Question: a) The EOQ for the workbooks is (round your response to the nearest whole number). b) What are the annual holding costs for the workbooks?
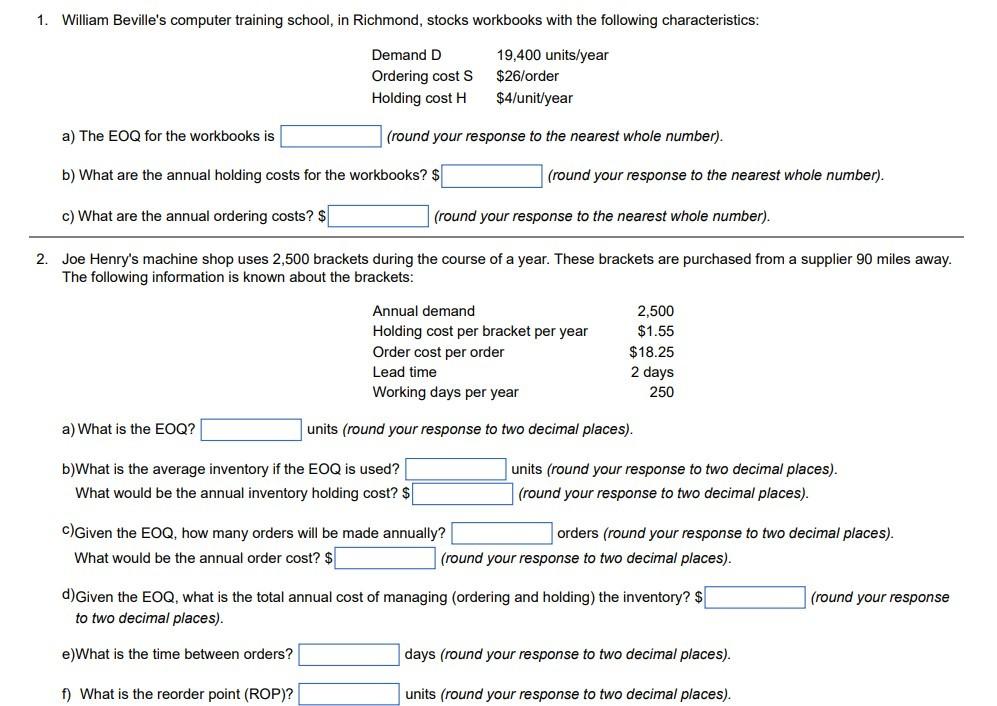

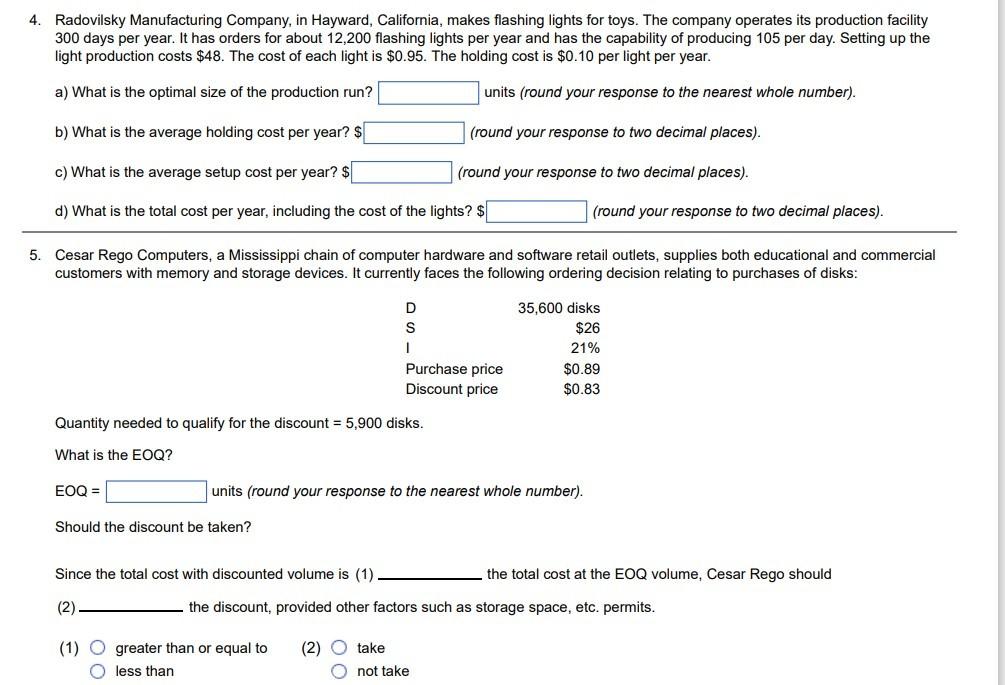
a) The EOQ for the workbooks is (round your response to the nearest whole number). b) What are the annual holding costs for the workbooks? \$ (round your response to the nearest whole number). c) What are the annual ordering costs? \$ (round your response to the nearest whole number). 2. Joe Henry's machine shop uses 2,500 brackets during the course of a year. These brackets are purchased from a supplier 90 miles away. The following information is known about the brackets: a) What is the EOQ? units (round your response to two decimal places). b)What is the average inventory if the EOQ is used? units (round your response to two decimal places). What would be the annual inventory holding cost? \$ (round your response to two decimal places). c) Given the EOQ, how many orders will be made annually? orders (round your response to two decimal places). What would be the annual order cost? \$ (round your response to two decimal places). d) Given the EOQ, what is the total annual cost of managing (ordering and holding) the inventory? \$ (round your response to two decimal places). e)What is the time between orders? days (round your response to two decimal places). f) What is the reorder point (ROP)? units (round your response to two decimal places). 3. M. Cotteleer Electronics supplies microcomputer circuitry to a company that incorporates microprocessors into refrigerators and other home appliances. One of the components has an annual demand of 250 units, and this is constant throughout the year. Carrying cost is estimated to be $0.25 per unit per year, and the ordering (setup) cost is $19 per order. a) To minimize cost, how many units should be ordered each time an order is placed? units (round your response to two decimal places). b) How many orders per year are needed with the optimal policy? orders (round your response to two decimal places). c) What is the average inventory if costs are minimized? units (round your response to two decimal places). d) Suppose that the ordering (setup) cost is not $19, and Cotteleer has been ordering 150 units each time an order is placed. For this order policy (of Q=150 ) to be optimal, the ordering (setup) cost would have to be $ (round your response to two decimal places). 4. Radovilsky Manufacturing Company, in Hayward, California, makes flashing lights for toys. The company operates its production facility 300 days per year. It has orders for about 12,200 flashing lights per year and has the capability of producing 105 per day. Setting up the light production costs $48. The cost of each light is $0.95. The holding cost is $0.10 per light per year. a) What is the optimal size of the production run? units (round your response to the nearest whole number). b) What is the average holding cost per year? \$ (round your response to two decimal places). c) What is the average setup cost per year? \$ (round your response to two decimal places). d) What is the total cost per year, including the cost of the lights? \$ (round your response to two decimal places). 5. Cesar Rego Computers, a Mississippi chain of computer hardware and software retail outlets, supplies both educational and commercial customers with memory and storage devices. It currently faces the following ordering decision relating to purchases of disks: Quantity needed to qualify for the discount =5,900 disks. What is the EOQ? EOQ= units (round your response to the nearest whole number). Should the discount be taken? Since the total cost with discounted volume is (1) the total cost at the EOQ volume, Cesar Rego should (2) the discount, provided other factors such as storage space, etc. permits. (1) greater than or equal to (2) take less than not take
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


