Question: a) b) c) If you write a class and do not include a no-arg constructor, Java will provide one for you by default that will
a)
 b)
b)
 c)
c)
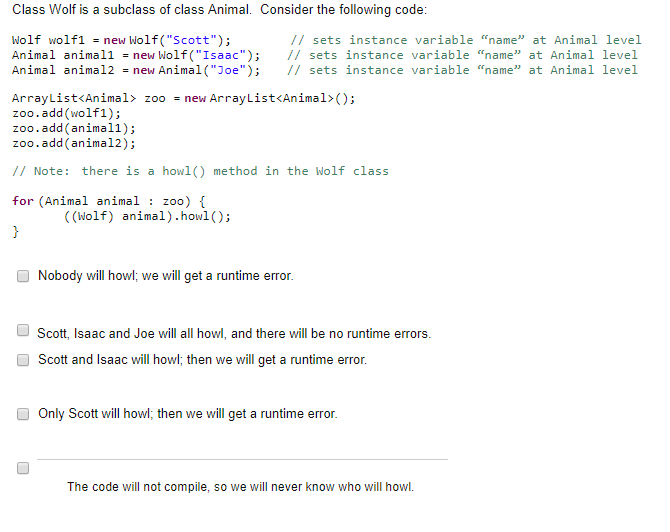
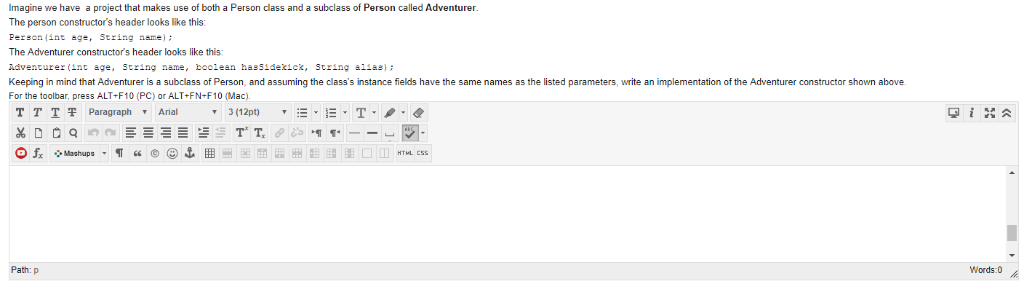
If you write a class and do not include a no-arg constructor, Java will provide one for you by default that will set all of the fields to their default values, object references will be set to NULL, numeric values set to 0, and booleans set to false. However for this to work, your class's parent must have its own no-arg constructor True False Imagine we have a project that makes use of both a Person class and a subclass of Person called Adventurer The person constructor's header looks like this Person (int age, String name) The Adventurer constructor's header looks like this Adventure(nage, String name, boolean haeSidexie, String alias) Keeping in mind that Adventurer is a subclass of Person, and assuming the class's instance fields have the same names as the listed parameters, write an implementation of the Adventurer constructor shown above For the toolbar, press ALT+F10 (PC) or ALT+FN-F10 (Mac) T T | Paragraph Anal 3(12pt) Path: p Words 0 Class Wolf is a subclass of class Animal. Consider the following code: wolf wolfi - new Wolf("Scott") Animal animall -new Wolf("Isaac"); Animal animal2 new Animal ("Joe"); // sets instance variable "name at Animal level // sets instance variable "name" at Animal level // sets instance variable "name" at Animal level ArrayList
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


