Question: a) Back-testing indicates how well the Value-at-Risk (VaR) estimates have performed in the past. For example, if the back-testing shows that 10-day 99% VaR has
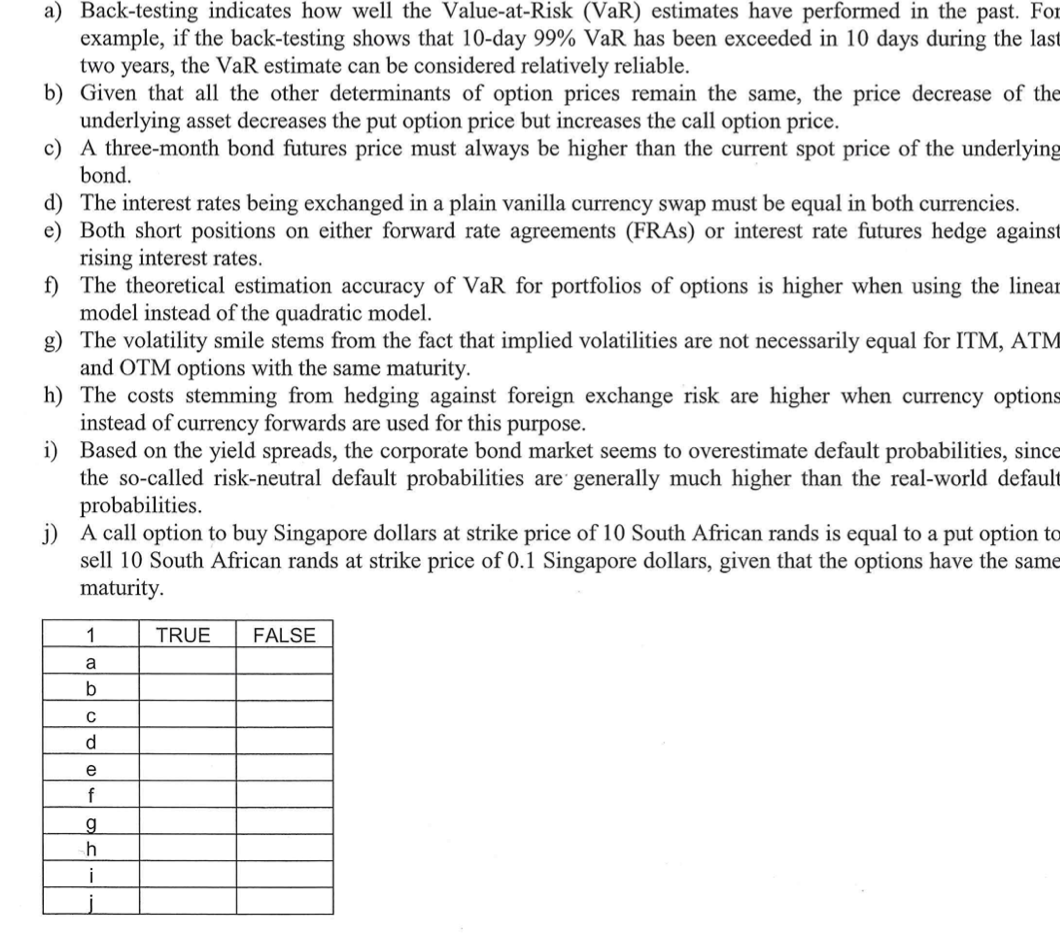
a) Back-testing indicates how well the Value-at-Risk (VaR) estimates have performed in the past. For example, if the back-testing shows that 10-day 99% VaR has been exceeded in 10 days during the last two years, the VaR estimate can be considered relatively reliable. b) Given that all the other determinants of option prices remain the same, the price decrease of the underlying asset decreases the put option price but increases the call option price. c) A three-month bond futures price must always be higher than the current spot price of the underlying bond. d) The interest rates being exchanged in a plain vanilla currency swap must be equal in both currencies. e) Both short positions on either forward rate agreements (FRAs) or interest rate futures hedge against rising interest rates. f) The theoretical estimation accuracy of VaR for portfolios of options is higher when using the linear model instead of the quadratic model. g) The volatility smile stems from the fact that implied volatilities are not necessarily equal for ITM, ATM and OTM options with the same maturity. h) The costs stemming from hedging against foreign exchange risk are higher when currency options instead of currency forwards are used for this purpose. i) Based on the yield spreads, the corporate bond market seems to overestimate default probabilities, since the so-called risk-neutral default probabilities are generally much higher than the real-world default probabilities. j) A call option to buy Singapore dollars at strike price of 10 South African rands is equal to a put option to sell 10 South African rands at strike price of 0.1 Singapore dollars, given that the options have the same maturity. 1 TRUE FALSE a b d e f g h i a) Back-testing indicates how well the Value-at-Risk (VaR) estimates have performed in the past. For example, if the back-testing shows that 10-day 99% VaR has been exceeded in 10 days during the last two years, the VaR estimate can be considered relatively reliable. b) Given that all the other determinants of option prices remain the same, the price decrease of the underlying asset decreases the put option price but increases the call option price. c) A three-month bond futures price must always be higher than the current spot price of the underlying bond. d) The interest rates being exchanged in a plain vanilla currency swap must be equal in both currencies. e) Both short positions on either forward rate agreements (FRAs) or interest rate futures hedge against rising interest rates. f) The theoretical estimation accuracy of VaR for portfolios of options is higher when using the linear model instead of the quadratic model. g) The volatility smile stems from the fact that implied volatilities are not necessarily equal for ITM, ATM and OTM options with the same maturity. h) The costs stemming from hedging against foreign exchange risk are higher when currency options instead of currency forwards are used for this purpose. i) Based on the yield spreads, the corporate bond market seems to overestimate default probabilities, since the so-called risk-neutral default probabilities are generally much higher than the real-world default probabilities. j) A call option to buy Singapore dollars at strike price of 10 South African rands is equal to a put option to sell 10 South African rands at strike price of 0.1 Singapore dollars, given that the options have the same maturity. 1 TRUE FALSE a b d e f g h
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


