Question: a. Assuming that ABC had no significant permanent differences between book income and taxable income, did income before taxes for financial reporting exceed or fall
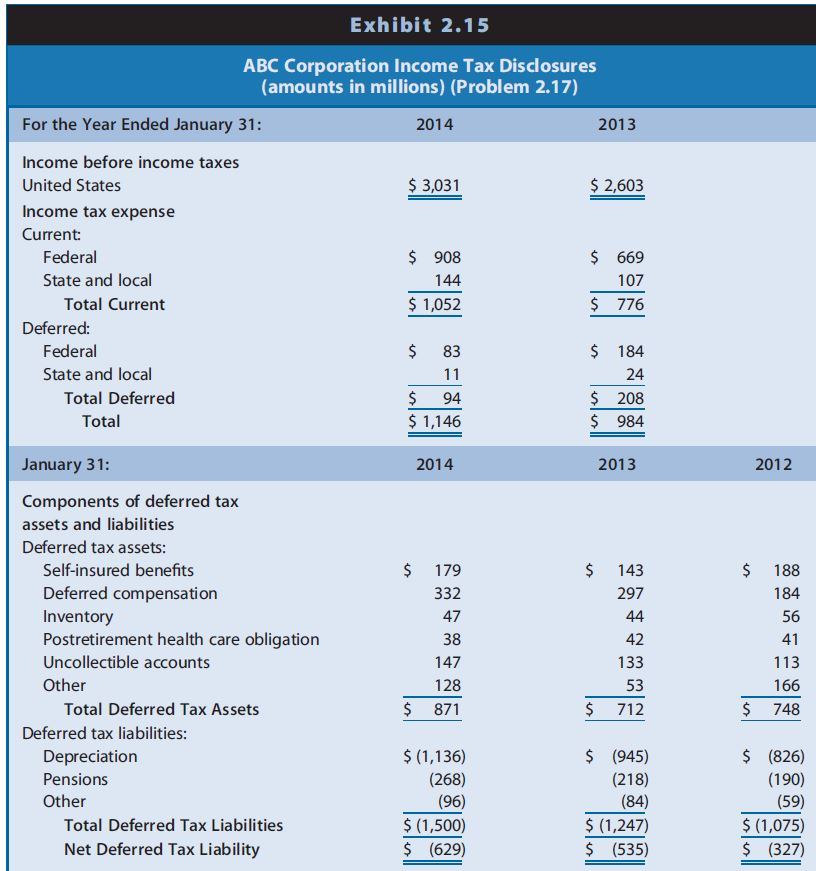
a. Assuming that ABC had no significant permanent differences between book income and taxable income, did income before taxes for financial reporting exceed or fall short of taxable income for 2013? Explain.
b. Did income before taxes for financial reporting exceed or fall short of taxable income for 2014? Explain.
c. Will the adjustment to net income for deferred taxes to compute cash flow from operations in the statement of cash flows result in an addition or a subtraction for 2013? For 2014?
d. ABC does not contract with an insurance agency for property and liability insurance; instead, it self-insures. ABC recognizes an expense and a liability each year for financial reporting to reflect its average expected long-term property and liability losses. When it experiences an actual loss, it charges that loss against the liability. The income tax law permits self-insured firms to deduct such losses only in the year sustained. Why are deferred taxes related to self-insurance disclosed as a deferred tax asset instead of a deferred tax liability? Suggest reasons for the direction of the change in amounts for this deferred tax asset between 2012 and 2014.
e. ABC treats certain storage and other inventory costs as expenses in the year incurred for financial reporting but must include these in inventory for tax reporting. Why are deferred taxes related to inventory disclosed as a deferred tax asset? Suggest reasons for the direction of the change in amounts for this deferred tax asset between 2012 and 2014.
f. Firms must recognize expenses related to postretirement health care and pension obligations as employees provide services, but claim an income tax deduction only when they make cash payments under the benefit plan. Why are deferred taxes related to health care obligation disclosed as a deferred tax asset? Why are deferred taxes related to pensions disclosed as a deferred tax liability? Suggest reasons for the direction of the change in amounts for these deferred tax items between 2012 and 2014.
g. Firms must recognize expenses related to uncollectible accounts when they recognize sales revenues, but claim an income tax deduction when they deem a particular customers accounts uncollectible. Why are deferred taxes related to this item disclosed as a deferred tax asset? Suggest reasons for the direction of the change in amounts for this deferred tax asset between 2012 and 2014.
h. ABC uses the straight-line depreciation method for financial reporting and accelerated depreciation methods for income tax purposes. Why are deferred taxes related to depreciation disclosed as a deferred tax liability? Suggest reasons for the direction of the change in amounts for this deferred tax liability between 2012 and 2014.
Exhibit 2.15 ABC Corporation Income Tax Disclosures amounts in millions) (Problem 2.17) For the Year Ended January 31 Income before income taxes United States Income tax expense Current: 2014 2013 3,031 2,603 Federal State and local $ 908 144 $1,052 669 107 $ 776 Total Current Deferred: $ 184 24 S 208 $984 $ 83 Federal State and local S 94 1,146 Total Deferred Total January 31: 2014 2013 2012 Components of deferred ta:x assets and liabilities Deferred tax assets Self-insured benefits Deferred compensation Inventory Postretirement health care obligation Uncollectible accounts Other $ 179 332 47 38 147 128 $ 871 $ 143 297 $ 188 184 56 42 133 53 113 166 $748 Total Deferred Tax Assets 712 Deferred tax liabilities: (1,136) (268) S (945) (218) Depreciation Pensions Other $ (826) (190) (59) $ (1,075) $ (327) (1,247) S(535) Total Deferred Tax Liabilities $ (1,500) S (629) Net Deferred Tax Liability
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


