Question: A circuit that detects a pattern 110 and 1010, from serial input data, with an overlap in the patterns is to be developed. The

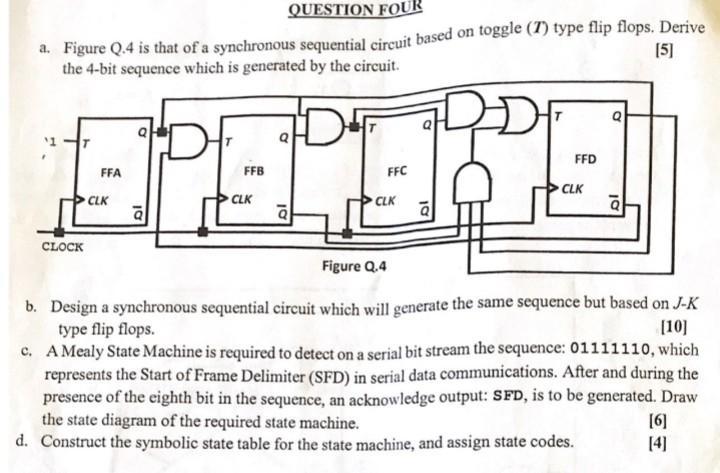
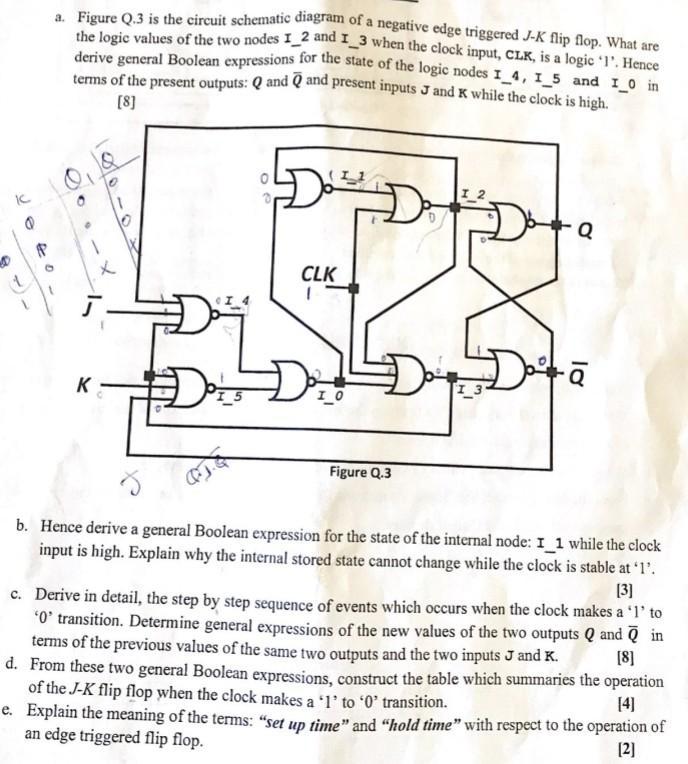
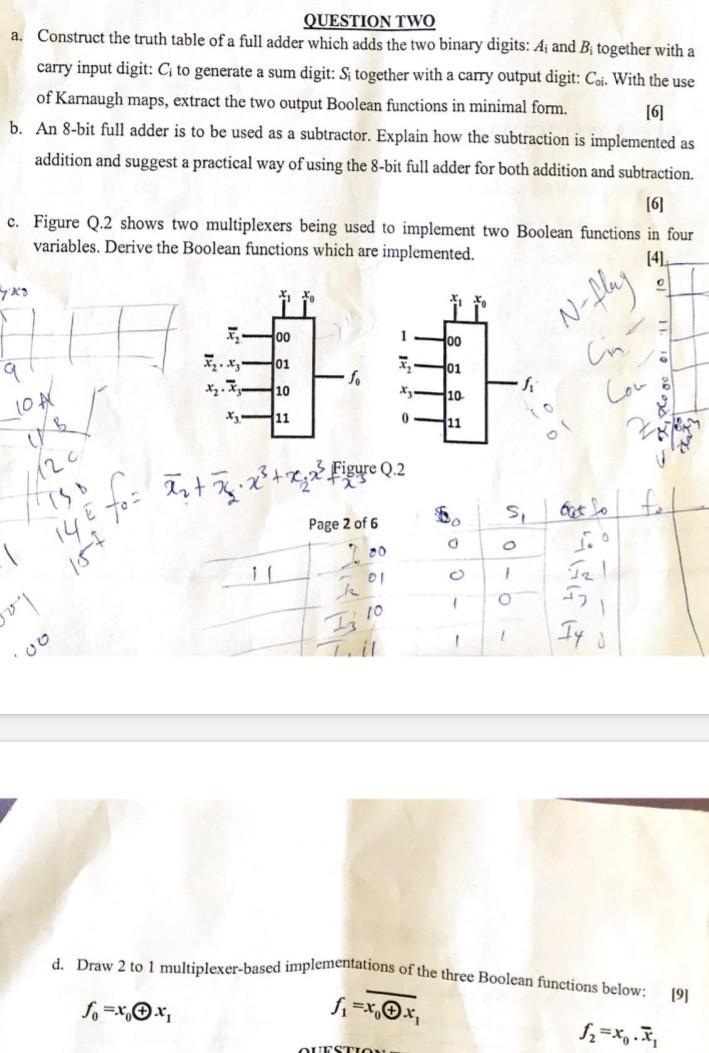

A circuit that detects a pattern 110 and 1010, from serial input data, with an overlap in the patterns is to be developed. The circuit is supposed to give an output of 'I' which coincides with the last bit of each of the patterns. a. Develop a state diagram for the pattern detector. b. Make a state assignment for the pattern detector. c. Using T flip flops Develop a state table for the pattern detector. d. Using Karnaugh maps deduce the steering functions for the pattern detector. [6] [2] [10] [7] QUESTION FOUR a. Figure Q.4 is that of a synchronous sequential circuit based on toggle (1) type flip flops. Derive the 4-bit sequence which is generated by the circuit. CLOCK FFA CLK PERERE CLK 10 FFB CLK FFC FFD CLK [5] Figure Q.4 b. Design a synchronous sequential circuit which will generate the same sequence but based on J-K type flip flops. [10] c. A Mealy State Machine is required to detect on a serial bit stream the sequence: 01111110, which represents the Start of Frame Delimiter (SFD) in serial data communications. After and during the presence of the eighth bit in the sequence, an acknowledge output: SFD, is to be generated. Draw the state diagram of the required state machine. d. Construct the symbolic state table for the state machine, and assign state codes. [6] [4] k a. Figure Q.3 is the circuit schematic diagram of a negative edge triggered J-K flip flop. What are the logic values of the two nodes 1-2 and 1-3 when the clock input, CLK, is a logic '1'. Hence derive general Boolean expressions for the state of the logic nodes I_4, 1_5 and I_0 in terms of the present outputs: Q and Q and present inputs J and K while the clock is high. [8] K I_5 CLK Figure Q.3 Q % I_3 b. Hence derive a general Boolean expression for the state of the internal node: I_1 while the clock input is high. Explain why the internal stored state cannot change while the clock is stable at '1'. [3] c. Derive