Question: {A} {B} {C} {D} {arias} Consider a Ricardian model with two countries [Home 8; Foreign], two goods [X :52 Y}. and one production factor {labor}.

![countries [Home 8; Foreign], two goods [X :52 Y}. and one production](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6677e67428ec2_8126677e67401578.jpg)

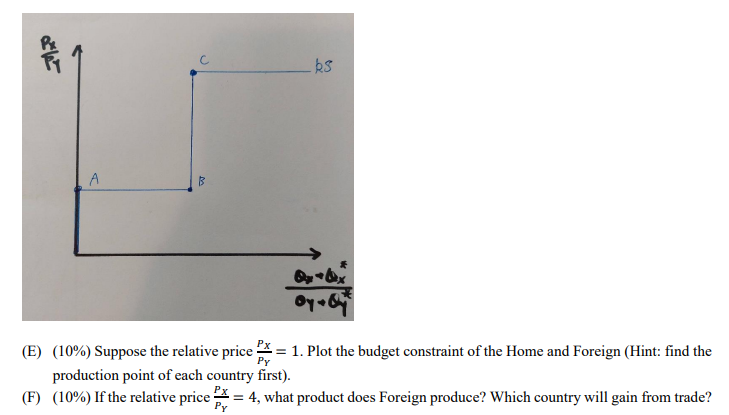
{A} {B} {C} {D} {arias} Consider a Ricardian model with two countries [Home 8; Foreign], two goods [X :52 Y}. and one production factor {labor}. Numbers in the table are labor requirement of each unit of production. Assume that the Home country is endowed with (it) units of labor and the Foreign country is endowed with 100 units of labor. {was} Draw the PP'F of the Home country and the Foreign country. Specify the intercepts and the slope of each PPF. (IUD/u} What is the relative price of '1' [to X} in the Home country and. the Foreign country before trade begins {autarkyj'f' tuna} Which country has an absolute advantage in X? In Y'? Which country has a comparative advantage in X? In Y? {was} The relative supply curve of the two counties is in the gure below. Compute the coordinates of point A, B, and C. C A (E) (10%) Suppose the relative price = = 1. Plot the budget constraint of the Home and Foreign (Hint: find the production point of each country first). (F) (10%) If the relative price -= 4, what product does Foreign produce? Which country will gain from trade
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


