Question: a) Write a generator function called gen_factorials(n) that generates the first n factorials, beginning with01 (which is 1 by definition), So, gen factorials(10) should generate
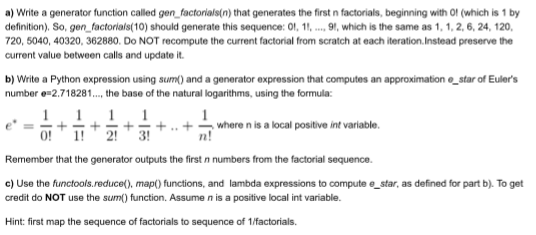
a) Write a generator function called gen_factorials(n) that generates the first n factorials, beginning with01 (which is 1 by definition), So, gen factorials(10) should generate this sequence: 0!, 1!, ... 9!, which is the same as 1, 1, 2, 6, 24, 120 720, 5040, 40320, 362880. Do NOT recompute the current factorial from scratch at each iteration. Instead preserve the current value between calls and update it. b) Write a Python expression using sum0 and a generator expression that computes an approximation e_star of Euler's number e = 2.718281..., the base of the natural logarithms, using the formula: e* = 1/0! + 1/1! + 1/2! + 1/3! + ..+ 1!, where n is a local positive int variable. Remember that the generator outputs the first n numbers from the factorial sequence. c) Use the functools.reduce(), map() functions, and lambda expressions to compute e_star, as defined for part b) To get credit do NOT use the sum() function. Assume n is a positive local int variable
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


