Question: A distribution company is considering two locations for the construction of a new automated warehouse: Chicago and Dallas. Two types of automation are also being
A distribution company is considering two locations for the construction of a new automated warehouse: Chicago and Dallas. Two types of automation are also being considered: bar coding and RF/ID (radio-frequency identification). The annual operating costs for each type of automation at the two locations are:
| | Bar Coding | RF/ID | ||
| Location | Fixed Cost | Variable Cost per 1,000 units | Fixed Cost | Variable Cost per 1,000 units |
| Chicago | $1,800,000 | $12.30 | $2,700,00 | $9.70 |
| Dallas | 1,500,000 | 13.10 | 2,300,000 | 9.40 |
For what range of annual product volume handled would each location and type of automation be preferred?
The point of indifference between two alternatives is the point at which the total costs are equal: TC A = TC B . The total cost of each alternative is: TC = FC +( VC * Q), where FC are the fixed costs, VC are the variable costs, and Q is some volume/quantity/units. Then the point of indifference would be:
FC A + (VC A * Q) = FC B + (VC B * Q). Plug the appropriate fixed and variable costs into the formula and solve for Q.
At Q, you are truly indifferent to the two options, so other information must be used to make the decision and that information is typically expected demand. For volume or demand between zero and Q, the option with the lowest fixed cost typically yield the lowest total costs. For volume or demand that is greater than Q, then the option with the lowest variable cost typically yields the lowest total cost (the investment begins to payoff).
Use Table for formulas to help explain
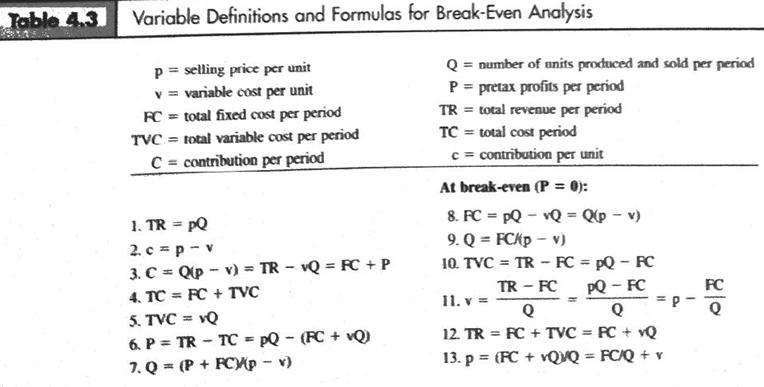
Table 4.3 Variable Definitions and Formulas for Break-Even Analysis p = selling price per unit v = variable cost per unit FC = total fixed cost per period TVC = total variable cost per period C= contribution per period 1. TR = PQ 2. c = p-v 3. C = Q(pv) = TRvQ = FC + P 4. TC FC + TVC 5. TVC = Q 6. P = TR - TC = PQ - (FC + vQ) 7. Q = (P + FC)/(p - v) = Q = number of units produced and sold per period P = pretax profits per period TR = total revenue per period TC = total cost period c = contribution per unit At break-even (P = 0): 8. FC = pQvQ = Q(pv) 9. Q = FC/p-v) 10. TVC = TR - FC = pQ - FC TR - FC PQ - FC Q Q 12. TR FC + TVC = PC + vQ 13. p= (FC+vQVQ = FC/Q + v 11. v = = FC 20
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (168 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To determine the preferred location and type of automation for different volumes we calculate the total costs for each option and find the point of in... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


