Question: A machine element simplified as a rectangular plate part is sketched in Figure Q2. The part is fixed rigidly at the top as indicated.
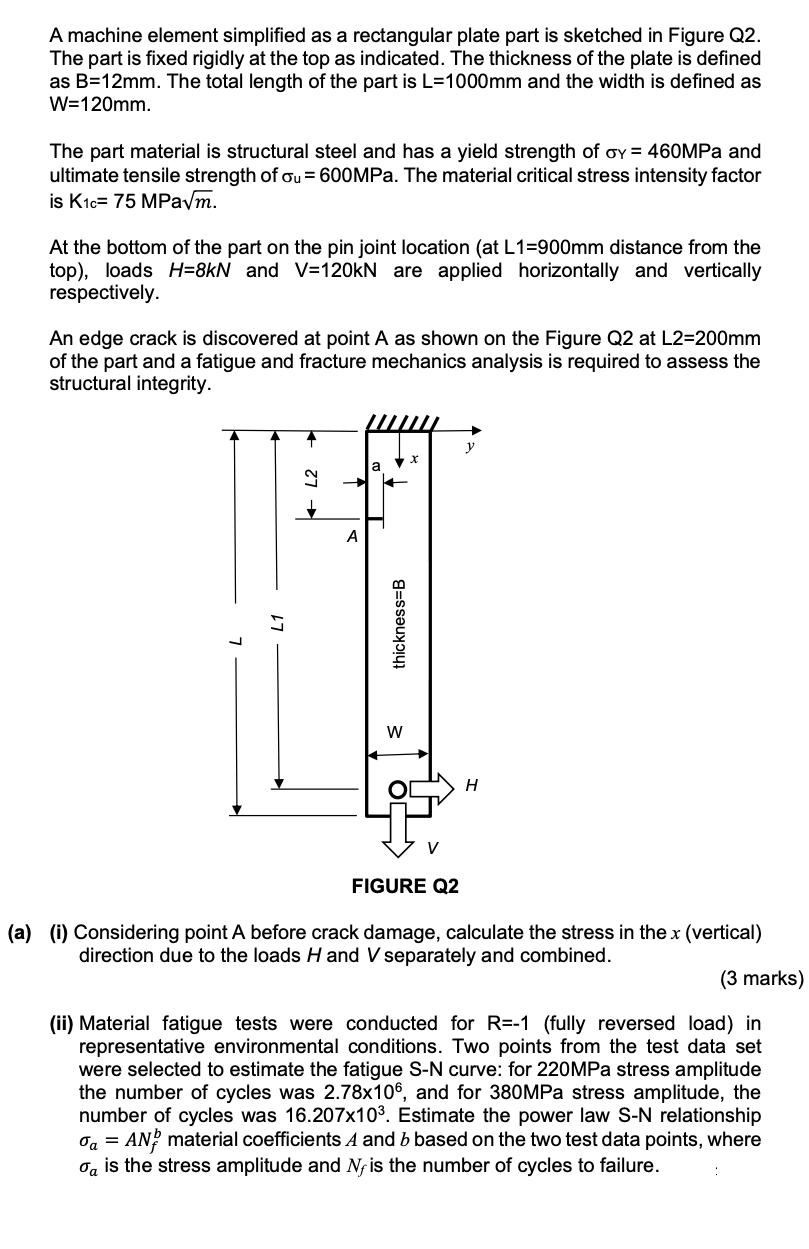
A machine element simplified as a rectangular plate part is sketched in Figure Q2. The part is fixed rigidly at the top as indicated. The thickness of the plate is defined as B=12mm. The total length of the part is L=1000mm and the width is defined as W=120mm. The part material is structural steel and has a yield strength of oy = 460MPa and ultimate tensile strength of ou= 600MPa. The material critical stress intensity factor is K1c= 75 MPam. At the bottom of the part on the pin joint location (at L1=900mm distance from the top), loads H=8kN and V=120kN are applied horizontally and vertically respectively. An edge crack is discovered at point A as shown on the Figure Q2 at L2=200mm of the part and a fatigue and fracture mechanics analysis is required to assess the structural integrity. 2 a + A thickness=B W X FIGURE Q2 y H (a) (i) Considering point A before crack damage, calculate the stress in the x (vertical) direction due to the loads Hand V separately and combined. (3 marks) (ii) Material fatigue tests were conducted for R=-1 (fully reversed load) in representative environmental conditions. Two points from the test data set were selected to estimate the fatigue S-N curve: for 220MPa stress amplitude the number of cycles was 2.78x106, and for 380MPa stress amplitude, the number of cycles was 16.207x10. Estimate the power law S-N relationship oa = AN material coefficients A and b based on the two test data points, where Ta is the stress amplitude and N, is the number of cycles to failure.
Step by Step Solution
3.48 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a i Heres how to calculate the stress in the x vertical direction due to the loads H and V separatel... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