in detail, the step by step sequence of events which occurs when the clock makes a '1' to '0' transition. Determine general expressions of the new values of the two outputs Q and in terms of the previous values of the same two outputs and the two inputs J and K. [8] d. From these two general Boolean expressions, construct the table which summaries the operation of the J-K flip flop when the clock makes a '1' to '0' transition. [4] e. Explain the meaning of the terms: "set up time" and "hold time" with respect to the operation of an edge triggered flip flop. [2] 00 QUESTION TWO a. Construct the truth table of a full adder which adds the two binary digits: A and B together with a carry input digit: Ci to generate a sum digit: S; together with a carry output digit: Coi. With the use of Karnaugh maps, extract the two output Boolean functions in minimal form. [6] b. An 8-bit full adder is to be used as a subtractor. Explain how the subtraction is implemented as addition and suggest a practical way of using the 8-bit full adder for both addition and subtraction. [6] c. Figure Q.2 shows two multiplexers being used to implement two Boolean functions in four variables. Derive the Boolean functions which are implemented. ' 9 10/ I 00 1 100 x.x 01 x 01 So X.X- 10 3 10 11 0 11 TO N-flay Cin Con [4] = 145 for + 76.2 + x2 Figure Q.2 Page 2 of 6 SI Get So 80 0 0 01 0 1 h 10 Is 1 1.0 d. Draw 2 to 1 multiplexer-based implementations of the three Boolean functions below: f =xx 1 =xx QUESTION [9] fol a. Convert -34 and -56into 8-bit signed two's complement numbers. [4] b. Add the two numbers in binary and write down the state of the five Arithmetic Status flags. [7] c. Comment on the validity of the 8-bit result and verify your observation by converting the 8-bit binary result back into decimal. d. Convert the following Hexadecimal numbers into Octal: [2] i. $9C ii. $F1 iii. $D0 e. Convert the following decimal numbers to their Gray Code equivalents: i. 90 [1] [1] [1] EEE [2] [2] [5] f. Convert 57 and 74 into Binary Coded Decimal (BCD), and show how these numbers can be ii. 45 added together in BCD.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


