Question: 9.4. Overriding Methods Coding Exercise In the following example the MeanGreeter inherits the greet() method from Greeter, but then overrides it. Run the program to
9.4. Overriding Methods Coding Exercise
In the following example the MeanGreeter inherits the greet() method from Greeter, but then overrides it. Run the program to see. Add another subclass called SpanishGreeter (or another language that you know) that extends Greeter and override the greet() method to return Hola! (or hi in another language) instead of Hi! Create an object to test it out. 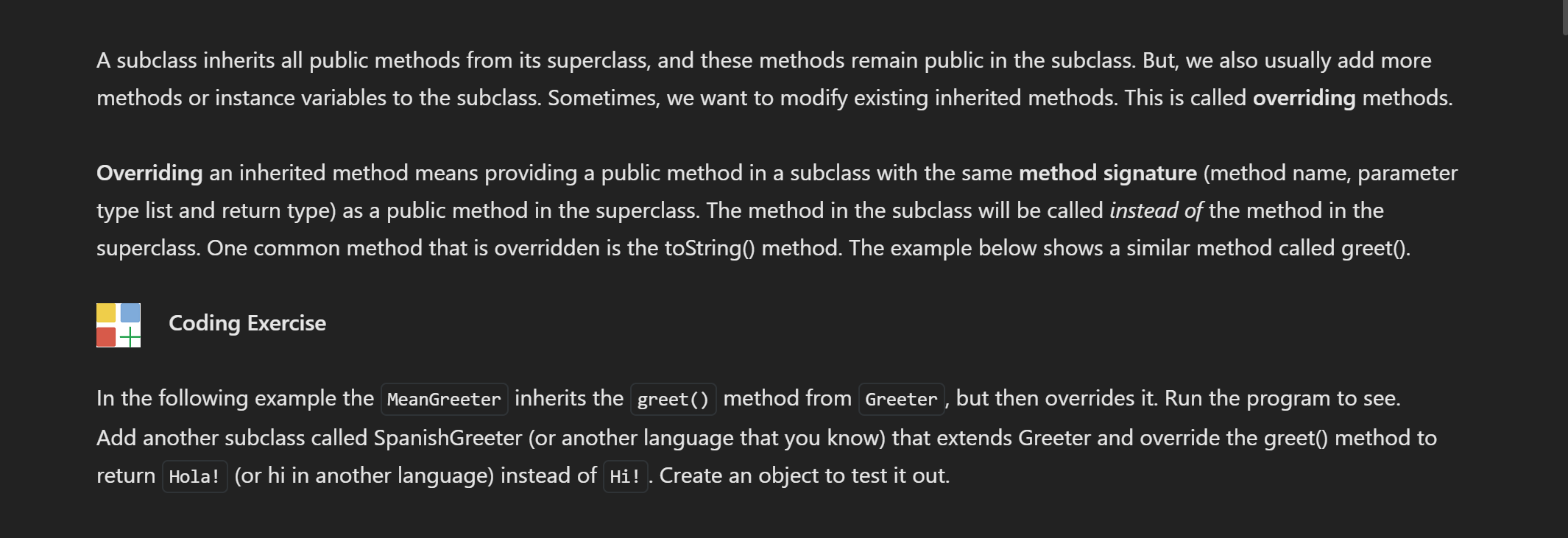
Greeter.java code 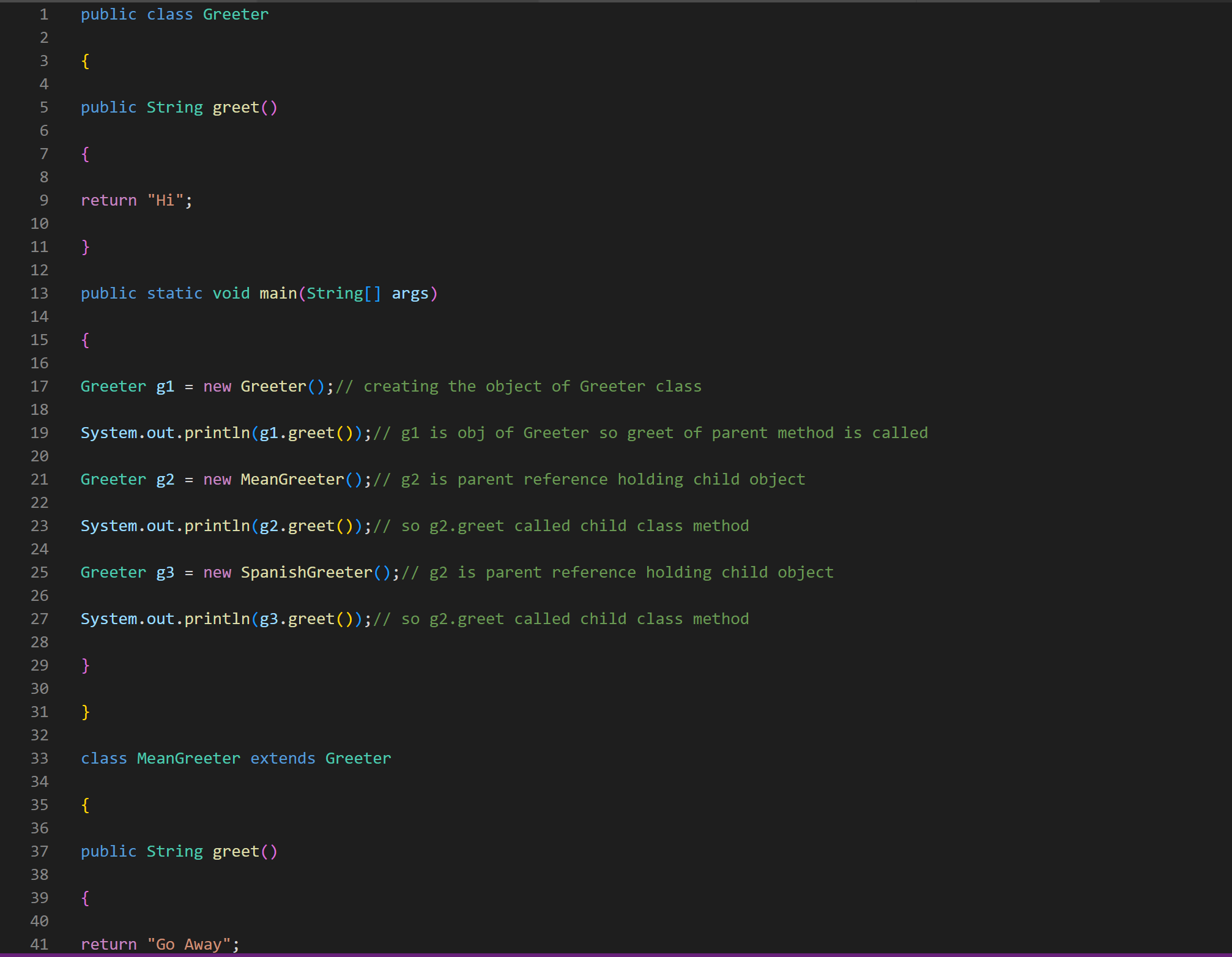
Please answer the coding exercise question and fill in the code completely. Thank you!
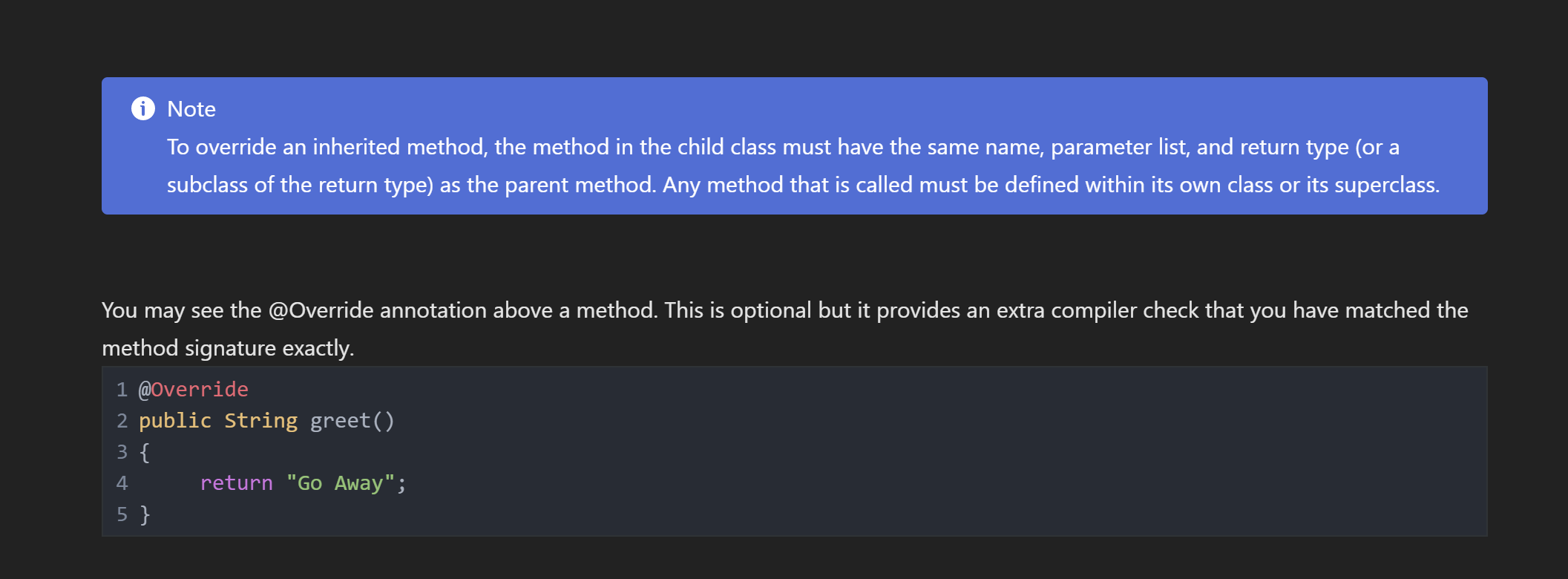
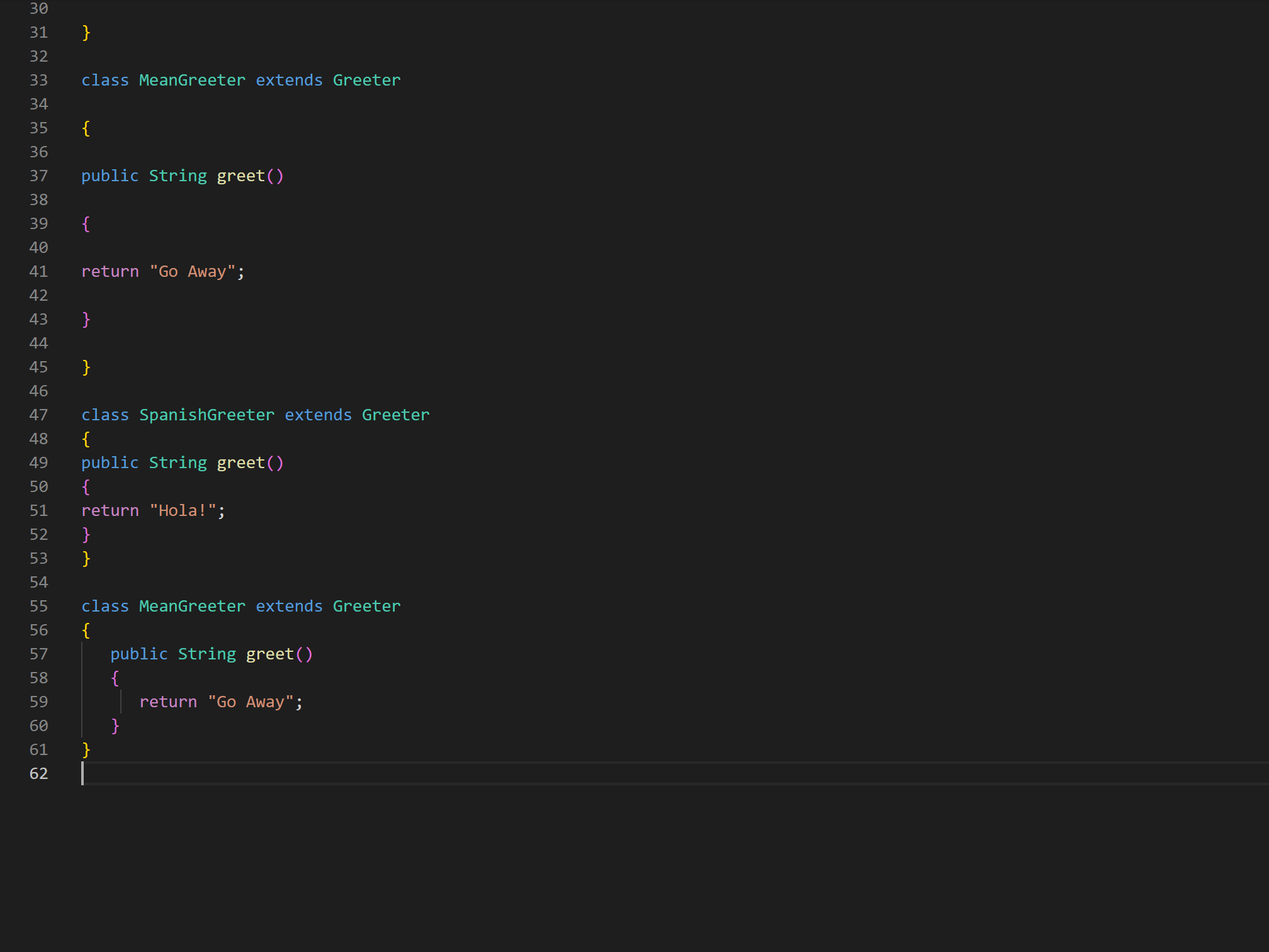
A subclass inherits all public methods from its superclass, and these methods remain public in the subclass. But, we also usually add more methods or instance variables to the subclass. Sometimes, we want to modify existing inherited methods. This is called overriding methods. Overriding an inherited method means providing a public method in a subclass with the same method signature (method name, parameter type list and return type) as a public method in the