Question: a) Air enters a reversible adiabatic diffuser as shown in Fig. Q3 at 90 kPa and 10C. The air enters the diffuser at a
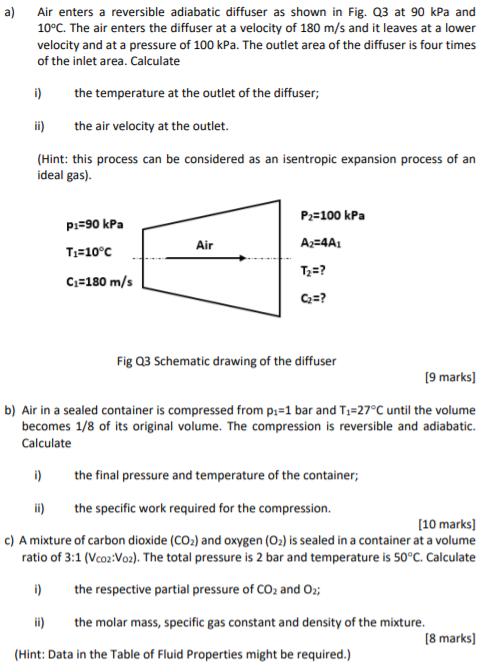
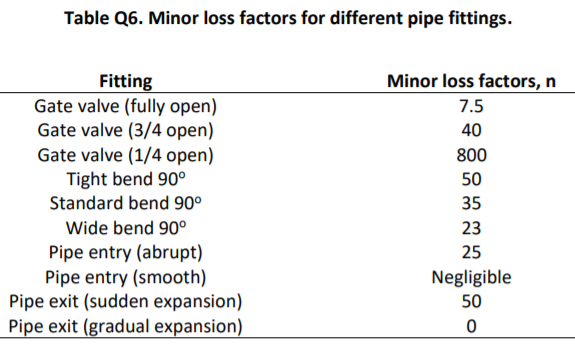
a) Air enters a reversible adiabatic diffuser as shown in Fig. Q3 at 90 kPa and 10C. The air enters the diffuser at a velocity of 180 m/s and it leaves at a lower velocity and at a pressure of 100 kPa. The outlet area of the diffuser is four times of the inlet area. Calculate i) the temperature at the outlet of the diffuser; ii) the air velocity at the outlet. (Hint: this process can be considered as an isentropic expansion process of an ideal gas). P=90 kPa T=10C C=180 m/s Air i) P=100 kPa A2=4A1 T=? C=? Fig Q3 Schematic drawing of the diffuser [9 marks] b) Air in a sealed container is compressed from p=1 bar and T-27C until the volume becomes 1/8 of its original volume. The compression is reversible and adiabatic. Calculate i) the final pressure and temperature of the container; ii) the specific work required for the compression. [10 marks] c) A mixture of carbon dioxide (CO) and oxygen (O) is sealed in a container at a volume ratio of 3:1 (Vcoz:Voz). The total pressure is 2 bar and temperature is 50C. Calculate the respective partial pressure of CO and O2; ii) the molar mass, specific gas constant and density of the mixture. (Hint: Data in the Table of Fluid Properties might be required.) [8 marks] Table Q6. Minor loss factors for different pipe fittings. Fitting Gate valve (fully open) Gate valve (3/4 open) Gate valve (1/4 open) Tight bend 90 Standard bend 90 Wide bend 90 Pipe entry (abrupt) Pipe entry (smooth) Pipe exit (sudden expansion) Pipe exit (gradual expansion) Minor loss factors, n 7.5 40 800 50 35 23 25 Negligible 50 0
Step by Step Solution
3.31 Rating (145 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


