Question: ac e. Conserva f. Conserv Experiment #2 - Acceleration down an inclined Plane Aim - a) To study the effect of the angle of an

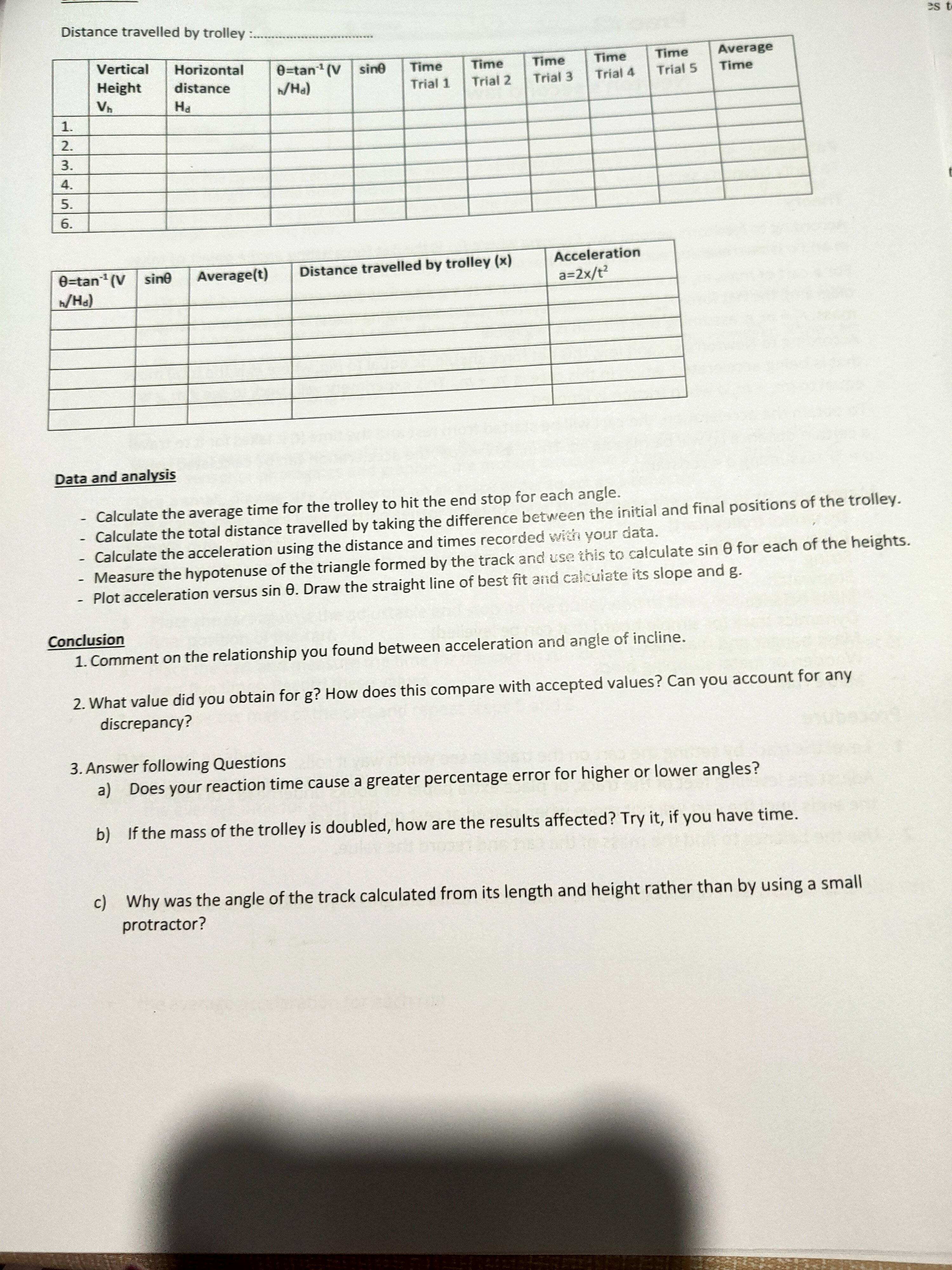


ac e. Conserva f. Conserv Experiment #2 - Acceleration down an inclined Plane Aim - a) To study the effect of the angle of an incline on the acceleration of an object. b) to analyse slope of acceleration vs sin 0 graph Theory: A trolley on an incline will roll down the incline as it is pulled by gravity. The force of gravity always acts vertically downwards. The component of gravity that is parallel to the inclined surface, is mg sin 0. If friction is ignored, the acceleration of the trolley will be constant as it rolls down the incline. To measure the acceleration, the trolley will be started from rest and the time (t) it takes to travel a certain distance (S) will be measured. Then, since the acceleration can be found using the formula a=2x/t2 A plot of acceleration versus sin 0 should give a straight line with a slope equal to the acceleration due to gravity (g). estions Materials . Dynamics trolley with mass Stopwatch Program . Dynamics track or board at least 1 m long . Metre rule . Graph paper Scales Procedure in Unit Trolley Dynamics track ation mgsing mgcose mg mgsine 1. 2. Set up the track as shown in the diagram, raising the end of the track from which the trolley is to start. released. Pull the trolley up to the top of the track and mark the initial position from where the trolley at rest will be 3 Release the trolley from rest and use the stopwatch to time how long it takes the trolley to hit the end stop. 4 . Repeat this measurement five times (with different people doing the timing). Record all the values in table. 5. Lower the end of the track to next level and measure the time five times. Repeat the experiment for a total of six/seven angles, lowering the track. 6Distance travelled by trolley :......... Vertical Horizontal 9=tan ' (V Average sine Time Time Time Time Time Height distance 1/Ha) Trial 1 Trial 3 Trial 4 Time Trial 2 Trial 5 Vn Ha 1. 2 . 3. 4. 5. 6 . 0=tan" (V sine Average(t) Distance travelled by trolley (x) Acceleration a=2x/t2 h/Ha) Data and analysis Calculate the average time for the trolley to hit the end stop for each angle. Calculate the total distance travelled by taking the difference between the initial and final positions of the trolley. Calculate the acceleration using the distance and times recorded with your data. Measure the hypotenuse of the triangle formed by the track and use this to calculate sin 0 for each of the heights. - Plot acceleration versus sin 0. Draw the straight line of best fit and calculate its slope and g. Conclusion 1. Comment on the relationship you found between acceleration and angle of incline. 2. What value did you obtain for g? How does this compare with accepted values? Can you account for any discrepancy? 3. Answer following Questions a) Does your reaction time cause a greater percentage error for higher or lower angles? b) If the mass of the trolley is doubled, how are the results affected? Try it, if you have time. c) Why was the angle of the track calculated from its length and height rather than by using a small protractor
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


