Question: A General BLU- % Conditional format Formatting Table Styles - Clwboard Font Alignment Numbes K5 X E 2 1 Given Data: Waverley Welding Company provides
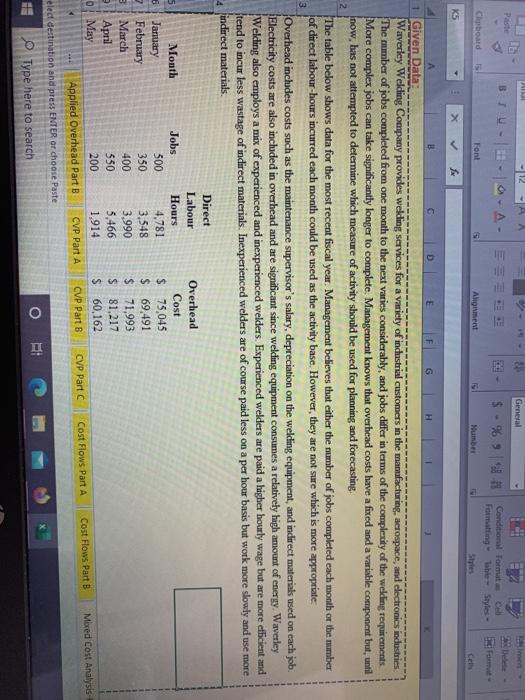
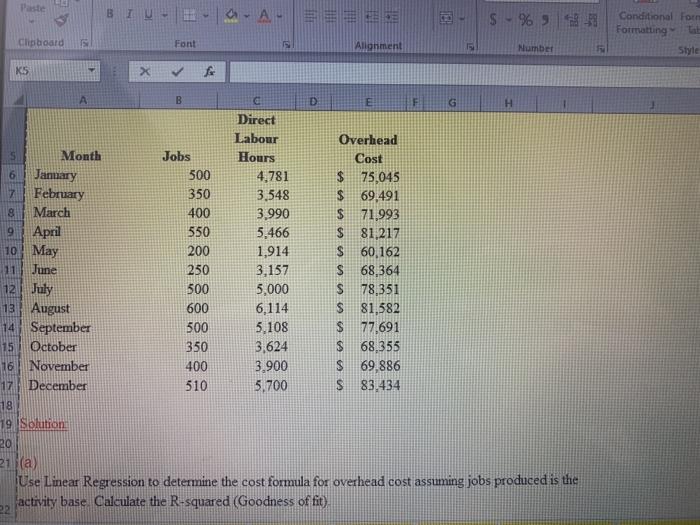

A General BLU- % Conditional format Formatting Table Styles - Clwboard Font Alignment Numbes K5 X E 2 1 Given Data: Waverley Welding Company provides welding services for a variety of industrial customers in the manufacturing, aerospace, and electronics industries The mmber of jobs completed from one month to the next varies considerably, and jobs differ in terms of the complexity of the welding requirements More complex jobs can take significantly longer to complete Management knows that overhead costs have a fixed and a variable component but, until now, has not attempted to determine which measure of activity should be used for planning and forecasting, The table below shows data for the most recent fiscal year. Management believes that either the mmber of jobs completed each month of the number of direct labour-hours incurred each month could be used as the activity base. However, they are not sure which is more appropriate Overhead includes costs such as the maintenance supervisor's salary, depreciation on the welcling equipment, and indirect materials used on each job. Electricity costs are also included in overhead and are significant since welding equipment consumes a relatively high amount of energy Waverley Welding also employs a mix of experienced and inexperienced welders. Experienced welders are paid a higher hourly wage but are more efficient and tend to incur less wastage of indirect materials. Inexperienced welders are of course paid less on a per hour basis but work more slowly and use more indirect materials 3 Direct Labour s Month Jobs Hours January 500 4,781 7 February 350 3,548 B March 400 3,990 April 550 5,466 0 May 200 1,914 Applied Overhead Part B CVP Part A Overhead Cost $ 75,045 $ 69,491 $ 71,993 $ 81,217 S 60,162 Mored Cost Analysis CVP Part 8 CVP Part Cost Flows Part 8 Cost Flows Part A elect destination and press ENTER or choose Paste O i 1 Type here to search - A - $ - 96 -13 Conditional for Formatting to Style Clipboard Font 1 Alignment Number KS x D 9 A B E F G H Direct Labour Overhead Month Jobs Hours Cost January 500 4,781 $ 75,045 February 350 3,548 $ 69.491 March 400 3,990 $ 71,993 April 550 5,466 $ 81.217 10 May 200 1,914 $ 60,162 11 June 250 3,157 S 68,364 12 July 500 5,000 $ 78,351 13 August 600 6,114 $ 81,582 14 September 500 5.108 $ 77.691 15 October 350 3,624 $ 68,355 16 November 400 3.900 $ 69,886 17 December 510 5,700 S 83,434 18 19. Solution 20 21 (a) Use Linear Regression to determine the cost formula for overhead cost assuming jobs produced is the activity base. Calculate the R-squared (Goodness of fit) 22 5 70 Formatting Clipboard Font Alignment Number K5 X B D H + per job R2- A E F 21 (a) Use Linear Regression to determine the cost formula for overhead cost assuming jobs prochaced is the activity base. Calculate the R-squared (Goodness of fit) 22 23 24 overhead cost = 25 26 27 28 (b) Use Linear Regression to determine the cost formula for overhead cost assuming direct labour hours is the activity base. Calculate the R-squared (Goodness of fit). 29 30 31 overhead cost = per Direct Labour hour 32 R2- 33 34(C) 35 Based on your answers in parts (a) and (b), which is the most appropriate cost driver for overhead costs? 