Question: A) State null and alternate hypothesisB) Give test statistic and p valueC) reject or do not reject null? Babies Learn Early Who They Can Trust
A) State null and alternate hypothesisB) Give test statistic and p valueC) reject or do not reject null?
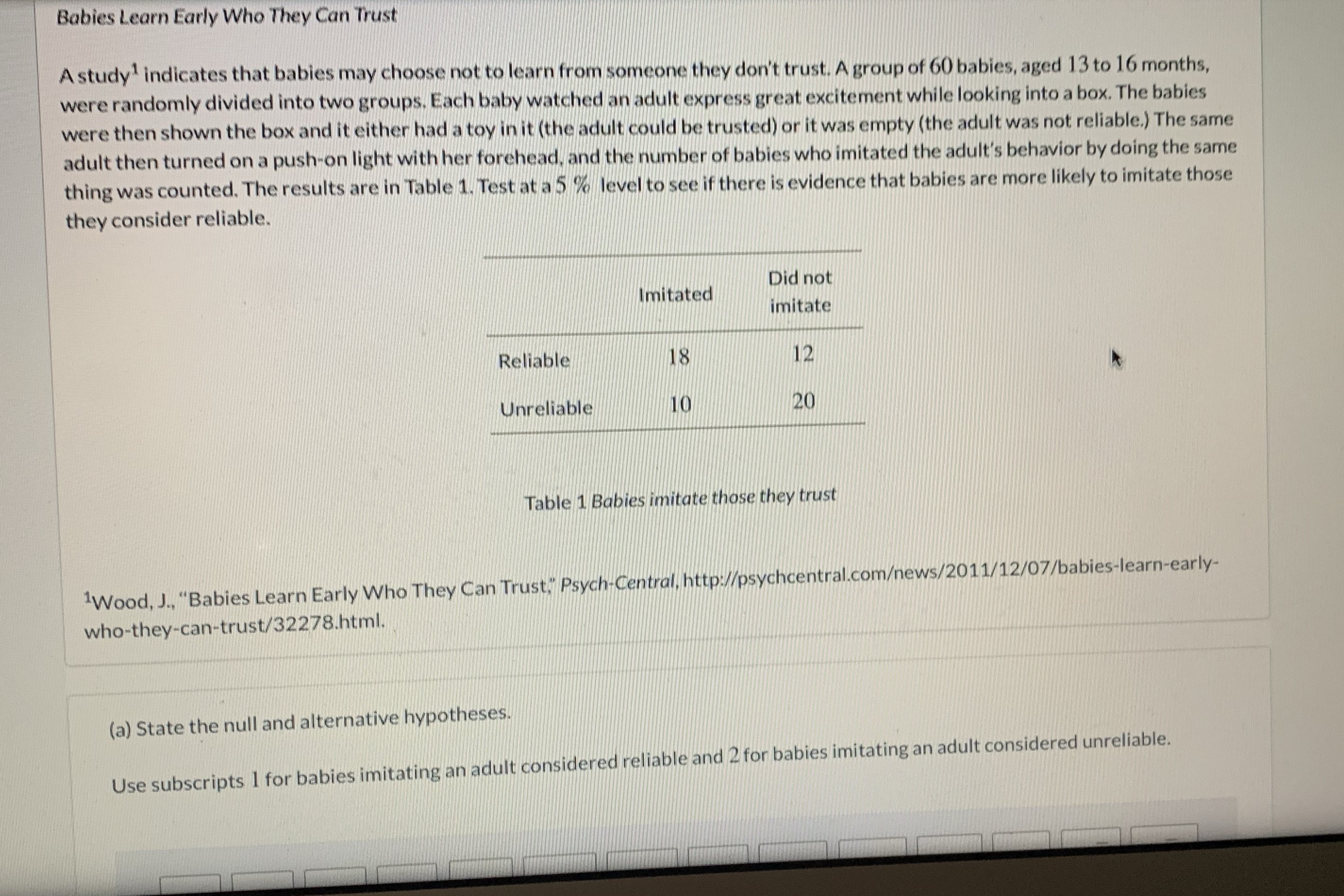
Babies Learn Early Who They Can Trust A study indicates that babies may choose not to learn from someone they don't trust. A group of 60 babies, aged 13 to 16 months, were randomly divided into two groups, Each baby watched an adult express great excitement while looking into a box. The babies were then shown the box and it either had a toy in it (the adult could be trusted) or it was empty (the adult was not reliable.) The same adult then turned on a push-on light with her forehead, and the number of babies who imitated the adult's behavior by doing the same thing was counted. The results are in Table 1, Test at a 5 % level to see if there is evidence that babies are more likely to imitate those they consider reliable. Did not Imitated imitate Reliable 18 12 Unreliable 10 20 Table 1 Babies imitate those they trust 1Wood, J., "Babies Learn Early Who They Can Trust," Psych-Central, http://psychcentral.comews/2011/12/07/babies-learn-early- who-they-can-trust/32278.html. (a) State the null and alternative hypotheses Use subscripts 1 for babies imitating an adult considered reliable and 2 for babies imitating an adult considered unreliable
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


