Question: A chilled air conditioning system is to be designed for a three-story office complex, as outlined in Figure. Ethylene glycol, a commonly employed heat
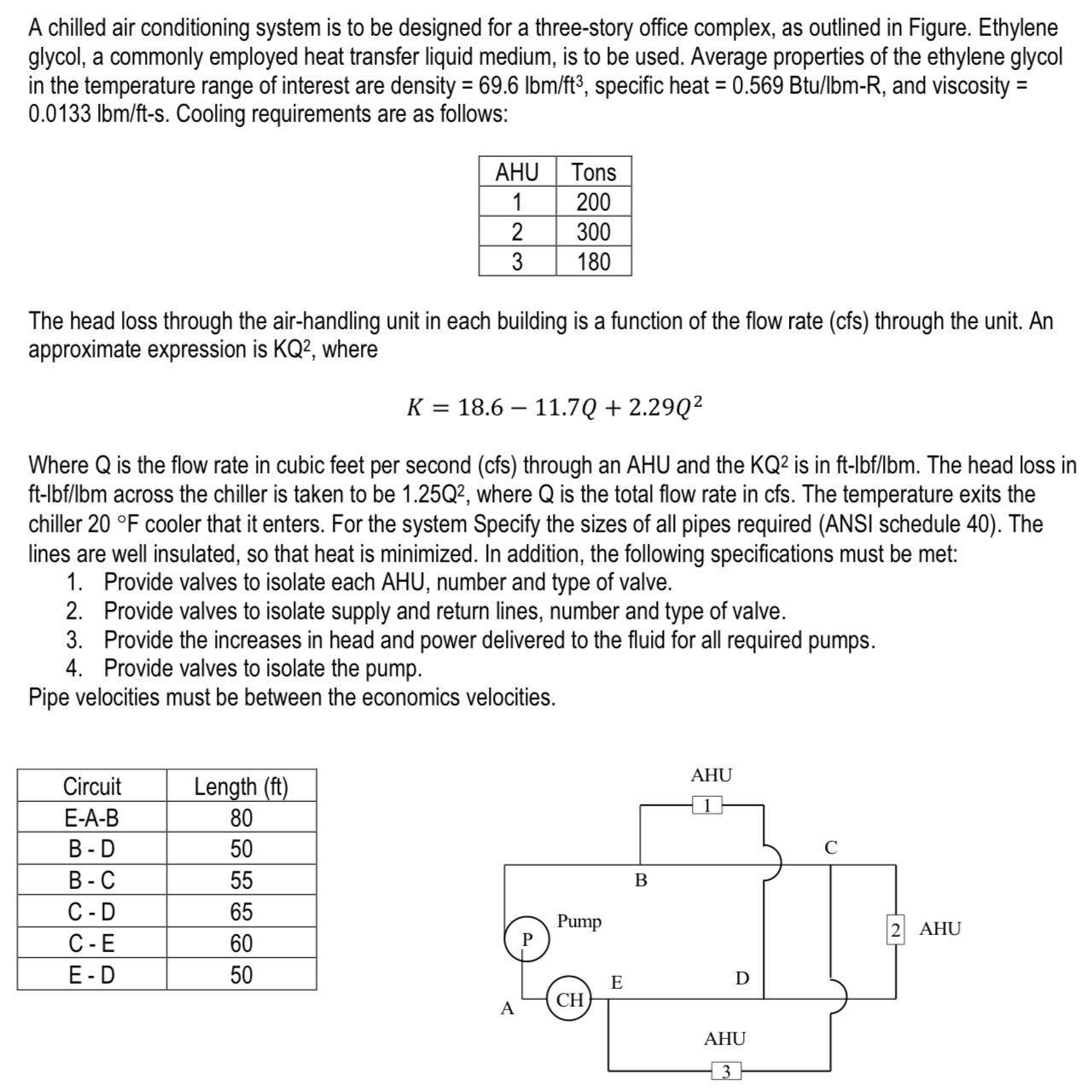
A chilled air conditioning system is to be designed for a three-story office complex, as outlined in Figure. Ethylene glycol, a commonly employed heat transfer liquid medium, is to be used. Average properties of the ethylene glycol in the temperature range of interest are density = 69.6 lbm/ft, specific heat = 0.569 Btu/lbm-R, and viscosity = 0.0133 lbm/ft-s. Cooling requirements are as follows: AHU Tons 1 200 300 3 180 The head loss through the air-handling unit in each building is a function of the flow rate (cfs) through the unit. An approximate expression is KQ2, where K = 18.6 11.70 +2.2902 Where Q is the flow rate in cubic feet per second (cfs) through an AHU and the KQ2 is in ft-lbf/lbm. The head loss in ft-lbf/lbm across the chiller is taken to be 1.25Q2, where Q is the total flow rate in cfs. The temperature exits the chiller 20 F cooler that it enters. For the system Specify the sizes of all pipes required (ANSI schedule 40). The lines are well insulated, so that heat is minimized. In addition, the following specifications must be met: 1. Provide valves to isolate each AHU, number and type of valve. 2. Provide valves to isolate supply and return lines, number and type of valve. 3. Provide the increases in head and power delivered to the fluid for all required pumps. 4. Provide valves to isolate the pump. Pipe velocities must be between the economics velocities. AHU Circuit Length (ft) E-A-B 80 B-D 50 B-C 55 B C-D 65 Pump AHU C-E 60 P E-D 50 E D CH A AHU 3
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


