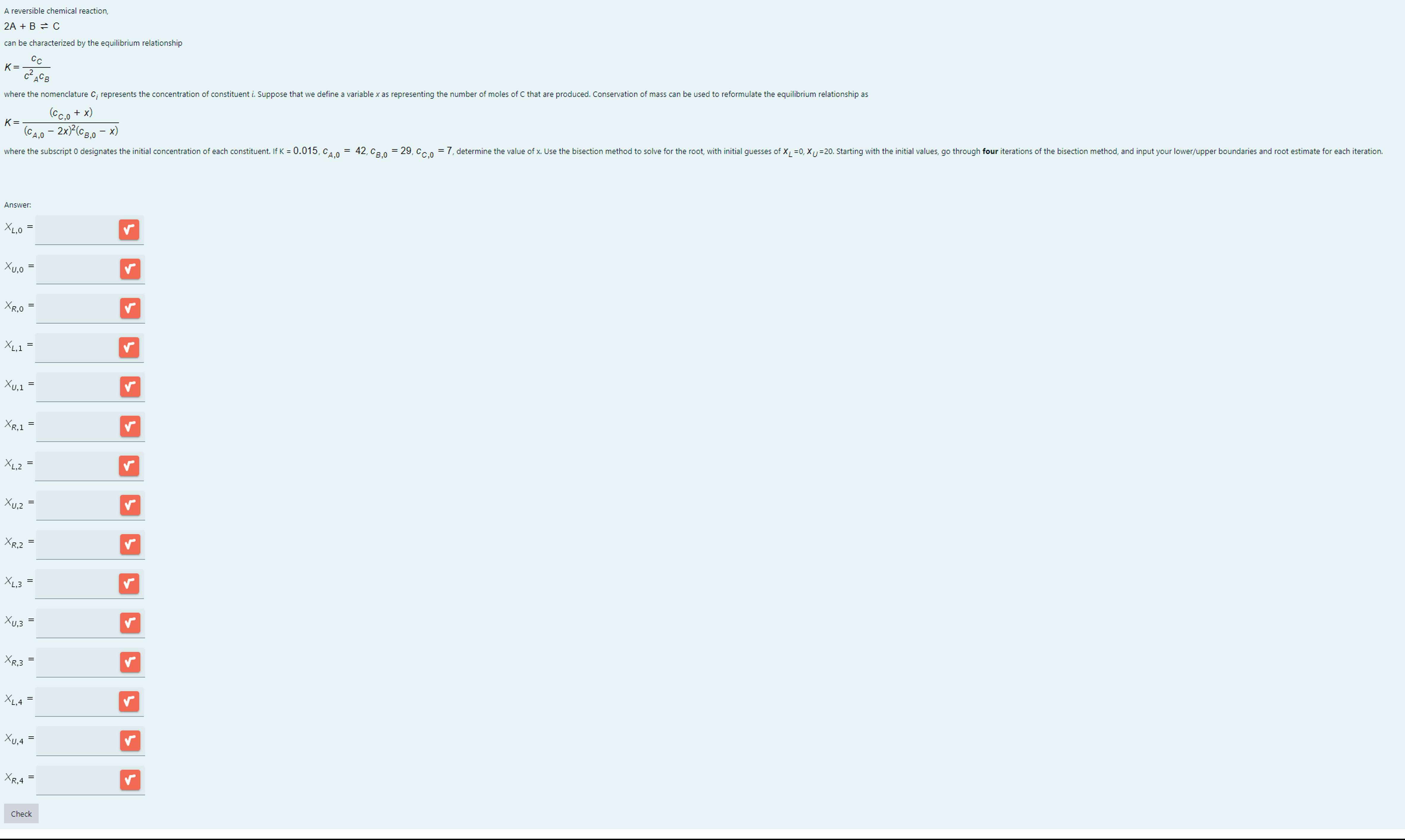
Question: A reversible chemical reaction 2 A + B = > C can be characterized by the equilibrium relationship K = ( C _ C )
A reversible chemical reaction
AB C
can be characterized by the equilibrium relationship
K CCCACB
where the nomenclature Ci represents the concentration of constituent i Suppose that we define a variable x as representing the number of moles of C that are produced. Conservation of mass can be used to reformulate the equilibrium relationship as
K CC xCAxCB X
where the subscript designates the initial concentration of each constituent. If K CA CB CC Determine the value of x Use the bisection method to solve for the root, with initial guesses of XL and XU Starting with the initial values, go through FOUR A reversible chemical reaction,
can be characterized by the equilibrium relationship
Answer:
iterations of the bisection method, and input your lowerupper boundaries and root estimate for each iteration.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


