Question: A i B i C i D I E i F i G i H _. The emblem to be solved: You have decided it

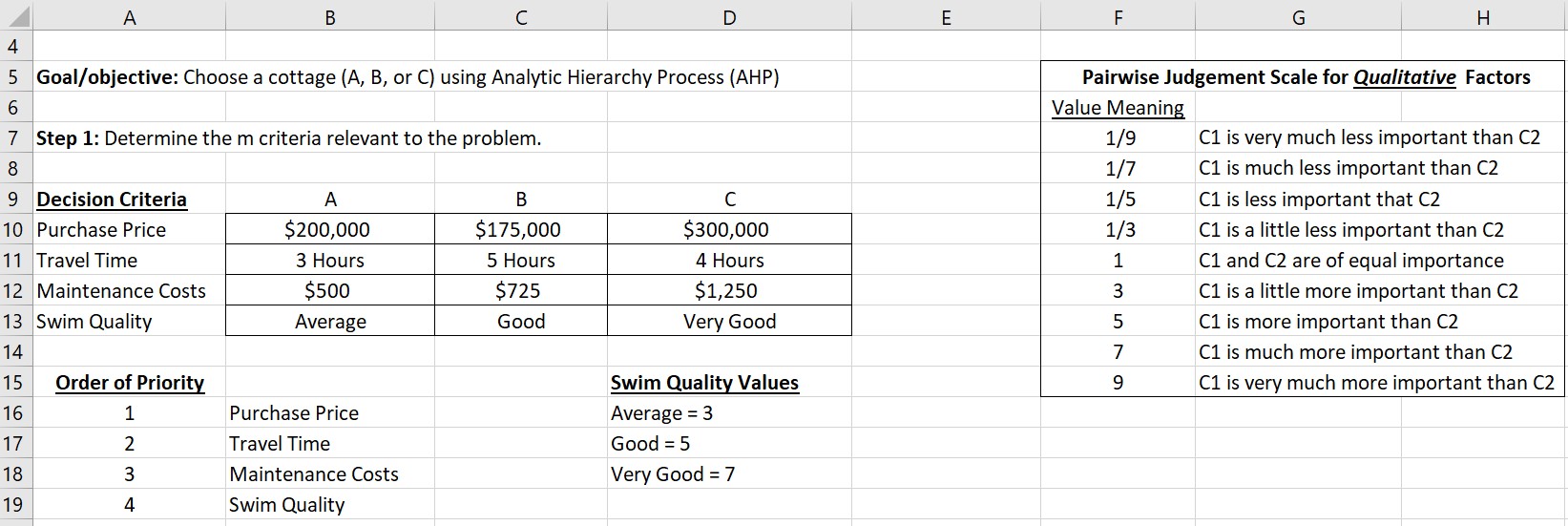
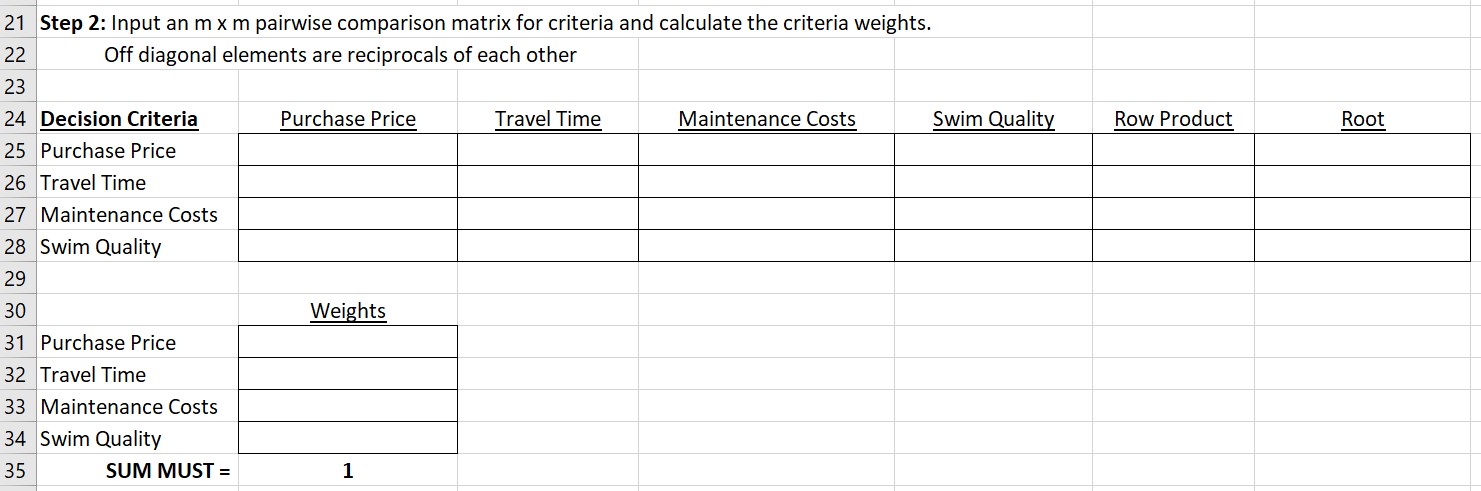
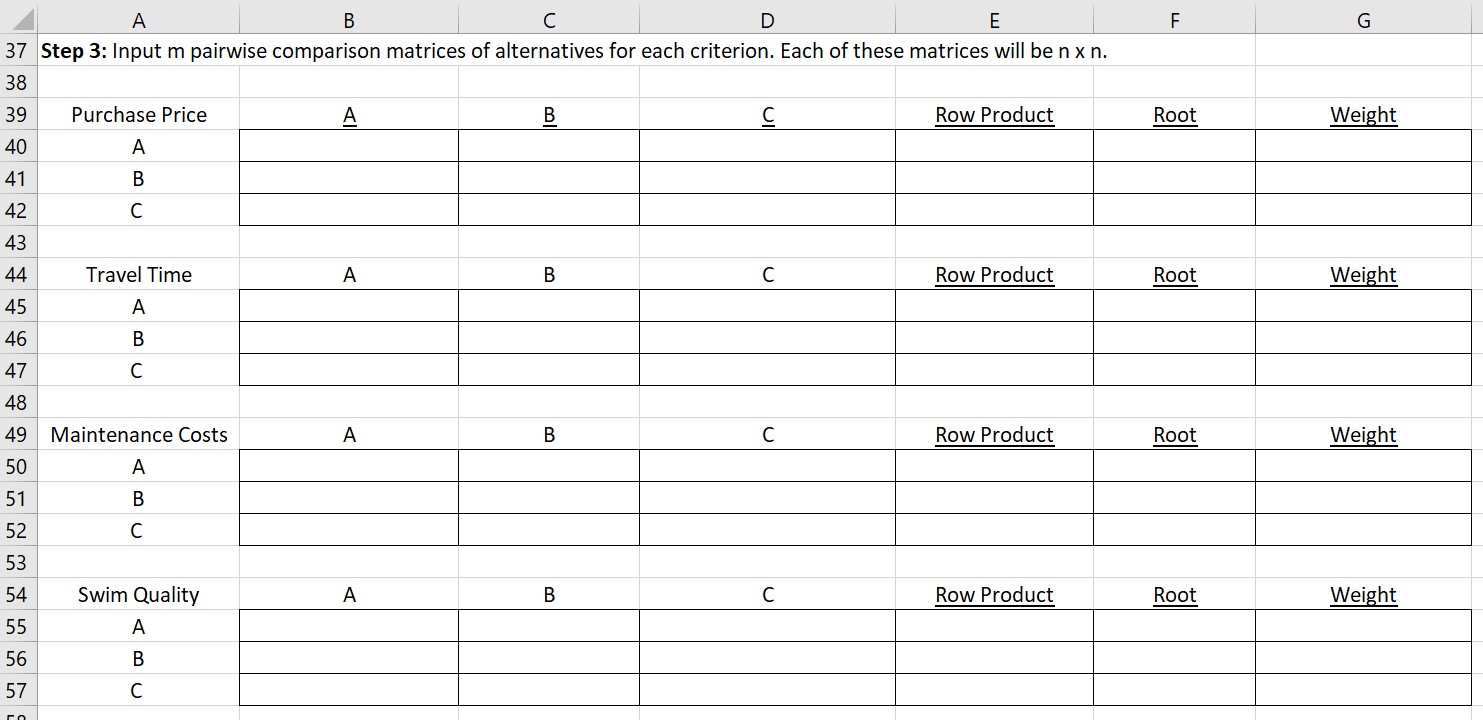
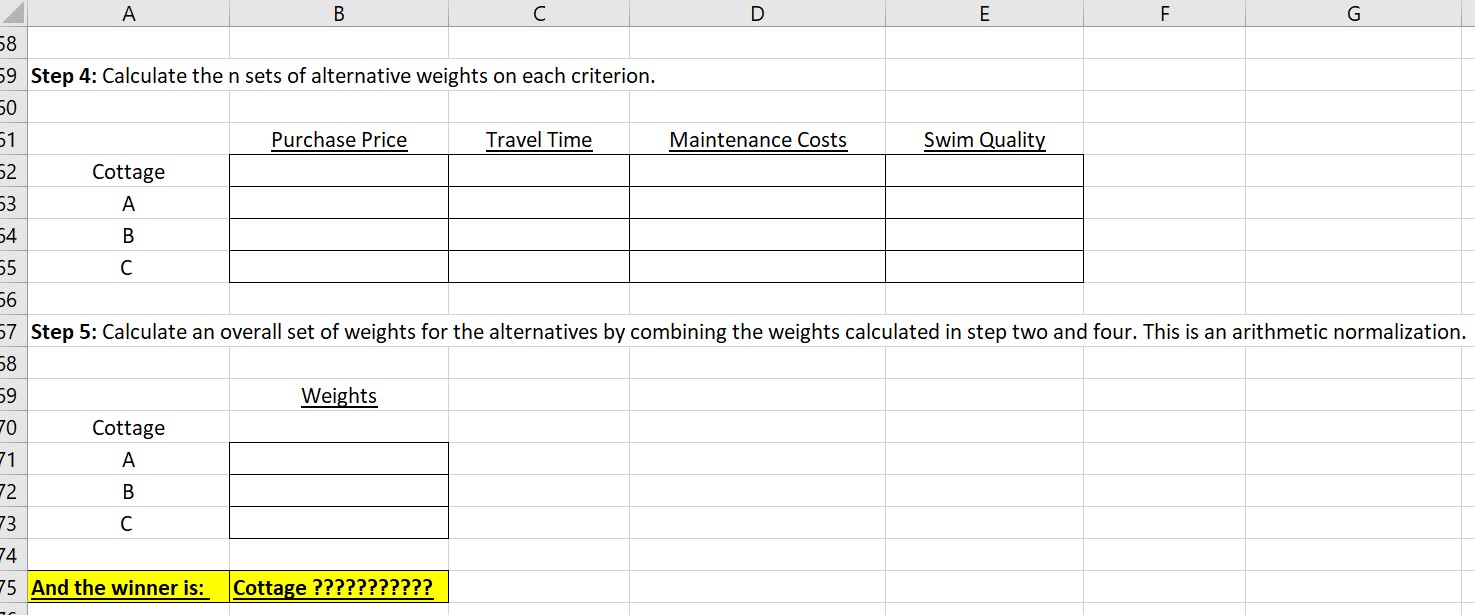
A i B i C i D I E i F i G i H _. The emblem to be solved: You have decided it is time to invest in a cottage and have narrowed your search down to three alternatives. Cottage A is a Show drive from home, has average quaiity swimming, and should be relatively low maintenance (about $500 per summer). Your agent suggests you can purchase cottageAfor $200,000. Cottage B is a 5-hour drive from home, has good quaiity swimming but will require a little more maintenance (about $725 per summer). It can likely be purchased for $175,000. Cottage C is a four- hour drive from home has great water for swimming but is a little heavy on the maintenance ($1250) per summer. It is also the most expensive at $300,000. Using travel time (quantitative), maintenance cost (quantitative) and swimming quality (qualitative) and cost (quantitative) as your four decision criteria, complete an AHP analysis to select the best cottage: A, B or C. Be sure to complete all consistency ratio (CR) calculations and make adjustments if necessary. Consider a CR less than 010 to be sufficiently consistent. A D F l G l H Goal/objective: Choose a cottage (A, B, or C) using Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) Step 1: Determine the m criteria relevant to the problem. Decision Criteria Purchase Price Travel Time Maintenance Costs Swim Quality Order of Priority 1 Z 3 4 A B C $200,000 $175,000 $300,000 3 Hours 5 Hours 4 Hours 5500 $725 51,250 Average Good Very Good Purchase Price Travel Time Maintenance Costs Swim Quality Swim Qualiy Values Average = 3 Good = 5 Very Good = 7 Paimise Judgement Scale for Qualitative Factors Value Meaning 1/9 C1 is very much less important than C2 1/7 C1 is much less important than C2 1/5 C1 is less important that C2 1/3 C1 is a little less important than C2 1 C1 and C2 are of equal importance 3 C1 is a little more important than C2 5 C1 is more important than C2 7 C1 is much more important than C2 9 C1 is very much more important than C2 21 Step 2: Input an m x m pairwise comparison matrix for criteria and calculate the criteria weights. 22 Off diagonal elements are reciprocals of each other 23 24 Decision Criteria Purchase Price Travel Time Maintenance Costs Swim Quality Row Product Root 25 Purchase Price 26 Travel Time 27 Maintenance Costs 28 Swim Quality 29 30 Weights 31 Purchase Price 32 Travel Time 33 Maintenance Costs 34 Swim Quality 35 SUM MUST = 1A A i B | c i D | E i F G 3L Step 3: Input rn pairwise comparison matrices of alternatives for each criterion. Each of these matrices will be n x n. 31 39 Purchase Price A B Q Row Product Root Weight 41 A 4L B 42 C 4i 44 Travel Time A B C Row Product H Weight 4; A 4i B 4L C 41 49 Maintenance Costs A B C Row Product m Weight 5g A 51_ B 5; c 53_ 54 Swim Quality A B C Row Product m Weight 5i A 51 B 57 C A A B c D E E Step 4: Calculate the n sets of alternative weights on each criterion. 3 51 Purchase Price Travel Time Maintenance Costs Swim Quality 52 Cottage 3 A 54 B 55 C E iStep 5: Calculate an overall set of weights for the alternatives by combining the weights calculated in step two and four. This is an arithmetic normalization. 58 a Weights 3 Cottage 1 A E B F3 C I 75 And the winner is: Cottage
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


