Question: Activity 2: Who does assign an IP address when your computer connects to the network? This is the role of DHCP. First, we are

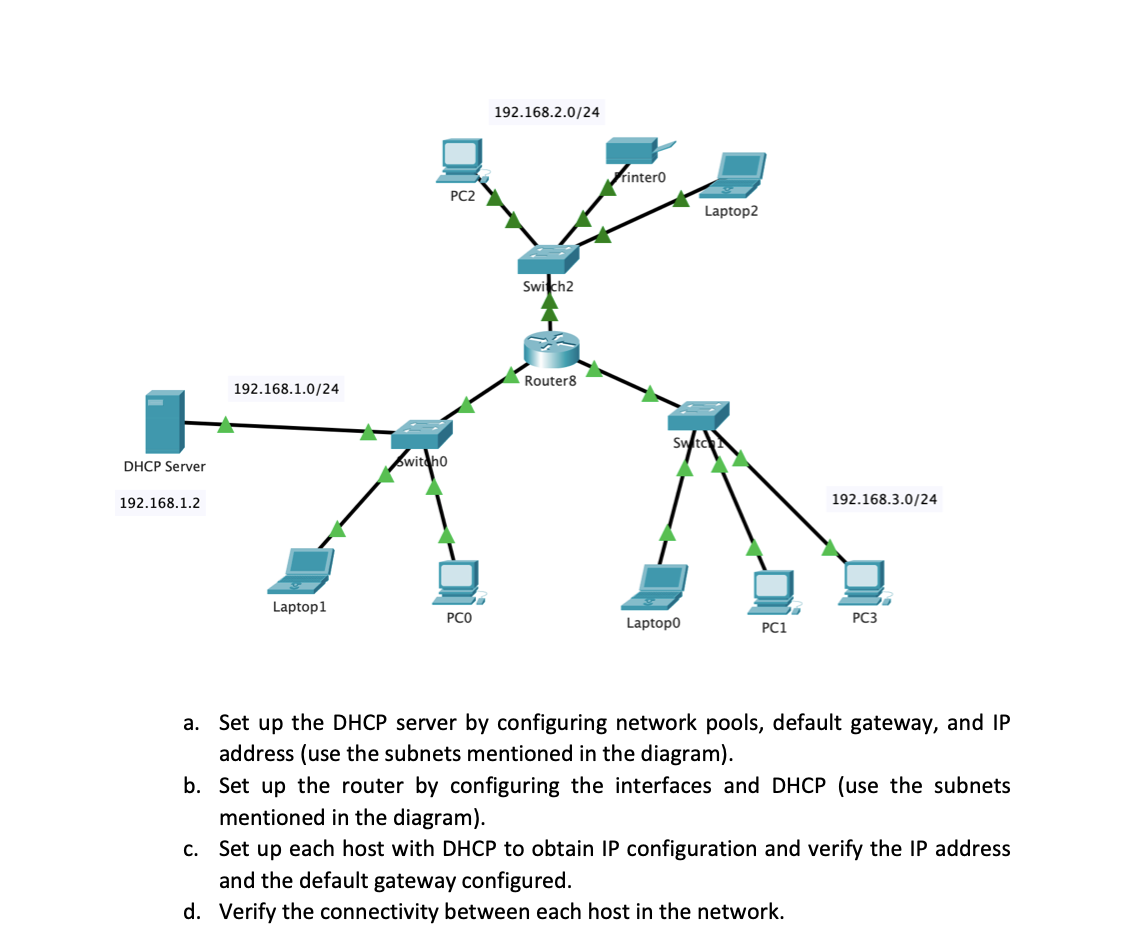
Activity 2: Who does assign an IP address when your computer connects to the network? This is the role of DHCP. First, we are going to do a small role play to mimic DHCP. Each member of the group has a role to play. Assume your group is your local area network (LAN). For example, you could consider a LAN at home or at Campus or at your workplace. 1. One group member can act as a router with a DHCP server and other three members are host devices that try to connect to the network. These host devices could be a PC, a printer, and network storage device. A sample network is shown in the below figure. Router K PC 1 Printer PC 2 Internet. 2. Assume the all the devices are physical connected as shown in the above figure. Now, your job is to set up the network and establish the connections with the router using DHCP. Each member needs to send/ respond with the correct message and message sequence to establish the connections and receive IP address for each host. 3. Draw a timing diagram to indicate the sequence of messages transferred between devices. 4. Next, we are going to implement a DHCP server in Cisco packet tracer and check the DHCP in action. Make use to take screenshots of the networks you build, analysis, and verifications. Open the packet tracer and implement the following network. You may need to use the same model of the devices shown in the diagram. Today, we are not going to use static IP configuration for the hosts as we are going to check the DHCP in action. Tips: You need to add a module with a fast ethernet port to the router, so that the router can support three LANs as shown in the below network diagram. DHCP Server 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.0/24 Laptop1 witcho PC2 PCO 10 192.168.2.0/24 Switch2 Router8 rinter0 Laptop0 Laptop2 PC1 192.168.3.0/24 PC3 a. Set up the DHCP server by configuring network pools, default gateway, and IP address (use the subnets mentioned in the diagram). b. Set up the router by configuring the interfaces and DHCP (use the subnets mentioned in the diagram). c. Set up each host with DHCP to obtain IP configuration and verify the IP address and the default gateway configured. d. Verify the connectivity between each host in the network.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


