Question: A. Consider a mine waste facility. The waste is silty sandy gravel and gravelly silty sand coarse rejected from coal washing. The potential disjoint failure
A. Consider a mine waste facility. The waste is silty sandy gravel and gravelly silty sand coarse rejected from coal washing. The potential disjoint failure modes of the facility are:
- Culvert runs full, water leaks, saturates downstream toe, and causes slide.
- Culvert collapses, flow saturates downstream toe, and causes slide.
- A bigger flood, causes the culvert overflow, saturates fill, and causes slide.
- Rainfall infiltrates the rock mass and remobilizes slide.
- Earthquake causes liquefaction.
Based on the hydrology of the catchment, the hydraulics of the culvert, stability analyses and engineering judgment, it is estimated that:
1) the frequency of landsliding of the waste for each one of the failure modes I to IV is 0.0014 per annum.
2) the frequency of landsliding for mode (V) is 0.0014 per annum.
Calculate the frequency of landsliding per annum. Enter the answer to 4 dp with no units.
B. A group of mining companies conducted an empirical study on flyrock in 2500 mine sites. The study showed that, over a period of 10 years, 467 flyrock incidents took place. 117 of these incidents caused injuries and 2 of the 117 injuries were fatal. The probability of flyrock affecting a person at risk is 0.05.
Estimate the probability of fatality given injury.
Provide your answer to 3 dp.
C. A survey finds that the probability a commercial van driver has a passenger in the van is 0.28. Expert opinion indicates that the likelihood of a commercial driver having an accident when the passenger seat is occupied is 0.30 of that of getting into a collision when the passender seat is not occupied.
Given a collision has occurred, what is the probability of the passenger seat in a commercial van was occupied?
Report results to 3 DP.
D. A group of mining companies conducted an empirical study on flyrock in 2355 mine sites. The study showed that, over a period of 10 years, 437 flyrock incidents took place. 106 of these incidents caused injuries and 2 of the 106 injuries were fatal.
Estimate the probability of a fatality associated with a fly rock at a single mine per annum.
