Question: A continuous process separates a mixture of two solvents A and B. The input (a mixture of 30% A and 70% B, by mole) and
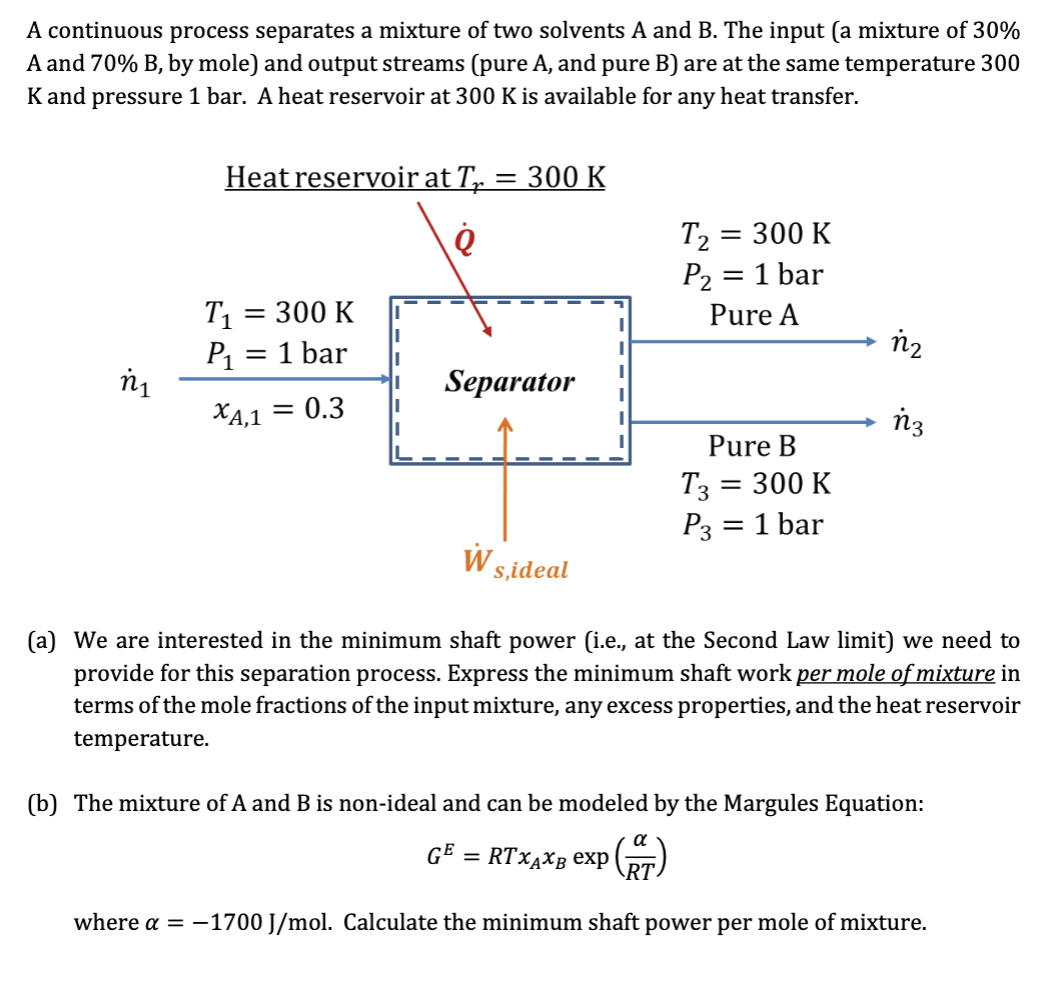
A continuous process separates a mixture of two solvents A and B. The input (a mixture of 30% A and 70% B, by mole) and output streams (pure A, and pure B) are at the same temperature 300 K and pressure 1 bar. A heat reservoir at 300 K is available for any heat transfer. Heat reservoir at Tp : = 300 K T2 = = 300 K P2 = 1 bar Pure A = T1 = 300 K P1 = 1 bar n2 - ni Separator = XA,1 = 0.3 n3 Pure B T3 - = 300 K P3 1 bar = WS sideal (a) We are interested in the minimum shaft power i.e., at the Second Law limit) we need to provide for this separation process. Express the minimum shaft work per mole of mixture in terms of the mole fractions of the input mixture, any excess properties, and the heat reservoir temperature. (b) The mixture of A and B is non-ideal and can be modeled by the Margules Equation: GE = RTXAXB exp CAT) where a = -1700 J/mol. Calculate the minimum shaft power per mole of mixture
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


