the pseudocode below. What is the scope of the variable yournum2? yournum2 as integer yournum2 - 5 Module AddNumbers (numi, num2): new_sum as integer new_sum- numi + num2 Print new_sum End Module Module Main() mynumi as integer mynuml - 7 Add Numbers (mynumi, yournun2) End Module O local O intermittent O constant global Check it In the sample code listed below, what do we consider mynum 1 and mynum 2? Module AddNumbers(numi, num2): new_sum as integer new_sum = num+ num2 Print new_sum End Module Module Main() mynumi as integer mynum2 as eger mynuml = 5 mynum2 - 7 AddNumbers(mynumi, mynum2) End Module O arguments O global variables constants parameters Check it! Fill in the blanks with the appropriate terms. Use all lower case letters when typing in your answer. A parameter contains the data of the argument along with the memory allocation address. While a parameter just contains the data of the argument. Check it
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