36 37 39 A General BLU- % Conditional format Formatting Table Styles - Clwboard Font Alignment Numbes K5 X E 2 1 Given Data: Waverley Welding Company provides welding services for a variety of industrial customers in the manufacturing, aerospace, and electronics industries The mmber of jobs completed from one month to the next varies considerably, and jobs differ in terms of the complexity of the welding requirements More complex jobs can take significantly longer to complete Management knows that overhead costs have a fixed and a variable component but, until now, has not attempted to determine which measure of activity should be used for planning and forecasting, The table below shows data for the most recent fiscal year. Management believes that either the mmber of jobs completed each month of the number of direct labour-hours incurred each month could be used as the activity base. However, they are not sure which is more appropriate Overhead includes costs such as the maintenance supervisor's salary, depreciation on the welcling equipment, and indirect materials used on each job. Electricity costs are also included in overhead and are significant since welding equipment consumes a relatively high amount of energy Waverley Welding also employs a mix of experienced and inexperienced welders. Experienced welders are paid a higher hourly wage but are more efficient and tend to incur less wastage of indirect materials. Inexperienced welders are of course paid less on a per hour basis but work more slowly and use more indirect materials 3 Direct Labour s Month Jobs Hours January 500 4,781 7 February 350 3,548 B March 400 3,990 April 550 5,466 0 May 200 1,914 Applied Overhead Part B CVP Part A Overhead Cost $ 75,045 $ 69,491 $ 71,993 $ 81,217 S 60,162 Mored Cost Analysis CVP Part 8 CVP Part Cost Flows Part 8 Cost Flows Part A elect destination and press ENTER or choose Paste O i 1 Type here to search - A - $ - 96 -13 Conditional for Formatting to Style Clipboard Font 1 Alignment Number KS x D 9 A B E F G H Direct Labour Overhead Month Jobs Hours Cost January 500 4,781 $ 75,045 February 350 3,548 $ 69.491 March 400 3,990 $ 71,993 April 550 5,466 $ 81.217 10 May 200 1,914 $ 60,162 11 June 250 3,157 S 68,364 12 July 500 5,000 $ 78,351 13 August 600 6,114 $ 81,582 14 September 500 5.108 $ 77.691 15 October 350 3,624 $ 68,355 16 November 400 3.900 $ 69,886 17 December 510 5,700 S 83,434 18 19. Solution 20 21 (a) Use Linear Regression to determine the cost formula for overhead cost assuming jobs produced is the activity base. Calculate the R-squared (Goodness of fit) 22 5 70 Formatting Clipboard Font Alignment Number K5 X B D H + per job R2- A E F 21 (a) Use Linear Regression to determine the cost formula for overhead cost assuming jobs prochaced is the activity base. Calculate the R-squared (Goodness of fit) 22 23 24 overhead cost = 25 26 27 28 (b) Use Linear Regression to determine the cost formula for overhead cost assuming direct labour hours is the activity base. Calculate the R-squared (Goodness of fit). 29 30 31 overhead cost = per Direct Labour hour 32 R2- 33 34(C) 35 Based on your answers in parts (a) and (b), which is the most appropriate cost driver for overhead costs? 36 37 39
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


