Question: Aggregate Planning Example Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total 200 300 400 500 200 1,800 Forecast 200 Costs Output Regular time =
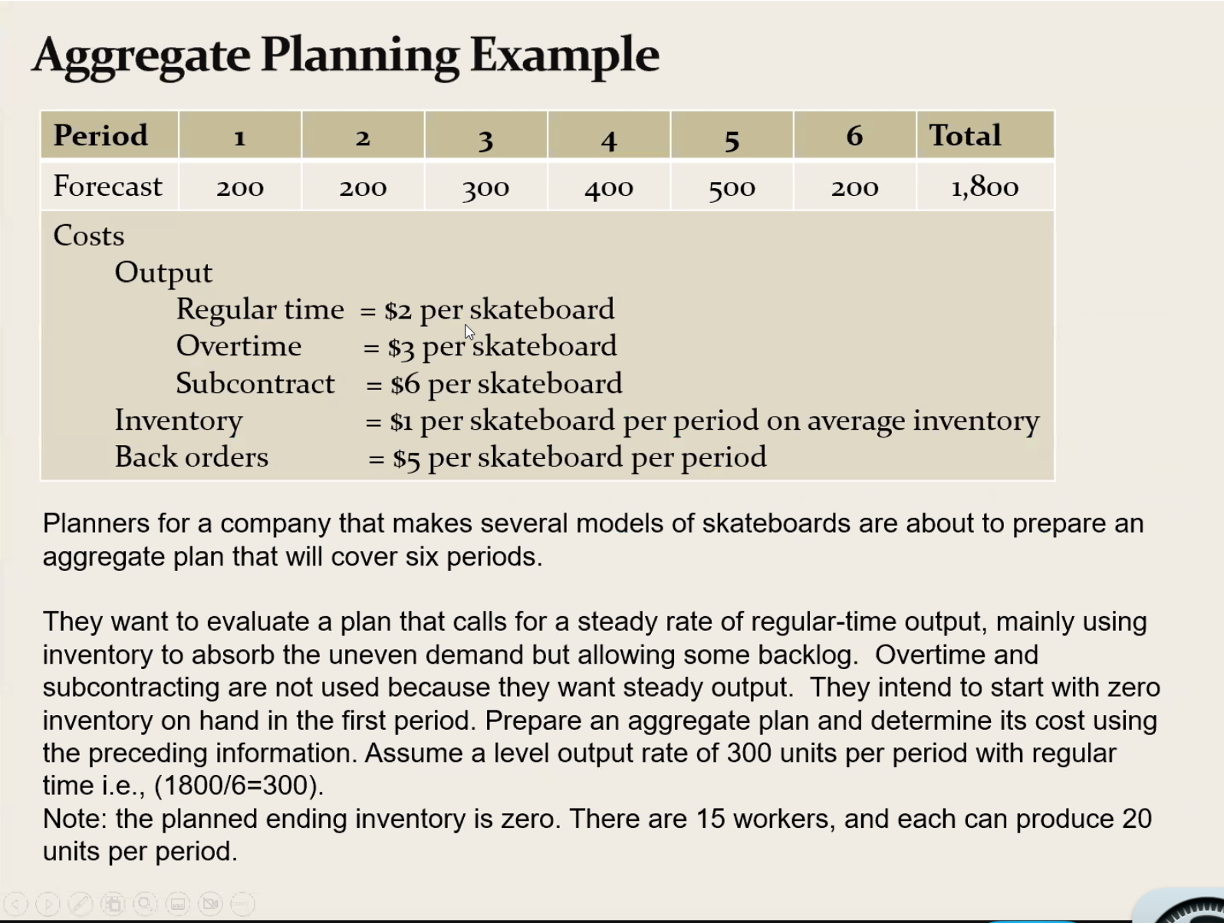
Aggregate Planning Example Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total 200 300 400 500 200 1,800 Forecast 200 Costs Output Regular time = $2 per skateboard Overtime = $3 per skateboard Subcontract = $6 per skateboard Inventory Back orders = $1 per skateboard per period on average inventory = $5 per skateboard per period Planners for a company that makes several models of skateboards are about to prepare an aggregate plan that will cover six periods. They want to evaluate a plan that calls for a steady rate of regular-time output, mainly using inventory to absorb the uneven demand but allowing some backlog. Overtime and subcontracting are not used because they want steady output. They intend to start with zero inventory on hand in the first period. Prepare an aggregate plan and determine its cost using the preceding information. Assume a level output rate of 300 units per period with regular time i.e., (1800/6=300). Note: the planned ending inventory is zero. There are 15 workers, and each can produce 20 units per period.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