superclass. The method in the subclass will be called instead of the method in the superclass. One common method that is overridden is the toString( method. The example below shows a similar method called greet(). Coding Exercise In the following example the MeanGreeter inherits the greet() method from Greeter, but then overrides it. Run the program to see. Add another subclass called SpanishGreeter (or another language that you know) that extends Greeter and override the greet() method to return Hola! (or hi in another language) instead of Hi! . Create an object to test it out. (i) Note To override an inherited method, the method in the child class must have the same name, parameter list, and return type (or a subclass of the return type) as the parent method. Any method that is called must be defined within its own class or its superclass. You may see the @Override annotation above a method. This is optional but it provides an extra compiler check that you have matched the method signature exactly. 1 @override 2 public String greet() 3\{ 4 5} return "Go Away"; \{ public String greet() \{ return "Hi"; public static void main(String [] args) \{ Greeter g1= new Greeter ();// creating the object of Greeter class System.out.println(g1.greet());// g1 is obj of Greeter so greet of parent method is called Greeter g2 = new MeanGreeter ();// g2 is parent reference holding child object System.out.println(g2.greet());// so g2.greet called child class method Greeter g3 = new Spanishgreeter();// g2 is parent reference holding child object System.out.println(g3.greet());// so g2.greet called child class method \} \} class Meangreeter extends Greeter \{ public String greet() \{ A subclass inherits all public methods from its superclass, and these methods remain public in the subclass. But, we also usually add more methods or instance variables to the subclass. Sometimes, we want to modify existing inherited methods. This is called overriding methods. Overriding an inherited method means providing a public method in a subclass with the same method signature (method name, parameter type list and return type) as a public method in the superclass. The method in the subclass will be called instead of the method in the superclass. One common method that is overridden is the toString( method. The example below shows a similar method called greet(). Coding Exercise In the following example the MeanGreeter inherits the greet() method from Greeter, but then overrides it. Run the program to see. Add another subclass called SpanishGreeter (or another language that you know) that extends Greeter and override the greet() method to return Hola! (or hi in another language) instead of Hi! . Create an object to test it out. (i) Note To override an inherited method, the method in the child class must have the same name, parameter list, and return type (or a subclass of the return type) as the parent method. Any method that is called must be defined within its own class or its superclass. You may see the @Override annotation above a method. This is optional but it provides an extra compiler check that you have matched the method signature exactly. 1 @override 2 public String greet() 3\{ 4 5} return "Go Away"; \{ public String greet() \{ return "Hi"; public static void main(String [] args) \{ Greeter g1= new Greeter ();// creating the object of Greeter class System.out.println(g1.greet());// g1 is obj of Greeter so greet of parent method is called Greeter g2 = new MeanGreeter ();// g2 is parent reference holding child object System.out.println(g2.greet());// so g2.greet called child class method Greeter g3 = new Spanishgreeter();// g2 is parent reference holding child object System.out.println(g3.greet());// so g2.greet called child class method \} \} class Meangreeter extends Greeter \{ public String greet() \{
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


