Question: (a) Given a correlation matrix A, 1.0 0.5 0.2 A 0.5 1.0 -0.4 0.2 -0.4 1.0 perform a Cholesky decomposition of the matrix A, which
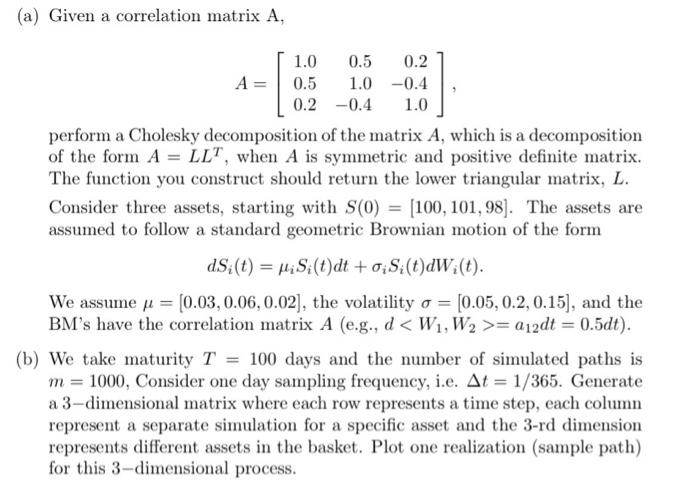
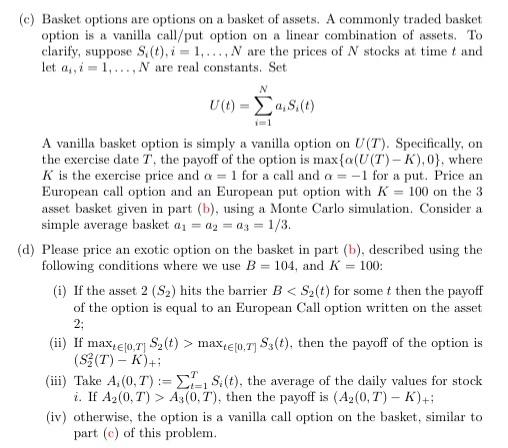
(a) Given a correlation matrix A, 1.0 0.5 0.2 A 0.5 1.0 -0.4 0.2 -0.4 1.0 perform a Cholesky decomposition of the matrix A, which is a decomposition of the form A = LL", when A is symmetric and positive definite matrix. The function you construct should return the lower triangular matrix, L. Consider three assets, starting with S(0) = [100, 101, 98). The assets are assumed to follow a standard geometric Brownian motion of the form ds (t) = HiS (t)dt + oiSi(t)dW (t). We assume u = (0.03, 0.06,0.02), the volatility o = [0.05,0.2, 0.15), and the BM's have the correlation matrix A (e.g., d = 212dt = 0.5dt). (b) We take maturity T = 100 days and the number of simulated paths is m= 1000, Consider one day sampling frequency, i.e. At = 1/365. Generate a 3-dimensional matrix where each row represents a time step, each column represent a separate simulation for a specific asset and the 3-rd dimension represents different assets in the basket. Plot one realization (sample path) for this 3-dimensional process. (c) Basket options are options on a basket of assets. A commonly traded basket option is a vanilla call/put option on a linear combination of assets. To clarify, suppose S. (t), i = 1,..., N are the prices of N stocks at time t and let a,, i = 1,...,N are real constants. Set (t) 8.6 A vanilla basket option is simply a vanilla option on U(T). Specifically, on the exercise date T, the payoff of the option is max{a(U(T)-K),0), where K is the exercise price and a = 1 for a call and a = -1 for a put. Price an European call option and an European put option with K = 100 on the 3 asset basket given in part (b), using a Monte Carlo simulation. Consider a simple average basket i = 02 = a3 = 1/3 (a) Please price an exotic option on the basket in part (b), described using the following conditions where we use B = 104, and K = 100: (i) If the asset 2 (S2) hits the barrier B max etor, Ss(t), then the payoff of the option is (S3(T) - K)+; (iii) Take A (0,T):= {1, S.(t), the average of the daily values for stock i. If Az(0,T) > A3(0.7'), then the payoff is (Az(0,T) - K)+; (iv) otherwise, the option is a vanilla call option on the basket, similar to part (c) of this problem (a) Given a correlation matrix A, 1.0 0.5 0.2 A 0.5 1.0 -0.4 0.2 -0.4 1.0 perform a Cholesky decomposition of the matrix A, which is a decomposition of the form A = LL", when A is symmetric and positive definite matrix. The function you construct should return the lower triangular matrix, L. Consider three assets, starting with S(0) = [100, 101, 98). The assets are assumed to follow a standard geometric Brownian motion of the form ds (t) = HiS (t)dt + oiSi(t)dW (t). We assume u = (0.03, 0.06,0.02), the volatility o = [0.05,0.2, 0.15), and the BM's have the correlation matrix A (e.g., d = 212dt = 0.5dt). (b) We take maturity T = 100 days and the number of simulated paths is m= 1000, Consider one day sampling frequency, i.e. At = 1/365. Generate a 3-dimensional matrix where each row represents a time step, each column represent a separate simulation for a specific asset and the 3-rd dimension represents different assets in the basket. Plot one realization (sample path) for this 3-dimensional process. (c) Basket options are options on a basket of assets. A commonly traded basket option is a vanilla call/put option on a linear combination of assets. To clarify, suppose S. (t), i = 1,..., N are the prices of N stocks at time t and let a,, i = 1,...,N are real constants. Set (t) 8.6 A vanilla basket option is simply a vanilla option on U(T). Specifically, on the exercise date T, the payoff of the option is max{a(U(T)-K),0), where K is the exercise price and a = 1 for a call and a = -1 for a put. Price an European call option and an European put option with K = 100 on the 3 asset basket given in part (b), using a Monte Carlo simulation. Consider a simple average basket i = 02 = a3 = 1/3 (a) Please price an exotic option on the basket in part (b), described using the following conditions where we use B = 104, and K = 100: (i) If the asset 2 (S2) hits the barrier B max etor, Ss(t), then the payoff of the option is (S3(T) - K)+; (iii) Take A (0,T):= {1, S.(t), the average of the daily values for stock i. If Az(0,T) > A3(0.7'), then the payoff is (Az(0,T) - K)+; (iv) otherwise, the option is a vanilla call option on the basket, similar to part (c) of this
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


