Question: A graph is a finite set of objects called nodes, together with some paths between some of the nodes, as illustrated below. A path of
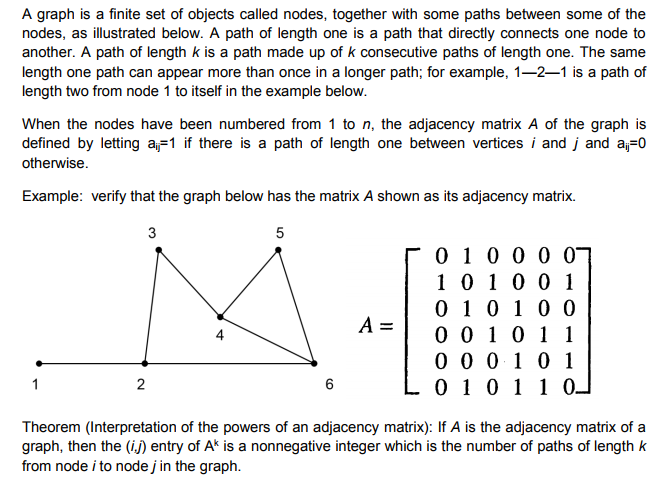

A graph is a finite set of objects called nodes, together with some paths between some of the nodes, as illustrated below. A path of length one is a path that directly connects one node to another. A path of length k is a path made up of k consecutive paths of length one. The same length one path can appear more than once in a longer path; for example, 1-2-1 is a path of length two from node 1 to itself in the example below When the nodes have been numbered from 1 to n, the adjacency matrix A of the graph is defined by letting a-1 if there is a path of length one between vertices i and j and a 0 otherwise Example: verify that the graph below has the matrix A shown as its adjacency matrix. 010 0 0 0 1010 0 1 0101 0 0 | 001011 000 1 0 1 01 01 1 0 4 2 Theorem (Interpretation of the powers of an adjacency matrix): If A is the adjacency matrix of a graph, then the (ij) entry of A* is a nonnegative integer which is the number of paths of lengthk from node i to nodej in the graph
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


