Question: A: B: C: D: E: Let's say the following code is executed on a little-endian computer. uint32_t *p = malloc(8); p[0] = 0x12345678; p[1] =
A:
B:![a little-endian computer. uint32_t *p = malloc(8); p[0] = 0x12345678; p[1] =](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f508ed03cf6_63666f508ec70f6a.jpg) C:
C: 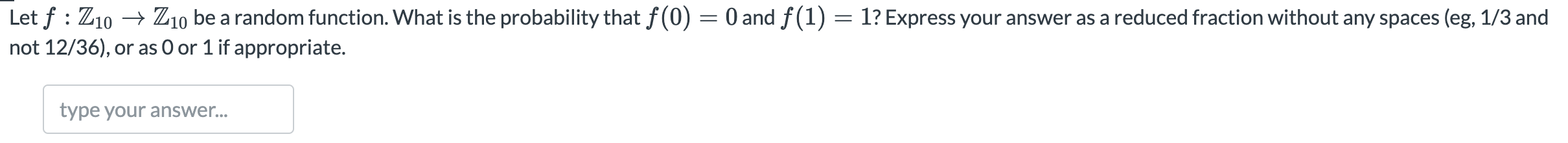 D:
D: 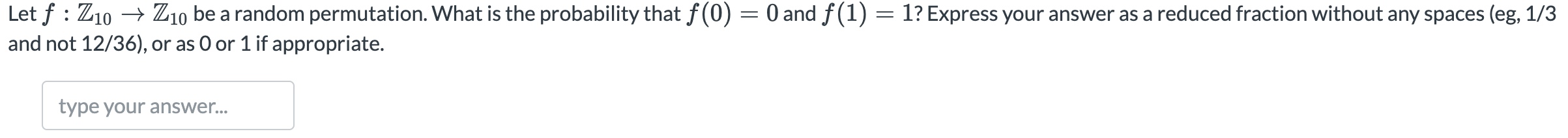 E:
E: 
Let's say the following code is executed on a little-endian computer. uint32_t *p = malloc(8); p[0] = 0x12345678; p[1] = 0x23456789; What are the 8 bytes in memory that begin at the address that's in p? Express as 8 two-digit hexadecimal values with a single space between each (eg, ab cd ef 01 02 03 04 50). You are given a black box f() that contains either a fair coin or a pair of six-sided dice. If f() is a pair of dice, then each invocation of f() rolls the dice, sums the die faces, and reports O if the sum is even and 1 if the sum is odd. If f() is a coin, then each invocation of f() flips the coin and reports O if it's heads and 1 if it's tails. What is the advantage of the following distinguisher? if f() 0 output "dice" else output "coin" The intuition behind this distinguisher is that there are 6 possible even dice outcomes and only five odd ones. Enter your answer as a reduced fraction without any spaces (eg, 1/3 and not 12/36), or as O or 1 if appropriate. Note that the probability that a pair of dice sum to 2,3,4,5,6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 is 1/36,2/36, 3/36, 4/36,5/36,6/36,5/36, 4/36, 3/36, 2/36, 1/36. Let f : Z10 + Z10 be a random function. What is the probability that f(0) = 0 and f(1) = 1? Express your answer as a reduced fraction without any spaces (eg, 1/3 and not 12/36), or as 0 or 1 if appropriate. type your answer... Let f : Z10 Z10 be a random permutation. What is the probability that f(0) = 0 and f(1) = 1? Express your answer as a reduced fraction without any spaces (eg, 1/3 and not 12/36), or as 0 or 1 if appropriate. type your answer... You are given a black box f : Z10 Z10 that contains either a random permutation or a random function. Your distinguisher is allowed to invoke f twice. What is the best advantage you can achieve? Express your answer as a reduced fraction without any spaces (eg, 1/3 and not 12/36), or as 0 or 1 if appropriate. type your answer... Let's say the following code is executed on a little-endian computer. uint32_t *p = malloc(8); p[0] = 0x12345678; p[1] = 0x23456789; What are the 8 bytes in memory that begin at the address that's in p? Express as 8 two-digit hexadecimal values with a single space between each (eg, ab cd ef 01 02 03 04 50). You are given a black box f() that contains either a fair coin or a pair of six-sided dice. If f() is a pair of dice, then each invocation of f() rolls the dice, sums the die faces, and reports O if the sum is even and 1 if the sum is odd. If f() is a coin, then each invocation of f() flips the coin and reports O if it's heads and 1 if it's tails. What is the advantage of the following distinguisher? if f() 0 output "dice" else output "coin" The intuition behind this distinguisher is that there are 6 possible even dice outcomes and only five odd ones. Enter your answer as a reduced fraction without any spaces (eg, 1/3 and not 12/36), or as O or 1 if appropriate. Note that the probability that a pair of dice sum to 2,3,4,5,6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 is 1/36,2/36, 3/36, 4/36,5/36,6/36,5/36, 4/36, 3/36, 2/36, 1/36. Let f : Z10 + Z10 be a random function. What is the probability that f(0) = 0 and f(1) = 1? Express your answer as a reduced fraction without any spaces (eg, 1/3 and not 12/36), or as 0 or 1 if appropriate. type your answer... Let f : Z10 Z10 be a random permutation. What is the probability that f(0) = 0 and f(1) = 1? Express your answer as a reduced fraction without any spaces (eg, 1/3 and not 12/36), or as 0 or 1 if appropriate. type your answer... You are given a black box f : Z10 Z10 that contains either a random permutation or a random function. Your distinguisher is allowed to invoke f twice. What is the best advantage you can achieve? Express your answer as a reduced fraction without any spaces (eg, 1/3 and not 12/36), or as 0 or 1 if appropriate. type your
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


