Question: A differentially - steered robot has the initial pose given by: Pose = [ 2 m 4 m 0 0 ] It is moving with
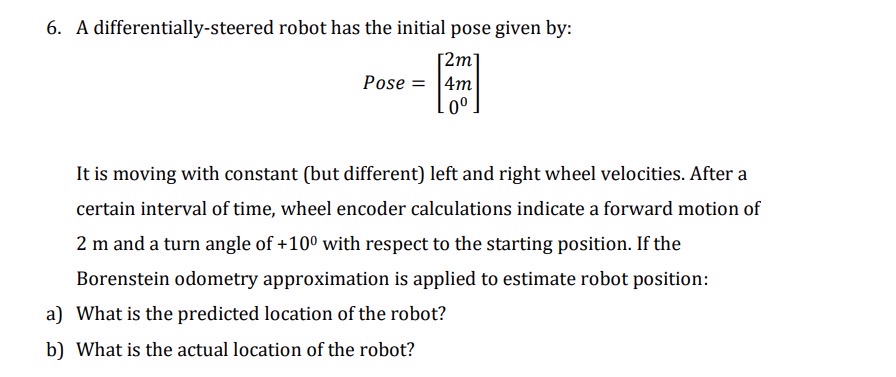
A differentiallysteered robot has the initial pose given by:
Pose
It is moving with constant but different left and right wheel velocities. After a certain interval of time, wheel encoder calculations indicate a forward motion of m and a turn angle of with respect to the starting position. If the Borenstein odometry approximation is applied to estimate robot position:
a What is the predicted location of the robot?
b What is the actual location of the robot?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


