Question: A relational database holds two relations: professor (ID, name, email) and researchInterest (ID, researchTopic) with the following information: Relation professor: Tuples are stored as fixed-format,

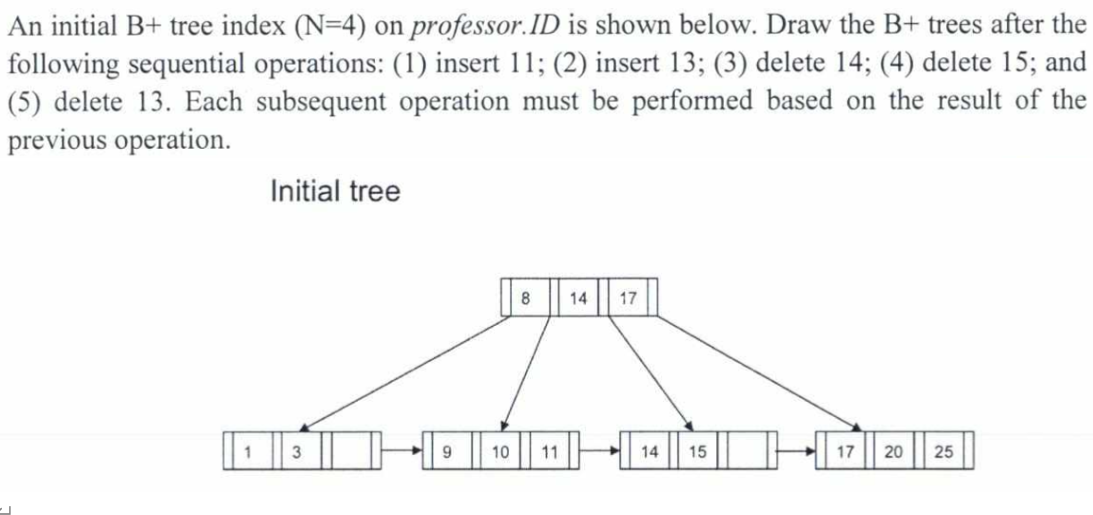
A relational database holds two relations: professor (ID, name, email) and researchInterest (ID, researchTopic) with the following information: Relation professor: Tuples are stored as fixed-format, fixed-length records, each of 400 bytes. There are 5,000 tuples. Each tuple contains a key attribute ID of length 20 bytes; other fields and the record header make up the rest Relation research Interest: Tuples are stored as fixed-format, fixed-length records, each of 100 bytes. There are 25,000 tuples. Tuples contain attribute research Interest. ID, referencing professor. ID. Assume that the size of one block is 4-kilobyte (4,096 bytes), and no tuple spans over more than one block. Each professor can specify up to five research interests, and space is allocated even if a professor specifies less than five interests. Tuples in professor are sequentially ordered by ID. The "clustered disk organisation strategy is used, which means that, for each professor tuple, the five tuples of researchInterest also reside in the same block. An initial B+ tree index (N=4) on professor. ID is shown below. Draw the B+ trees after the following sequential operations: (1) insert 11; (2) insert 13; (3) delete 14; (4) delete 15; and (5) delete 13. Each subsequent operation must be performed based on the result of the previous operation. Initial tree 8 14 17 1 9 10 11 14 15 -| .7 || 20 | 25 |
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


