Question: Activity Overview: In this graded activity, students will determine subnet scopes, assess routing metrics and paths, identify aspects of ACL's and Firewalls, and design an
Activity Overview: In this graded activity, students will determine subnet scopes, assess routing metrics and paths, identify aspects of ACL's and Firewalls, and design an IPv4 address space.
Activity Outcomes: After completing this activity you should be able to
- Apply IP-Addressing conventions to subnet composition
- Identify ACL and Firewall rules, and their components
- Understand routing metrics and path determination
- Identify commonly used TCP/UDP ports
Subnet Scope Exercises
Determine the Network ID, Host Range, and Broadcast ID for the following IP Addresses:
You are permitted to utilize an online subnet calculator (https://www.subnet-calculator.com/)
or Subnet Calculator 2
| 192.168.100.215 /28 |
| 10.12.140.99 /17 |
| 172.16.24.101 /21 |
| 195.100.0.66 /30 |
| 13.100.23.3 /10 |

Subnetting Cheat Sheet
IP-Address Space Design
You are permitted to utilize an online subnet calculator (https://www.subnet-calculator.com/) or Subnet Calculator 2
come up with a subnet scheme that includes the following:
A) Subnet scheme that can fit 200 subnets with a minimum size of 1,024 IP's using a Class A private address space (10.x.x.x)
B) Subnet scheme that can fit 80 subnets with a minimum size of 256 IP's each, using a Class B private address space (172.16.x.x)
C) 3 (three) subnets for Router-to-Router connections using private Class C /30 address space (192.168.x.x.)
Document your subnets as written below (You only need to list the first subnet for part A and B):
Class A - x.x.x.x /xx
Class B - x.x.x.x /xx
Router to Router 1 - x.x.x.x /30
Router to Router 2 - x.x.x.x /30
Router to Router 3 - x.x.x.x /30
Please join us for live lecture or watch the archive if you need a reminder on this process.
Routing Metric Exercise
