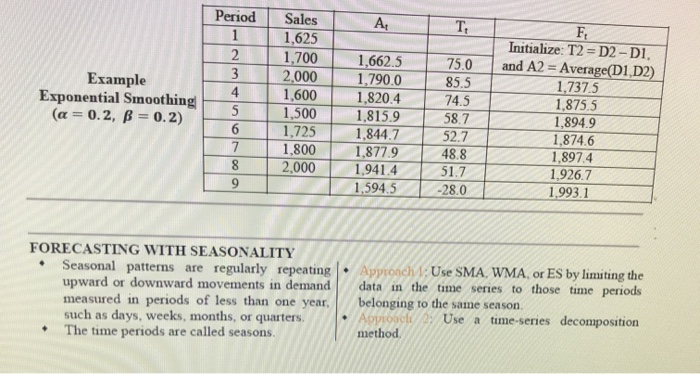
Question: A. T. Example Exponential Smoothing (a=0.2, B = 0.2) Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Sales 1,625 1,700 2,000 1,600 1,500
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


