Question: A spanning tree is a selection of edges from a connected graph that are connected but don't form a cycle. We formed them when deciding
A spanning tree is a selection of edges from a connected graph that are connected but don't form a cycle. We formed them when deciding if a graph was connected, and in FordFulkerson. If the edges are weighted, then a minimal spanning tree is one whose sum of weights is minimum. Kruskal's algorithm is a simple algorithm that builds a minimal spanning tree as follows. Order the edges from smallest weight to largest, and begin the tree with just the vertices and no edges. For every edge in order, if adding the edge won't form a cycle both adjacent vertices are already connected add it While the edges won't initially be connected, by the end of the process we have a single connected tree.
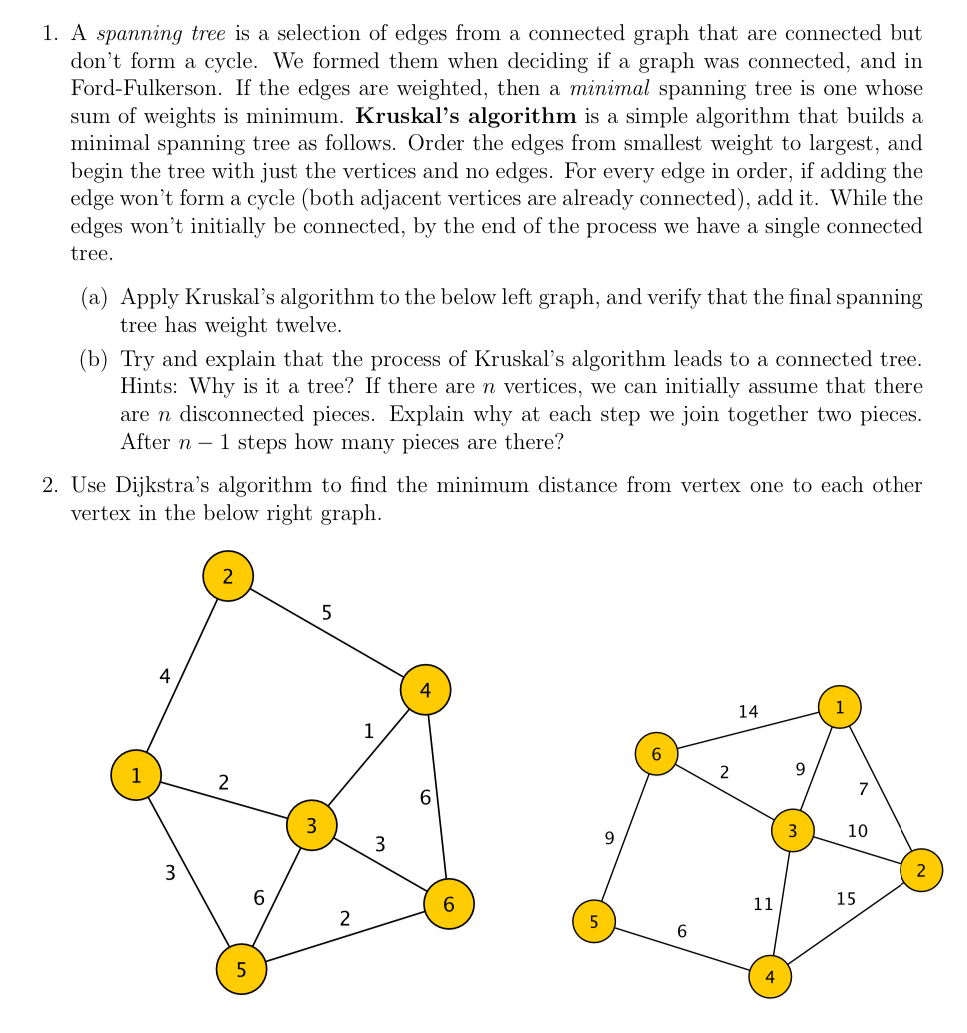
a Apply Kruskal's algorithm to the below left graph, and verify that the final spanning tree has weight twelve.
b Try and explain that the process of Kruskal's algorithm leads to a connected tree. Hints: Why is it a tree? If there are vertices, we can initially assume that there are disconnected pieces. Explain why at each step we join together two pieces. After steps how many pieces are there?
Use Dijkstra's algorithm to find the minimum distance from vertex one to each other vertex in the below right graph. Detailed solution to a please
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


