Question: A student runs two experiments with a constant-volume bomb calorimeter containing 1000. g of water (see sketch at right). First, a 5.500g tablet of benzoic
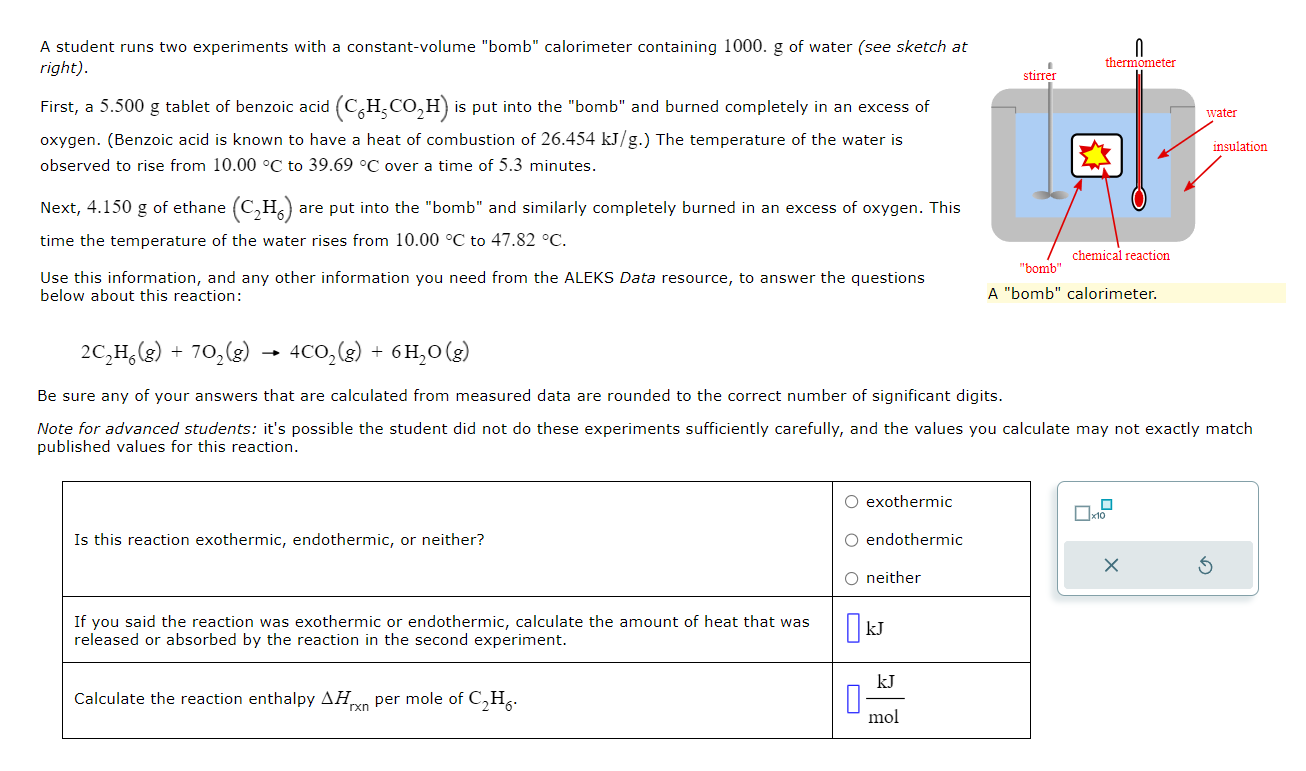
A student runs two experiments with a constant-volume "bomb" calorimeter containing 1000. g of water (see sketch at right). First, a 5.500g tablet of benzoic acid (C6H5CO2H) is put into the "bomb" and burned completely in an excess of oxygen. (Benzoic acid is known to have a heat of combustion of 26.454kJ/g.) The temperature of the water is observed to rise from 10.00C to 39.69C over a time of 5.3 minutes. Next, 4.150g of ethane (C2H6) are put into the "bomb" and similarly completely burned in an excess of oxygen. This time the temperature of the water rises from 10.00C to 47.82C. Use this information, and any other information you need from the ALEKS Data resource, to answer the questions below about this reaction: 2C2H6(g)+7O2(g)4CO2(g)+6H2O(g) Be sure any of your answers that are calculated from measured data are rounded to the correct number of significant digits. Note for advanced students: it's possible the student did not do these experiments sufficientlv carefullv. and the values vou calculate mav not exactlv match
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


