Question: a) Consider a depth-first search on the graph above, starting with node a. Which nodes are visited, and in what order? Use the convention that
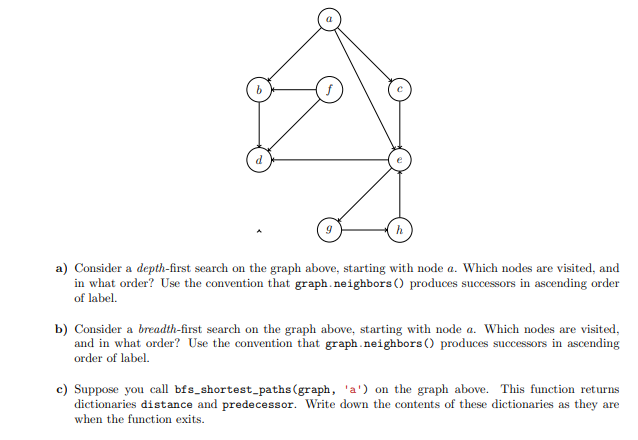
a) Consider a depth-first search on the graph above, starting with node a. Which nodes are visited, and in what order? Use the convention that graph neighbors () produces successors in ascending order of label. b) Consider a breadth-first search on the graph above, starting with node a. Which nodes are visited, and in what order? Use the convention that graph.neighbors () produces successors in ascending order of label. c) Suppose you call bfs_shortest_paths (graph, 'a') on the graph above. This function returns dictionaries distance and predecessor. Write down the contents of these dictionaries as they are when the function exits. a) Consider a depth-first search on the graph above, starting with node a. Which nodes are visited, and in what order? Use the convention that graph neighbors () produces successors in ascending order of label. b) Consider a breadth-first search on the graph above, starting with node a. Which nodes are visited, and in what order? Use the convention that graph.neighbors () produces successors in ascending order of label. c) Suppose you call bfs_shortest_paths (graph, 'a') on the graph above. This function returns dictionaries distance and predecessor. Write down the contents of these dictionaries as they are when the function exits
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


