Question: A) O(nlogn) B) O(n) C) O(n2) D) O(n3) E) None Suppose f(n) is O(g(n)), and g(n) is O(h(n)). What is the best big-O for f(n)h(n)



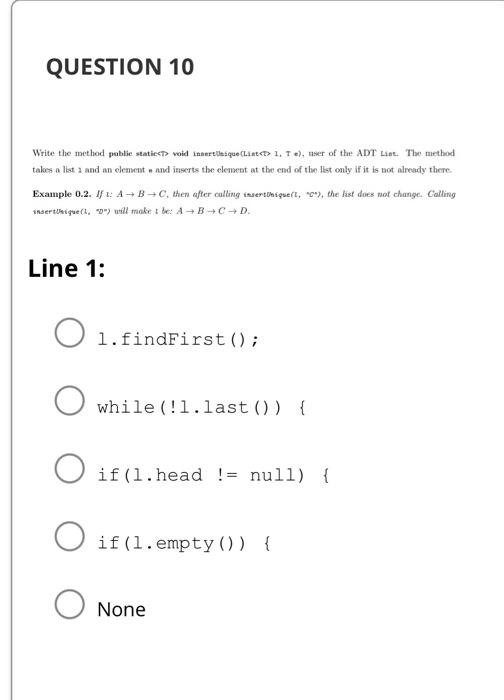



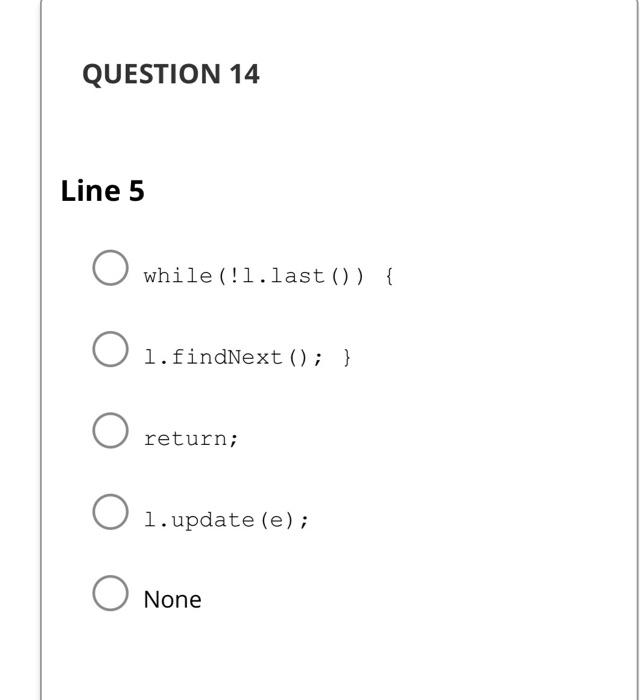
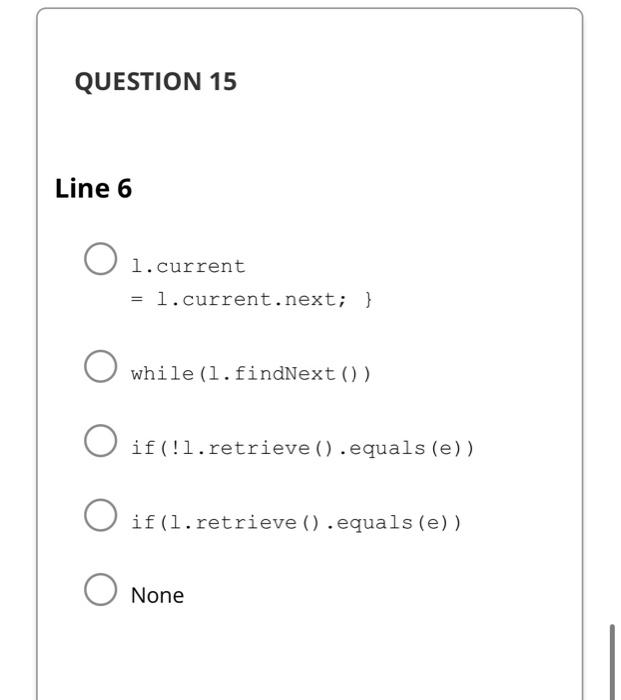



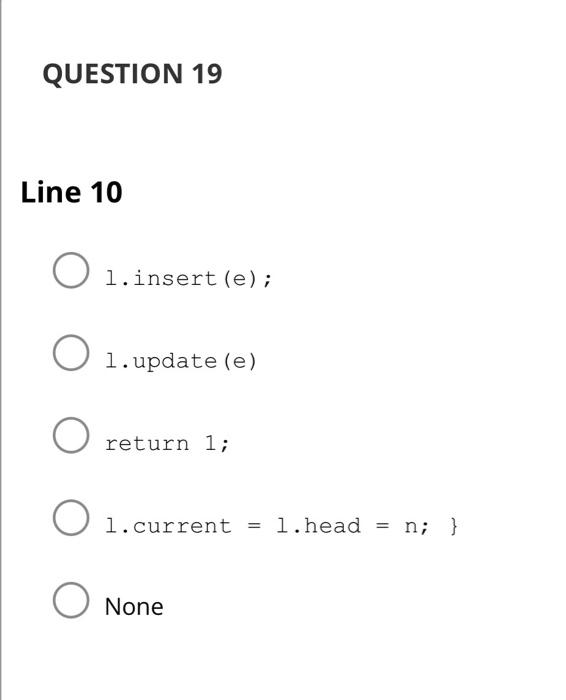
A) O(nlogn) B) O(n) C) O(n2) D) O(n3) E) None Suppose f(n) is O(g(n)), and g(n) is O(h(n)). What is the best big-O for f(n)h(n) ? A) O(h(n)) B) O(f(n)g(n)) C) O(f(n)h(n)) D) O(f(n)+g(n)) E) None Suppose f(n) is O(g(n)), and g(n) is O(h(n)). What is the best big-O for f(n)h(n) ? A) O(h(n)) B) O(f(n)g(n)) C) O(f(n)h(n)) D) O(f(n)+g(n)) E) None Write the method pablic statiects void inaertlesque(Lintets 1, e), nser of the ADT Lac. The method takes a list 2 and an element n and inserts the elemest at the end of the lest only if it is aot already there Example 0.2. If t:ABC, then after calling issertonique(t, "C"), the list does not change. Calling insertbwigue(t, whe) will make I be: ABCD. Line 1: l.findFirst(); while(!l.last()) \{ if(l.head != null) \{ if(l.empty()) \{ None QUESTION 11 Line 2 1. current = l.head; l.insert (e); while(!l. last()) \{ if (l.retrieve (). equals (e)) None QUESTION 12 Line 3 l.findNext () ; return; } while(l.current != null) \{ if (l.retrieve (). equals (e)) None QUESTION 13 Line 4 l.insert (e); l.findFirst(); if (l. current. data. equals (e)) return; None QUESTION 14 Line 5 while(!l.last()) \{ l.findNext (); \} return; 1. update (e); None QUESTION 15 Line 6 l. current =1. current.next; } while (l.findNext()) if(!l.retrieve (). equals (e)) if(l.retrieve (). equals (e)) None return; l.current.next = new Node
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