Complete both sets of routing metric exercises below. The goal is to determine the path between each network with the lowest total "cost". The metrics for each path are identified on each connecting line.
- What is the most efficient path to take, based upon the metrics given? (Remember: the lower the metric, the more efficient the path)
- Network A - Network B
- Network A - Network C
- Network A - Network D
- Network B - Network C
- Network B - Network D
- Network C - Network D
Format "Router #(Total Path Cost)":
"Network A - Network D: 1(0), 2(1), 3(2), 5(4), 8(5), 10(6), 11(8)"
Use the image above to answer the first set of routing metric questions
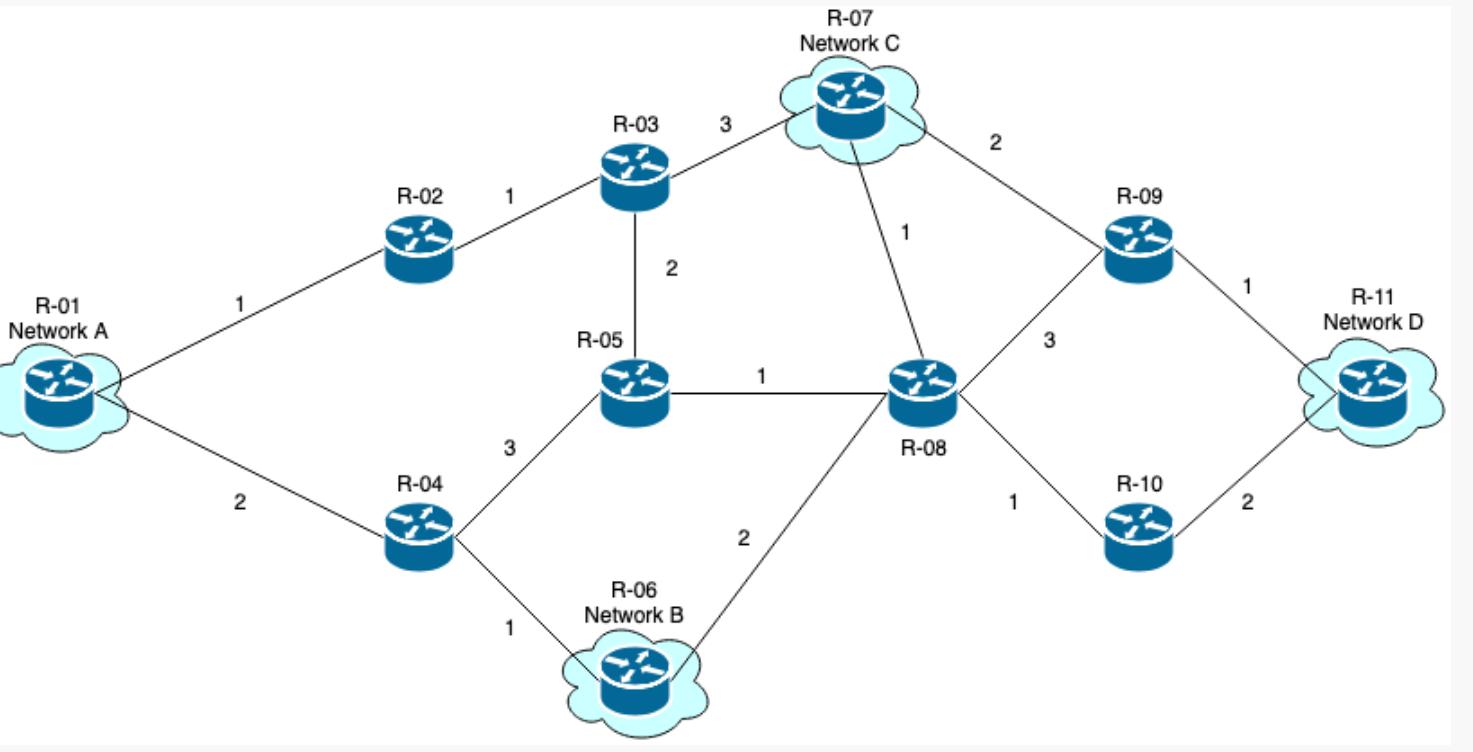
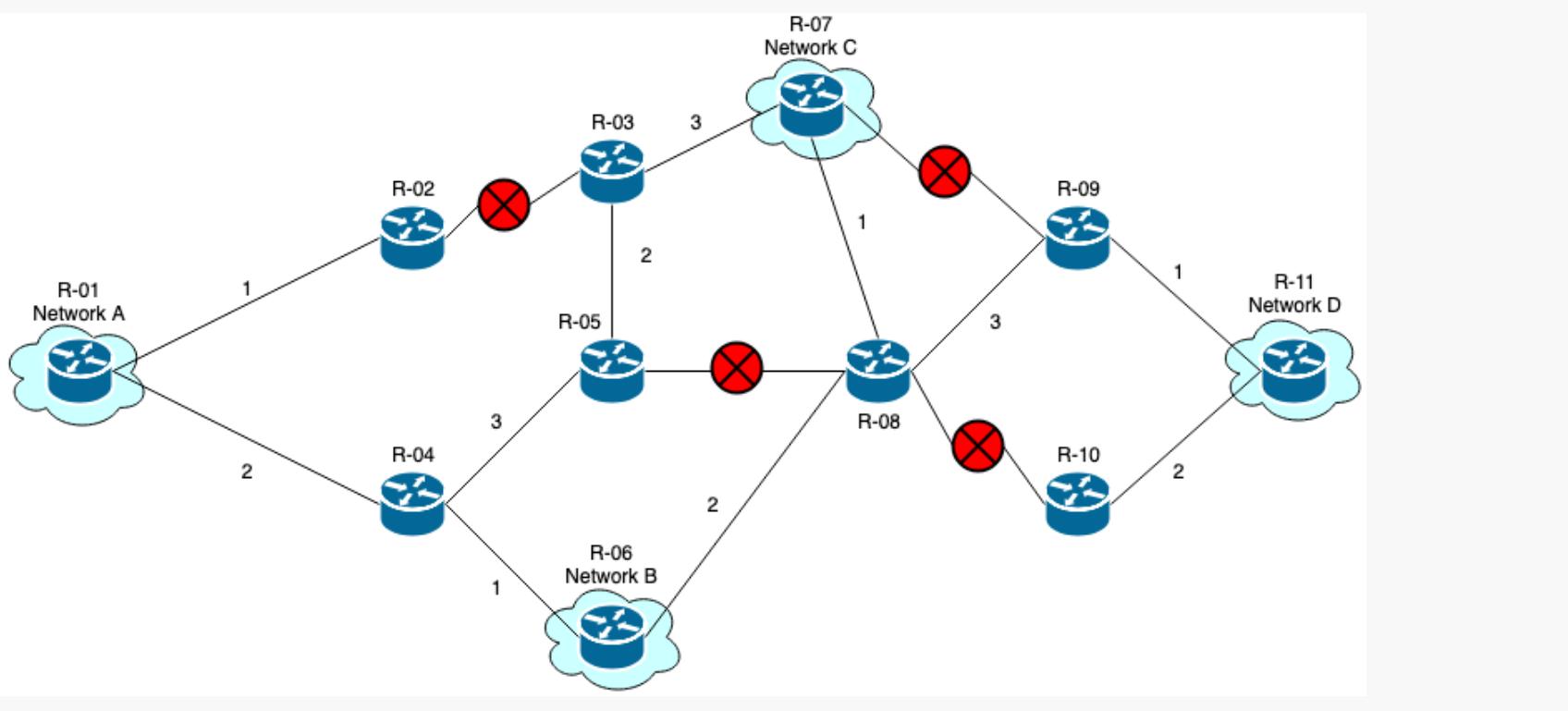
- What is the most efficient path to take, based upon the metrics given?
- Network A - Network B
- Network A - Network C
- Network A - Network D
- Network B - Network C
- Network B - Network D
- Network C - Network D
Format "Router #(Total Path Cost)":
"Network A - Network D: 1(0), 2(1), 3(2), 5(4), 8(5), 10(6), 11(8)"
10.12.40.100/12 (Class A Private IP: Default subnet of /8) NETWORK SUBNET HOST IP Address in BINARY: 00001010.00001100.00101000. 01100100 Subnet in BINARY: 1111111111110000.00000000.00000000 Logical AND Process: 00001010.00000000.00000000.00000000 Convert back to Dotted Decimal: 10.0.0.0/12 Change Host O's into 1's: Network ID for the Host (The HOST portion is all O's) 00001010.00001111. 11111111 11111111 Broadcast Address for the Host (The HOST portion is all 1's) Convert back to Dotted Decimal: 10.15.255.255/12 Then find the first and last available IP addresses by adding 1 to the Network ID (1st), and subtracting 1 from the Broadcast Address (Last). 10.0.0.1 10.15.255.254
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Subnet Scope Exercises Lets determine the Network ID Host Range and Broadcast ID for the given IP Addresses 192168100215 28 Subnet Mask 255255255240 N... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


