Question: A) Draw the three indifference curves through (1, 1),(3, 3) and (3, 6). B) Calculate the MRS as a function of ?, x1, x2. C)
A) Draw the three indifference curves through (1, 1),(3, 3) and (3, 6).
B) Calculate the MRS as a function of ?, x1, x2.
C) For a fixed x1 and x2, what happens to the MRS as ? ? ???
D) Solve for the consumer's choices (x1, x2) in terms of y, p1, p2 and ?.
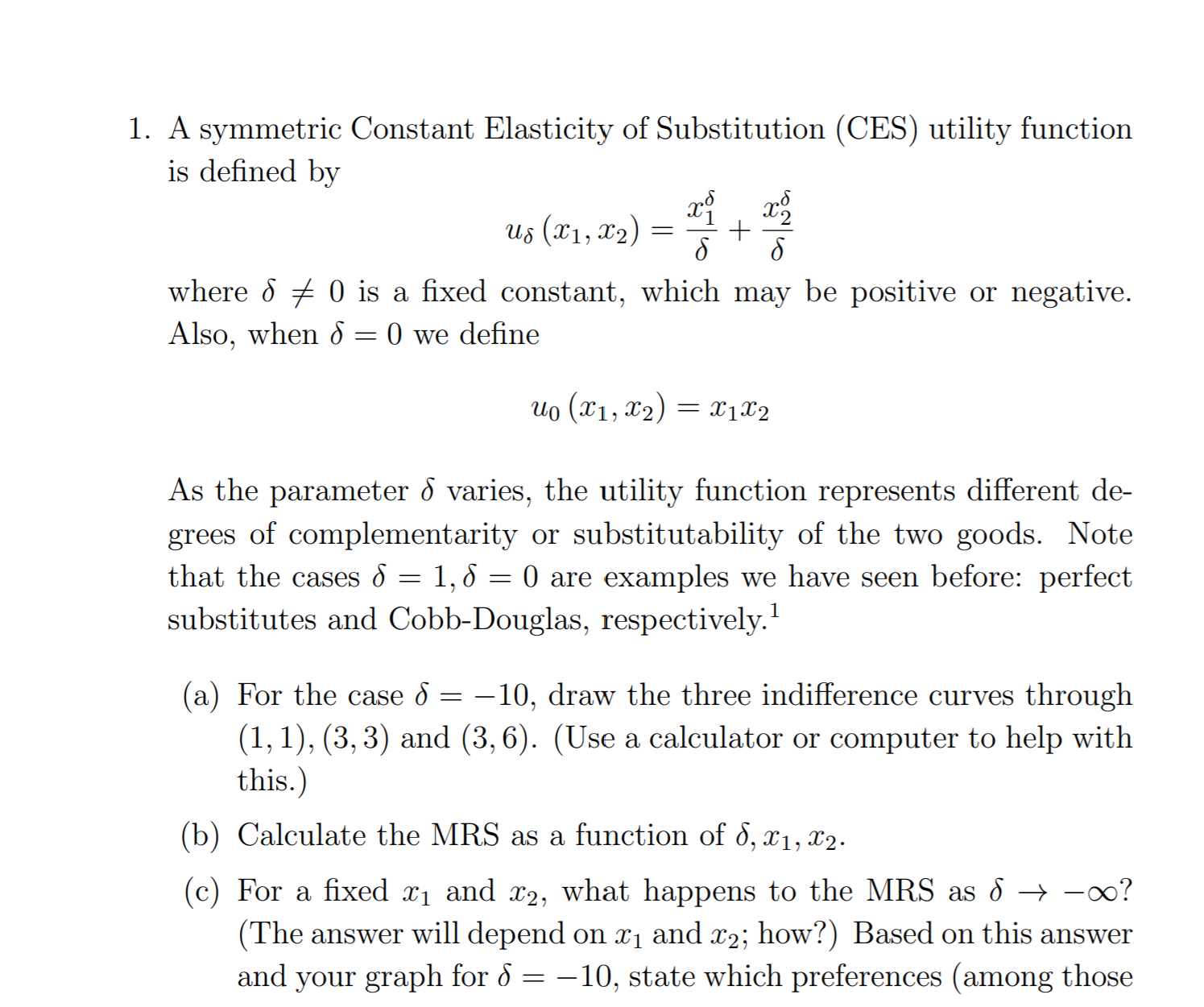
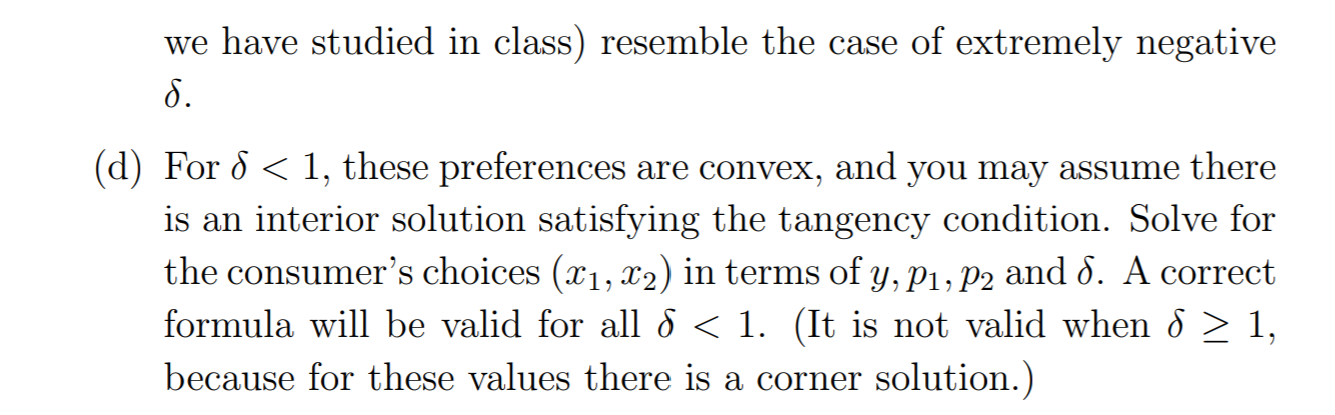
1. A symmetric Constant Elasticity of Substitution (CES) utility function is defined by us (21 , 2 ) = + where 8 * 0 is a fixed constant, which may be positive or negative. Also, when d = 0 we define uo (X1, X2) = 122 As the parameter o varies, the utility function represents different de- grees of complementarity or substitutability of the two goods. Note that the cases 6 = 1, 8 = 0 are examples we have seen before: perfect substitutes and Cobb-Douglas, respectively.' a) For the case S = -10, draw the three indifference curves through (1, 1), (3, 3) and (3, 6). (Use a calculator or computer to help with this.) (b) Calculate the MRS as a function of 8, x1, 22. (c) For a fixed x1 and x2, what happens to the MRS as d - -co? (The answer will depend on x1 and x2; how?) Based on this answer and your graph for 6 = -10, state which preferences (among thosewe have studied in class) resemble the case of extremely negative 6. (d) For 6
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


