Question: (a) Define equivalent variation and compensating variation. Given an example of a problem for which equivalent variation would be an appropriate concept to apply. (b)
(a) Define equivalent variation and compensating variation. Given an example of a
problem for which equivalent variation would be an appropriate concept to apply.
(b) Find the Hicksian demand function for a consumer with u(x1, x2) = ?x1 + x2.
(c) The traditional celebration of Thanksgiving in the United States involves families
gathering together and eating a large meal that includes a whole roasted turkey. The
tradition is widely followed: over 95% of Thanksgiving meals include a turkey and twenty
times more turkeys are sold during the Thanksgiving week than in a normal week. An
initially puzzling observation is that supermarkets typically put turkeys on sale during this
week. Why might this occur?
2. (20 Minutes - 27 Points)
Suppose that Glenn Ellison is considering purchasing flood insurance for his house. If
Glenn does not buy flood insurance, his wealth will be w if there is no flood and w ? L if
there is a flood. The probability of a flood is ?.
The price of a policy that pays K if a flood occurs is cK. Assume that c
that the problem is otherwise uninteresting because Glenn would never buy any insurance.)
Assume that Glenn can choose any K ? [0,L], and that his choice of how much insurance
to buy maximizes his expected utility. Assume that Glenn's von Neumann Morgenstern
utility function u is a differentiable, strictly increasing and concave function of his final
wealth, i.e. Glenn maximizes (1 ? ?)u(w ? cK) + ?u(w ? L ? cK + K).
(a) Find the firstorder condition that characterizes Glenn's choice of K (assuming that
the parameters are such that an interior optimum exists.)
(b)For what value(s) of c will Glenn purchase full insurance? Does the answer depend
on the form of the utility function u? Why is this?
(c) Drop the assumptions that u is differentiable and concave - assume only that u is
strictly increasing and that a utilitymaximizing choice exists. Show that the K that Glenn
chooses is weakly increasing in the probability ? of a flood occurring.

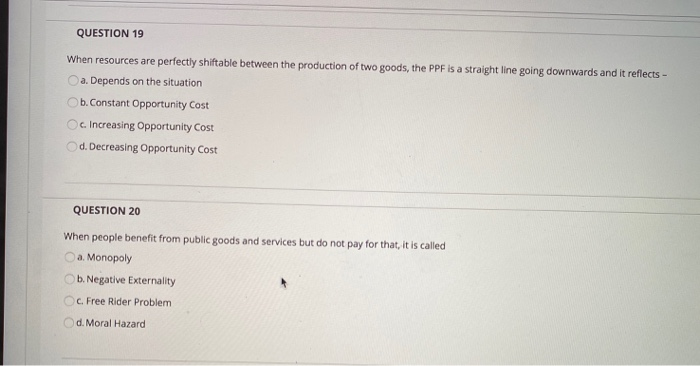
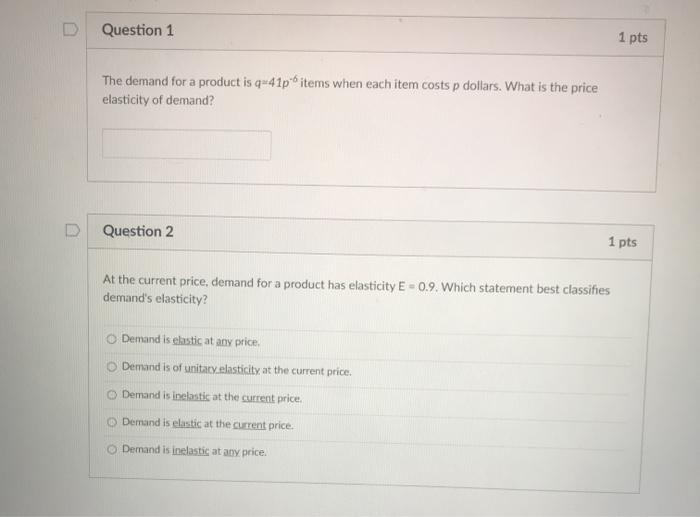
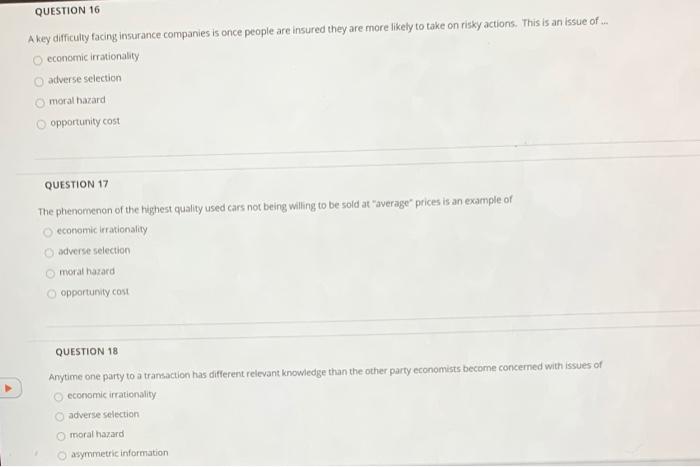
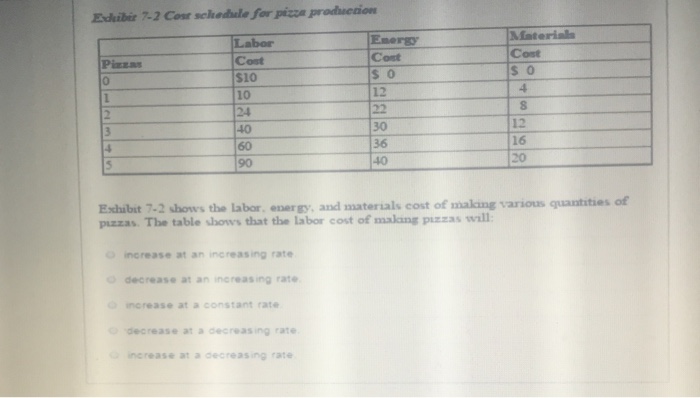
