Question: Above file contains implementation of sequential search and binary search. You will use the program to compare the performance of these two search techniques. Run
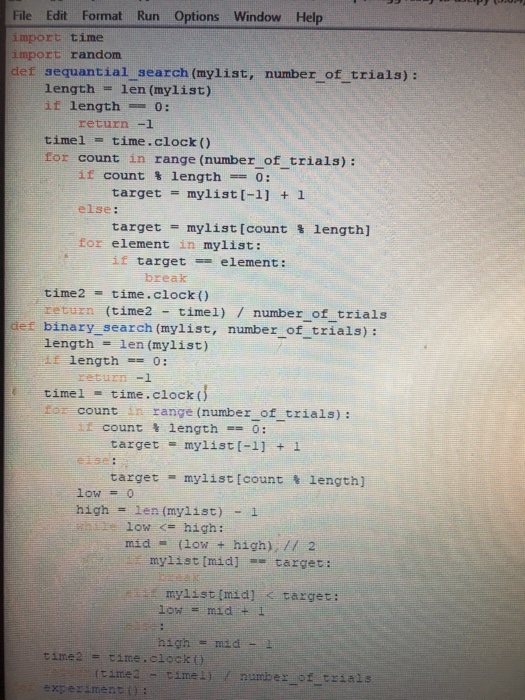
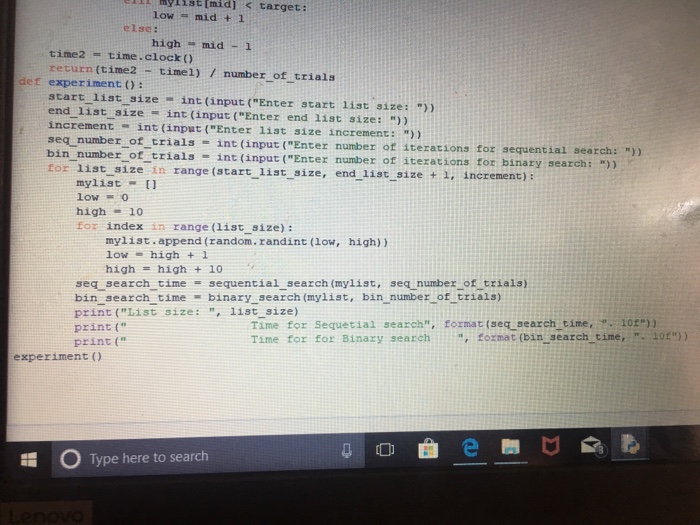
File Edit Format Run Options Window Help import time import random def sequantial search (mylist, number_of trials): length- 1en (mylist) if length =-0: return -1 time1 = time . clock ( ) for count in range (number of trials): if count % length 0: else: for element in mylist: target mylist [-1] + 1 target =mylist [count % length] if target element: break time2 time. clock ( ) return (time2 timel) / number of trials length = len (mylist) def binary search (mylist, number of trials): length 0: burn -1 time1-time.clock ( tor count in range (number of trials): it count % length-_ 0 target mylist[-1] + 1 target-mylist [count length) low = O high#len (mylist) -1 low high: mid (1ow + high), // 2 my1ist [mid] target: i mylist(mid]target: time2 time.clock) ttime2 timel number of trials xperiment
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


