Question: A Pointer Is A Variable That Provides An Indirect Reference To A Data Value; Instead Of Storing The Value Itself, It Stores The 1. A
A Pointer Is A Variable That Provides An Indirect Reference To A Data Value; Instead Of Storing The Value Itself, It Stores The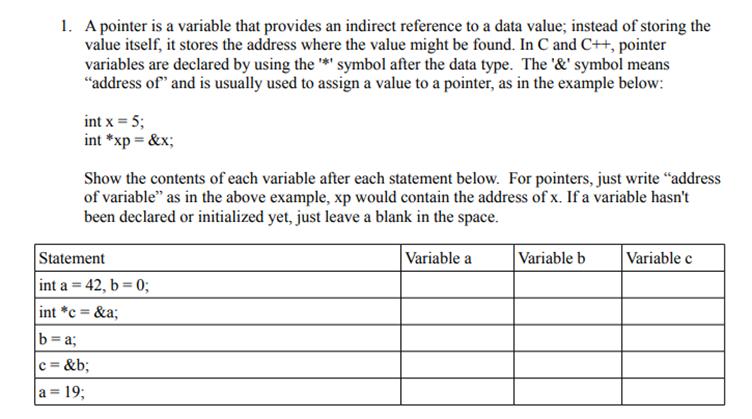
1. A pointer is a variable that provides an indirect reference to a data value; instead of storing the value itself, it stores the address where the value might be found. In C and C++, pointer variables are declared by using the '*' symbol after the data type. The '&' symbol means "address of" and is usually used to assign a value to a pointer, as in the example below: int x=5; int *xp=&x; Show the contents of each variable after each statement below. For pointers, just write "address of variable" as in the above example, xp would contain the address of x. If a variable hasn't been declared or initialized yet, just leave a blank in the space. Statement int a 42, b = 0; int *c=&a; b=a; c=&b; a=19; Variable a Variable b Variable c
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