Provide your answer to 5 dp.
E. The probability of an earthquake incident at a mine site in a single year is 0.40.
Consider a particular mine site X where 73 employees work 12 hours/day, 329 days/year in the pit and are therefore in the exposure zone of the incident. For people in the exposure zone there is a 0.10 probability that an earthquake incident will result in injury.
What is the probability that there is injury from earthquake on that site in a year?
Enter your answer to 3 dp.
F.
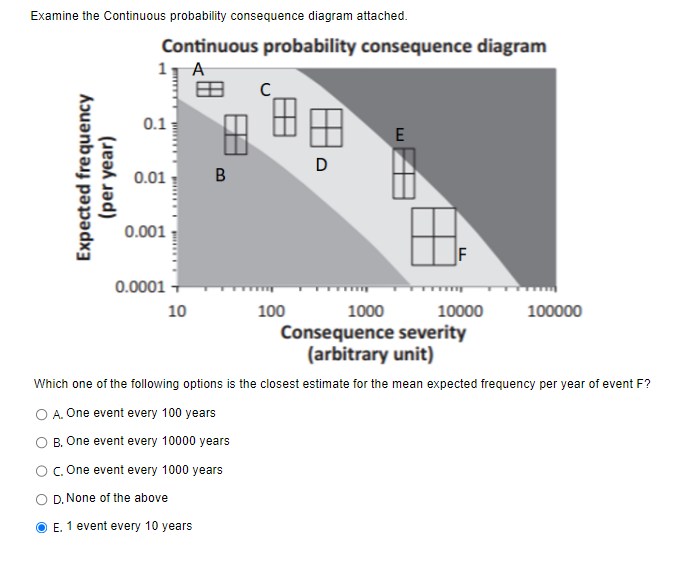
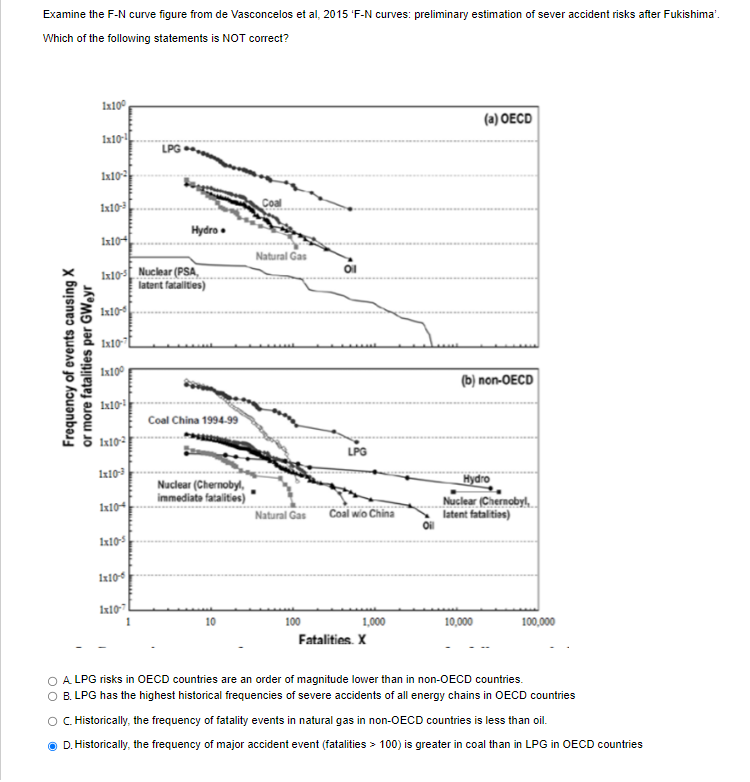
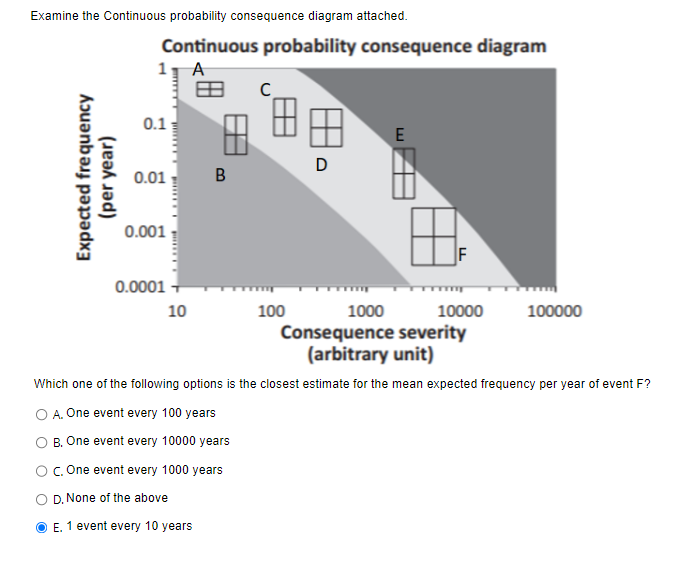
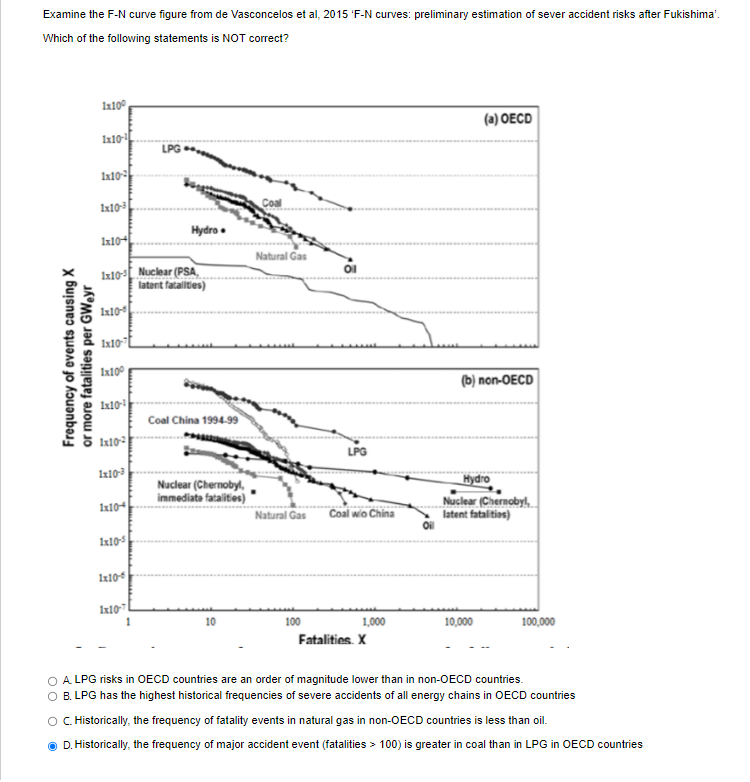
Examine the Continuous probability consequence diagram attached. Continuous probability consequence diagram A EB C 0.1 E D (per year) Expected frequency 0.01 B 0.001 0.0001 + 10 100 1000 10000 100000 Consequence severity (arbitrary unit) Which one of the following options is the closest estimate for the mean expected frequency per year of event F? O A. One event every 100 years O B. One event every 10000 years O c. One event every 1000 years O D. None of the above O E. 1 event every 10 yearsExamine the F-N curve figure from de Vasconcelos et al, 2015 'F-N curves: preliminary estimation of sever accident risks after Fukishima'. Which of the following statements is NOT correct? 1x100 (a) OECD 1x10-2 1x10-3 Coal. Hydro . 1x10+[ Natural Gas Ix10-4 Nuclear (PSA, latent fatalities) 1x10-4 1x10- Frequency of events causing X or more fatalities per GW.yr 1x100 (b) non-OECD Coal China 1994-99 1x10-2 LPG 1x10-3 Nuclear (Chernobyl, -Hydro immediate fatalities) 1x10+ Nuclear (Chernobyl Natural Gas Coal wip China latent fatal tips) 1x10-5 1x10- 1x10-7 10 100 1,000 10,000 100,000 Fatalities. X O A LPG risks in OECD countries are an order of magnitude lower than in non-OECD countries. O B. LPG has the highest historical frequencies of severe accidents of all energy chains in OECD countries O C. Historically, the frequency of fatality events in natural gas in non-OECD countries is less than oil. D. Historically, the frequency of major accident event (fatalities > 100) is greater in coal than in LPG in OECD countries
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


