Question: A java problem within eclipse that uses the two classes I labeled in bold below. SortMethods.Java: import java.util.Comparator; public class SortMethods { public static >
A java problem within eclipse that uses the two classes I labeled in bold below.

![> void selectionSort (T [ ] data) { int mindex; for (int](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/09/66db998f3e873_72666db998eb3e9c.jpg)
SortMethods.Java:
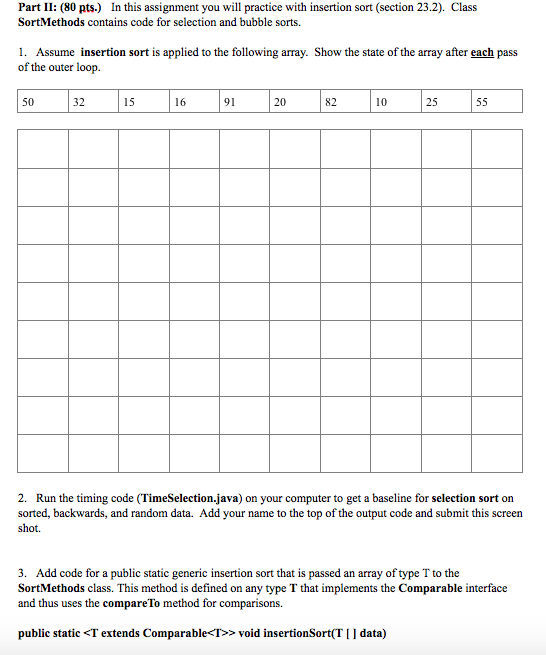
import java.util.Comparator; public class SortMethods { public static > void selectionSort (T [ ] data) { int mindex; for (int index=0; index> void bubbleSort (T [ ] data) { for (int ct1 = 0; ct1 0) swap (data, ct2, ct2+1); } public static > void betterBubbleSort (T [ ] data) { boolean needPass = true; for (int ct1 = 0; ct1 0) { swap (data, ct2, ct2+1); needPass = true; } } } public static > void swap (T[ ] data, int index1, int index2) { T temp = data[index1]; data[index1] = data[index2]; data[index2] = temp; } public static > void insertionSort(T [ ] data) { } public static void insertionSort(T [ ] data, Comparator comp) { } public static > boolean isSorted (T [ ] data) { return true; } }
TimeSelectionSort.Java:
import java.util.Random; public class TimeSelectionSort { public static void main(String[] args) { long start; // start time for timing long end; // end time for timing int size1 = 10000; // initial array size, adjust as needed int size2 = size1 * 2; // increase original size by factor of 2 int size3 = size1 * 4; // increase original size by factor of 4 Double [ ] a1 = new Double [size1]; // arrays of increasing sizes Double [ ] a2 = new Double [size2]; Double [ ] a3 = new Double [size3]; // best case test - fill arrays with sorted data for (int k = 0; k Part II: (80 pts.) In this assignment you will practice with insertion sort (section 23.2). Class SortMethods contains code for selection and bubble sorts. 1. Assume insertion sort is applied to the following array. Show the state of the array after each pass of the outer loop. 50 32 15 16 91 20 10 25 2. Run the timing code (TimeSelection.java) on your computer to get a baseline for selection sort on sorted, backwards, and random data. Add your name to the top of the output code and submit this screen shot 3. Add code for a public static generic insertion sort that is passed an array of type T to the SortMethods class. This method is defined on any type T that implements the Comparable interface and thus uses the compareTo method for comparisons. public static > void insertionSort(T I I data) Part II: (80 pts.) In this assignment you will practice with insertion sort (section 23.2). Class SortMethods contains code for selection and bubble sorts. 1. Assume insertion sort is applied to the following array. Show the state of the array after each pass of the outer loop. 50 32 15 16 91 20 10 25 2. Run the timing code (TimeSelection.java) on your computer to get a baseline for selection sort on sorted, backwards, and random data. Add your name to the top of the output code and submit this screen shot 3. Add code for a public static generic insertion sort that is passed an array of type T to the SortMethods class. This method is defined on any type T that implements the Comparable interface and thus uses the compareTo method for comparisons. public static > void insertionSort(T I I data) Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


