Question: A student is interested in quantifying the resultant force and moment ( F T and M T ) through the talar joint when a ballerina
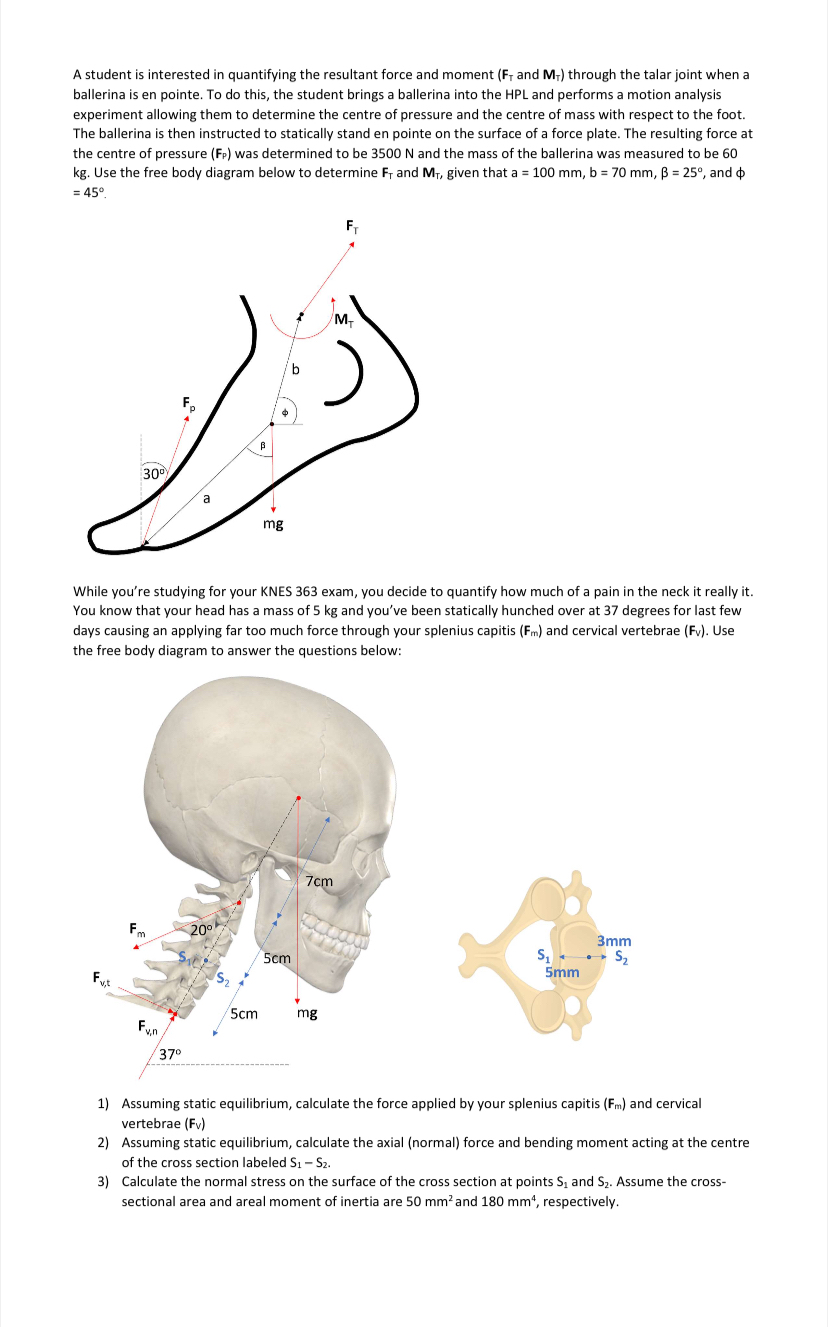
A student is interested in quantifying the resultant force and moment and through the talar joint when a ballerina is en pointe. To do this, the student brings a ballerina into the HPL and performs a motion analysis experiment allowing them to determine the centre of pressure and the centre of mass with respect to the foot. The ballerina is then instructed to statically stand en pointe on the surface of a force plate. The resulting force at the centre of pressure was determined to be N and the mass of the ballerina was measured to be kg Use the free body diagram below to determine and given that and
While you're studying for your KNES exam, you decide to quantify how much of a pain in the neck it really it You know that your head has a mass of kg and you've been statically hunched over at degrees for last few days causing an applying far too much force through your splenius capitis and cervical vertebrae Use the free body diagram to answer the questions below:
Assuming static equilibrium, calculate the force applied by your splenius capitis and cervical vertebrae
Assuming static equilibrium, calculate the axial normal force and bending moment acting at the centre of the cross section labeled
Calculate the normal stress on the surface of the cross section at points and Assume the crosssectional area and areal moment of inertia are and respectively.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


