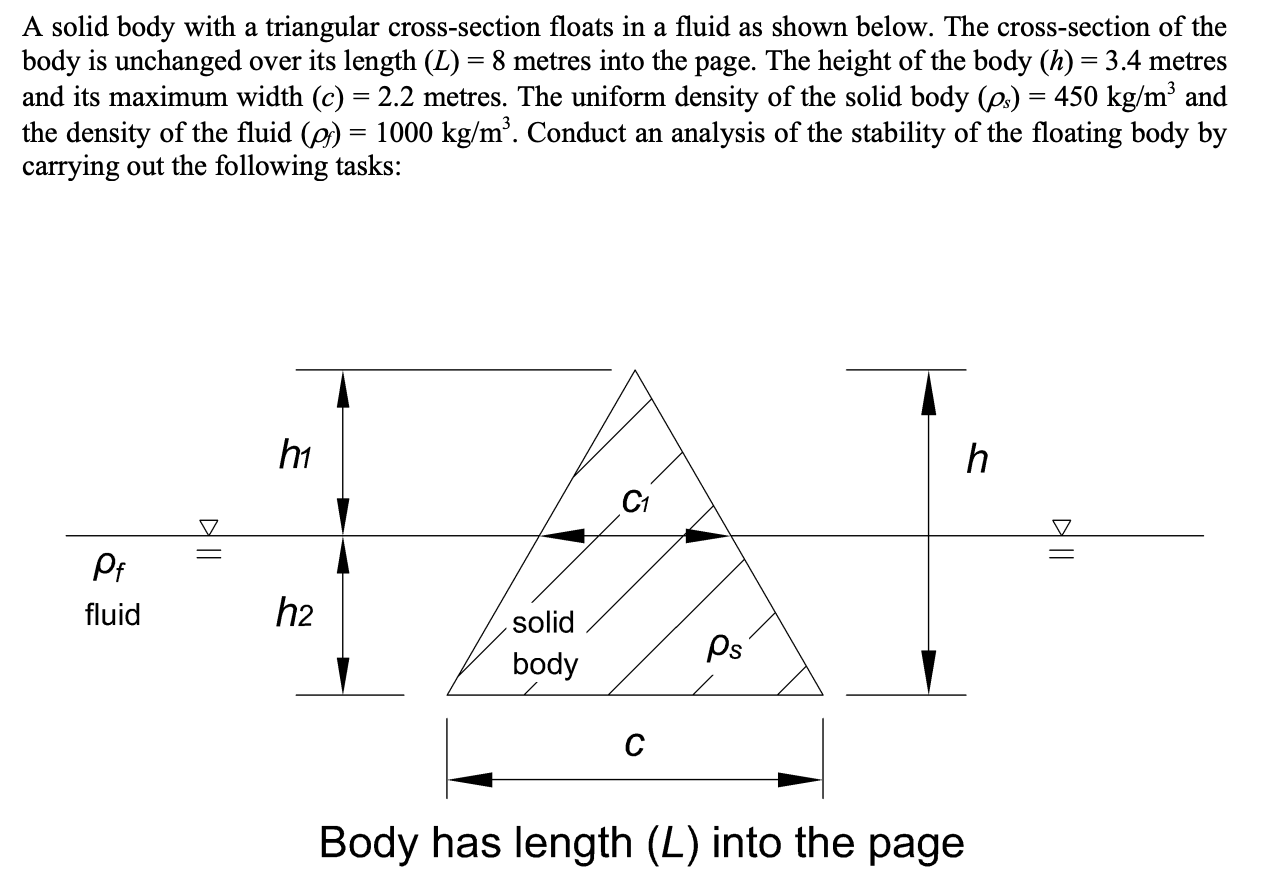
Question: A solid body with a triangular cross - section floats in a fluid as shown below. The cross - section of the 2 ( d
A solid body with a triangular crosssection floats in a fluid as shown below. The crosssection of the d: Noting that the submerged volume can be written as the difference between the total
volume of the floating object and the volume of the floating body above the free surface,
determine the value of in the figure above in metres. Hint: you might find the concept of
similar triangles usefiul here
Note: If you are unable to complete this part of the question, you can assume and
proceed with the remainder of the question.
e: Determine the submerged depth of the floating object in metres:
f: Determine the width of the triangle at the waterline crosssection in metres: g: Noting that the distance from the base of the floating object to the centroid of
the submerged volume can be written as:
Determine the distance GB between the centre of gravity and the centre of buoyancy
B of the floating bodv in metres:
h: Determine the second moment of area about the waterline crosssection of the body in
Note: Adopt the combination of and ; that generates the smallest second moment
of area. This is because the smallest second moment of area is critical in terms of stability.
i: Determine the distance BM between the centre of buoyancy B and metacentre M in
metres:
j: Determine the metacentric height GM for the floating body in metres.
k: State the value of the metacentric height necessary for neutral stability in metres: c: Determine the submerged volume of the body in :
Answer:
d: Determine the value of in the figure above in metres.
Answer:
Note: If you are unable to complete this part of the question, you can assume and
proceed with the remainder of the question.
e: Determine the submerged depth of the floating object in metres:
f: Determine the width of the triangle at the waterline crosssection in metres:
g: Determine the distance GB between the centre of gravity and the centre of buoyancy
B of the floating hodv in metres:
h: Determine the second moment of area about the waterline crosssection of the body in
Note: Adopt the combination of and ; that generates the smallest second moment
of area. This is because the smallest second moment of area is critical in terms of stability.
i: Determine the distance BM between the centre of buoyancy B and metacentre M in
metres:
j: Determine the metacentric height GM for the floating body in metres.
Answer:
body is unchanged over its length metres into the page. The height of the body metres
and its maximum width metres. The uniform density of the solid body and
the density of the fluid Conduct an analysis of the stability of the floating body by
carrying out the following tasks: Answers are provided, just confused on the working and the steps to take for each question. Please solve the quesstions to arrive at the given answers :)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


