Question: (a) Instruction format 1 Magnitude (b) Integer format Program Counter (PC)= Address of instruction Instruction Register (IR) = Instruction being executed Accumulator (AC)= Temporary storage
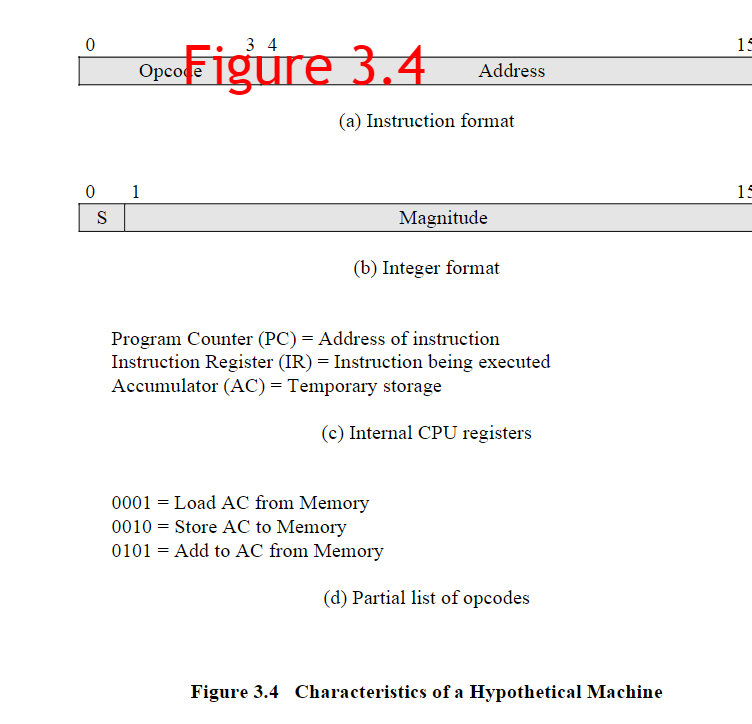
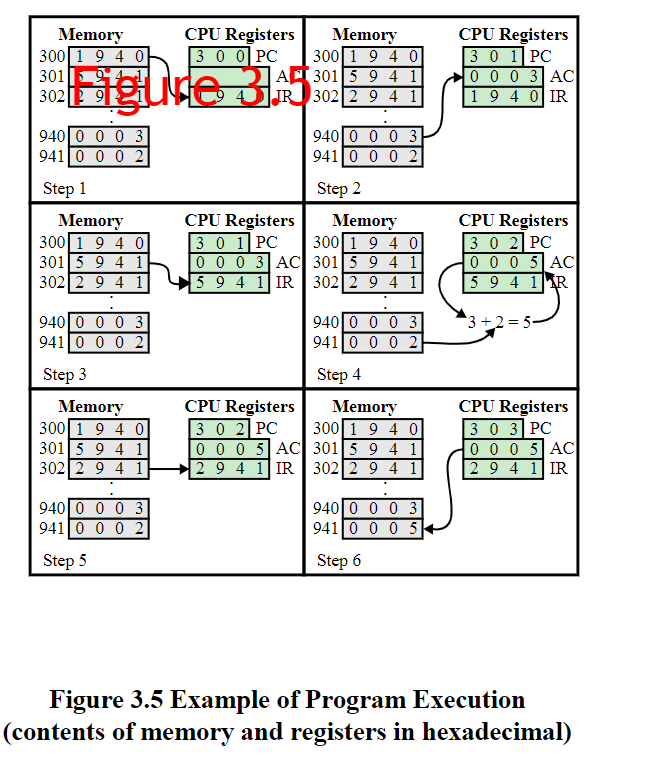
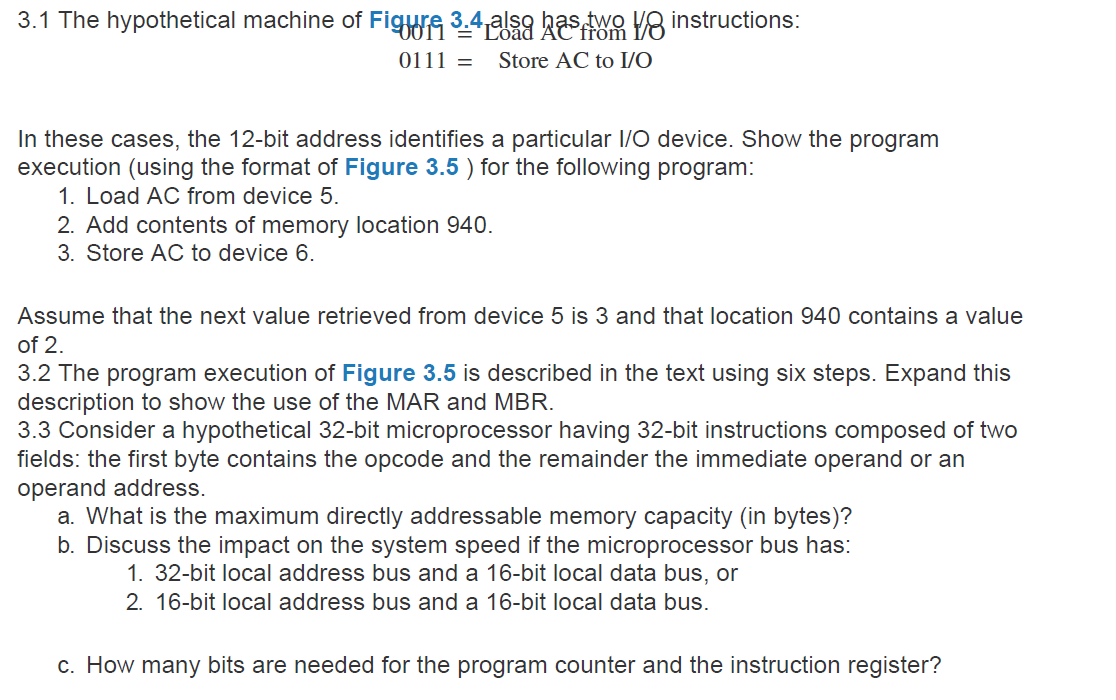
(a) Instruction format 1 Magnitude (b) Integer format Program Counter (PC)= Address of instruction Instruction Register (IR) = Instruction being executed Accumulator (AC)= Temporary storage (c) Internal CPU registers 0001=LoadAC from Memory 0010= Store AC to Memory 0101=Add to AC from Memory (d) Partial list of opcodes Figure 3.4 Characteristics of a Hypothetical Machine Figure 3.5 Example of Program Execution (contents of memory and registers in hexadecimal) 0111= Store AC to I/O In these cases, the 12-bit address identifies a particular I/O device. Show the program execution (using the format of Figure 3.5 ) for the following program: 1. Load AC from device 5. 2. Add contents of memory location 940 . 3. Store AC to device 6. Assume that the next value retrieved from device 5 is 3 and that location 940 contains a value of 2. 3.2 The program execution of Figure 3.5 is described in the text using six steps. Expand this description to show the use of the MAR and MBR. 3.3 Consider a hypothetical 32-bit microprocessor having 32-bit instructions composed of two fields: the first byte contains the opcode and the remainder the immediate operand or an operand address. a. What is the maximum directly addressable memory capacity (in bytes)? b. Discuss the impact on the system speed if the microprocessor bus has: 1. 32-bit local address bus and a 16-bit local data bus, or 2. 16-bit local address bus and a 16 -bit local data bus. c. How many bits are needed for the program counter and the instruction register
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