Help Center ? Question 1 6 pts (If eyeballing quantities to match up with price is worrying you just tell me which ones you're looking at so I know that you still understood the question) 1. If the market equilibrium price is $120, how much is total consumer surplus? (1 point) 2. If the market equilibrium price falls from $120 to $80, how much is the change in total consumer surplus in the market? (1 point) 3.If the market equilibrium price falls from $120 to $80, how much is the increase in consumer surplus to the consumers who were initially in the market at the $120 price? (2 points] 4.If the market equilibrium price falls from $120 to $80, how much consumer surplus do consumers entering the market after the price drop receive? (2 points) MacBook ProQUESTION 19 When resources are perfectly shiftable between the production of two goods, the PPF is a straight line going downwards and it reflects - Ca. Depends on the situation Ob. Constant Opportunity Cost Oe Increasing Opportunity Cost Od. Decreasing Opportunity Cost QUESTION 20 When people benefit from public goods and services but do not pay for that, it is called a. Monopoly Ob. Negative Externality c. Free Rider Problem Od. Moral HazardD Question 1 1 pts The demand for a product is q=41pitems when each item costs p dollars. What is the price elasticity of demand? D Question 2 1 pts At the current price, demand for a product has elasticity E = 0.9. Which statement best classifies demand's elasticity? O Demand is elastic at any price. 'Demand is of unitary elasticity at the current price. Demand is inelastic at the current price. Demand is clastic at the current price. Demand is inelastic at any price.QUESTION 16 A key difficulty facing insurance companies is once people are insured they are more likely to take on risky actions. This is an issue of .. O economic irrationality @ adverse selection moral hazard O opportunity cost QUESTION 17 The phenomenon of the highest quality used cars not being willing to be sold at "average" prices is an example of economic irrationality G adverse selection moral hazard opportunity cost QUESTION 18 Anytime one party to a transaction has different relevant knowledge than the other party economists become concerned with issues of @ economic irrationality @ adverse selection O moral hazard asymmetric informationExhibit 7-2 Cost schedule for pizza production Labor Energy Material Cost Cost Cost $10 10 12 4 24 22 S 40 30 12 60 36 16 90 40 20 Exhibit 7-2 shows the labor, energy, and materials cost of making various quantities of pizzas. The table shows that the labor cost of making pizzas will: O increase at an increasing rate O decrease at an increasing rate @ increase at a constant rate @ decrease at a decreasing rate @ increase at a decreasing rate
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


