Question: A. Inputs Initial investment ($ thousands) Salvage value ($ thousands) Initial revenues ($ thousands) Variable costs % of revenues) Initial fixed costs ($ thousands) Inflation
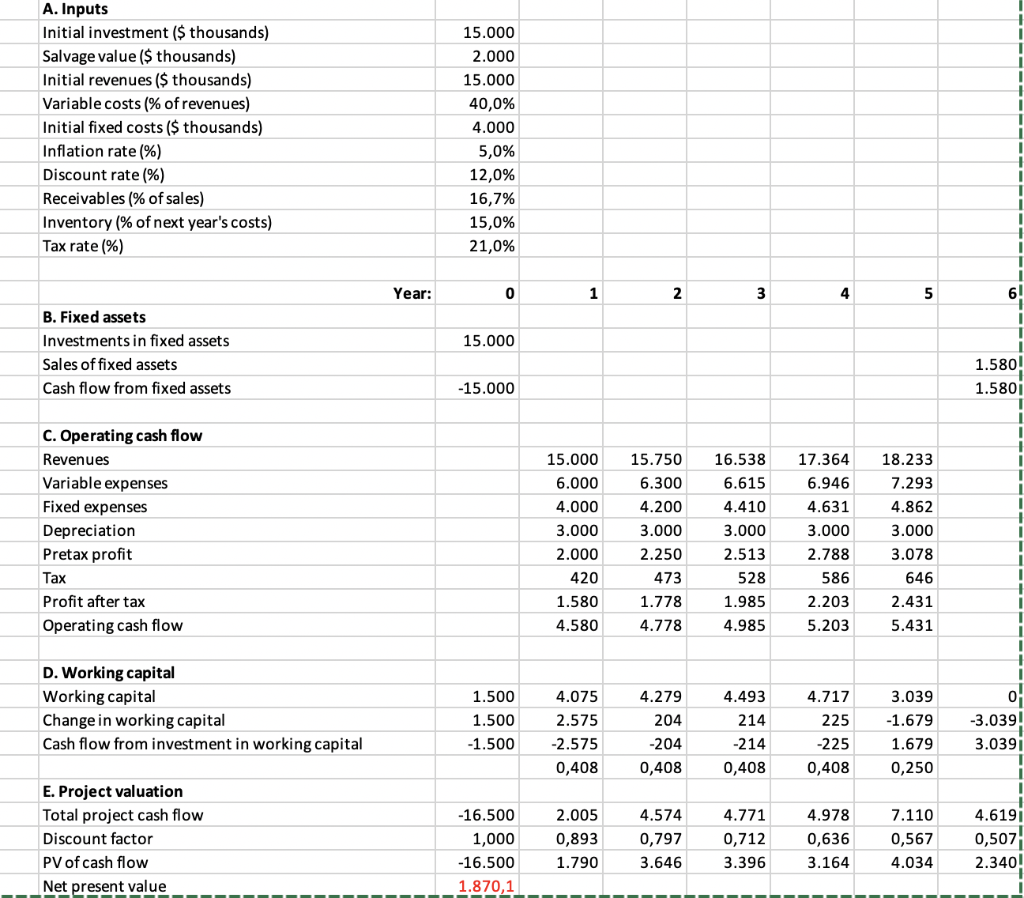
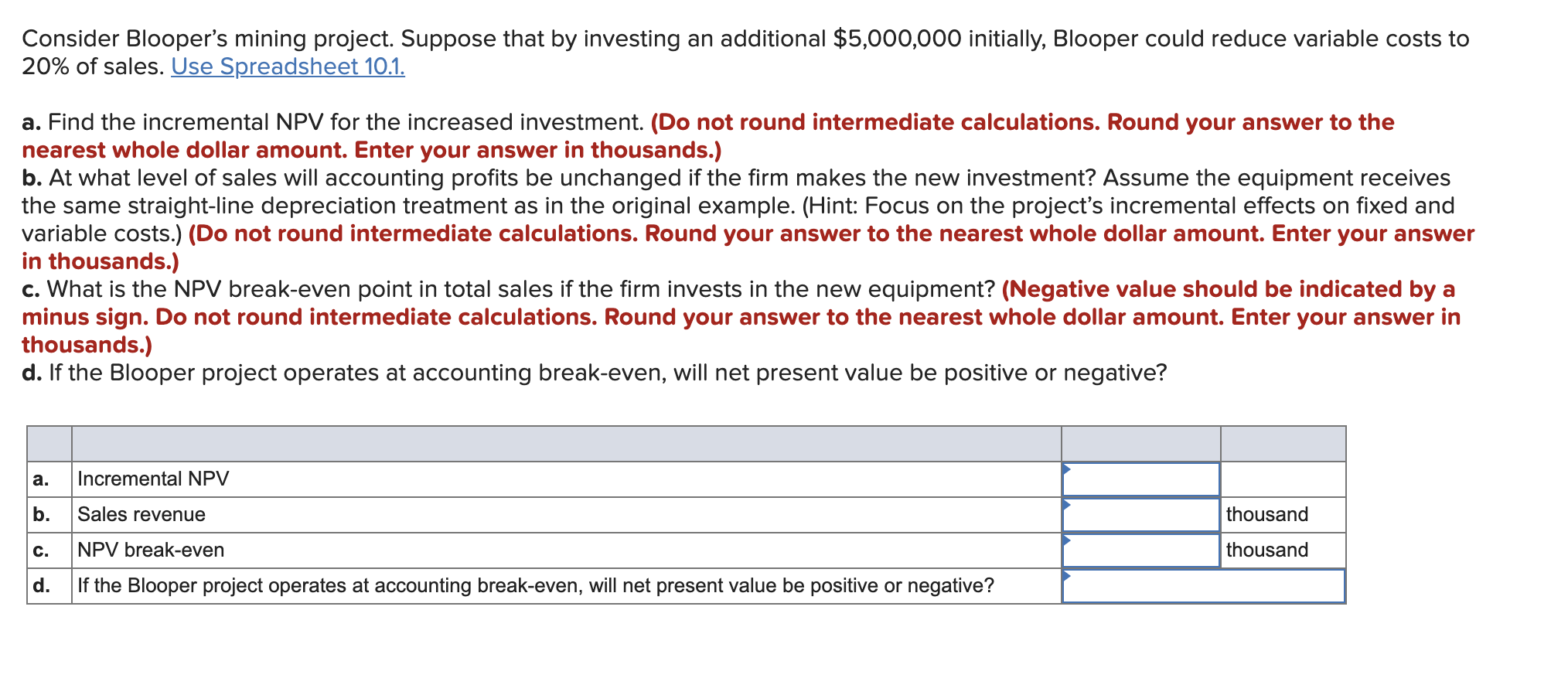
A. Inputs Initial investment ($ thousands) Salvage value ($ thousands) Initial revenues ($ thousands) Variable costs % of revenues) Initial fixed costs ($ thousands) Inflation rate (%) Discount rate (%) Receivables (% of sales) Inventory (% of next year's costs) Tax rate (%) 15.000 2.000 15.000 40,0% 4.000 5,0% 12,0% 16,7% 15,0% 21,0% Year: 15.000 B. Fixed assets Investments in fixed assets Sales of fixed assets Cash flow from fixed assets 1.580! 1.580i -15.000 C. Operating cash flow Revenues Variable expenses Fixed expenses Depreciation Pretax profit Tax Profit after tax Operating cash flow 15.000 6.000 4.000 3.000 2.000 420 1.580 4.580 15.750 6.300 4.200 3.000 2.250 473 1.778 4.778 16.538 6.615 4.410 3.000 2.513 528 1.985 4.985 17.364 6.946 4.631 3.000 2.788 586 2.203 5.203 18.233 7.293 4.862 3.000 3.078 646 2.431 5.431 D. Working capital Working capital Change in working capital Cash flow from investment in working capital 0 1.500 1.500 -1.500 4.075 2.575 -2.575 0,408 4.2794.493 204 214 -204 -214 0,408 0,408 4.717 225 -225 0,408 3.039 -1.679 1.679 0,250 -3.039! 3.0391 4.6197 E. Project valuation Total project cash flow Discount factor PV of cash flow Net present value -16.500 1,000 -16.500 1.870,1 2.005 0,893 1.790 4.574 0,797 3.646 4.771 0,712 3.396 4.978 0,636 3.164 7.110 0,567 4.034 0,507 2.340! Consider Blooper's mining project. Suppose that by investing an additional $5,000,000 initially, Blooper could reduce variable costs to 20% of sales. Use Spreadsheet 10.1. a. Find the incremental NPV for the increased investment. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest whole dollar amount. Enter your answer in thousands.) b. At what level of sales will accounting profits be unchanged if the firm makes the new investment? Assume the equipment receives the same straight-line depreciation treatment as in the original example. (Hint: Focus on the project's incremental effects on fixed and variable costs.) (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest whole dollar amount. Enter your answer in thousands.) c. What is the NPV break-even point in total sales if the firm invests in the new equipment? (Negative value should be indicated by a minus sign. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest whole dollar amount. Enter your answer in thousands.) d. If the Blooper project operates at accounting break-even, will net present value be positive or negative? b. thousand a. Incremental NPV Sales revenue c. NPV break-even d. If the Blooper project operates at accounting break-even, will net present value be positive or negative? thousand A. Inputs Initial investment ($ thousands) Salvage value ($ thousands) Initial revenues ($ thousands) Variable costs % of revenues) Initial fixed costs ($ thousands) Inflation rate (%) Discount rate (%) Receivables (% of sales) Inventory (% of next year's costs) Tax rate (%) 15.000 2.000 15.000 40,0% 4.000 5,0% 12,0% 16,7% 15,0% 21,0% Year: 15.000 B. Fixed assets Investments in fixed assets Sales of fixed assets Cash flow from fixed assets 1.580! 1.580i -15.000 C. Operating cash flow Revenues Variable expenses Fixed expenses Depreciation Pretax profit Tax Profit after tax Operating cash flow 15.000 6.000 4.000 3.000 2.000 420 1.580 4.580 15.750 6.300 4.200 3.000 2.250 473 1.778 4.778 16.538 6.615 4.410 3.000 2.513 528 1.985 4.985 17.364 6.946 4.631 3.000 2.788 586 2.203 5.203 18.233 7.293 4.862 3.000 3.078 646 2.431 5.431 D. Working capital Working capital Change in working capital Cash flow from investment in working capital 0 1.500 1.500 -1.500 4.075 2.575 -2.575 0,408 4.2794.493 204 214 -204 -214 0,408 0,408 4.717 225 -225 0,408 3.039 -1.679 1.679 0,250 -3.039! 3.0391 4.6197 E. Project valuation Total project cash flow Discount factor PV of cash flow Net present value -16.500 1,000 -16.500 1.870,1 2.005 0,893 1.790 4.574 0,797 3.646 4.771 0,712 3.396 4.978 0,636 3.164 7.110 0,567 4.034 0,507 2.340! Consider Blooper's mining project. Suppose that by investing an additional $5,000,000 initially, Blooper could reduce variable costs to 20% of sales. Use Spreadsheet 10.1. a. Find the incremental NPV for the increased investment. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest whole dollar amount. Enter your answer in thousands.) b. At what level of sales will accounting profits be unchanged if the firm makes the new investment? Assume the equipment receives the same straight-line depreciation treatment as in the original example. (Hint: Focus on the project's incremental effects on fixed and variable costs.) (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest whole dollar amount. Enter your answer in thousands.) c. What is the NPV break-even point in total sales if the firm invests in the new equipment? (Negative value should be indicated by a minus sign. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest whole dollar amount. Enter your answer in thousands.) d. If the Blooper project operates at accounting break-even, will net present value be positive or negative? b. thousand a. Incremental NPV Sales revenue c. NPV break-even d. If the Blooper project operates at accounting break-even, will net present value be positive or negative? thousand
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


