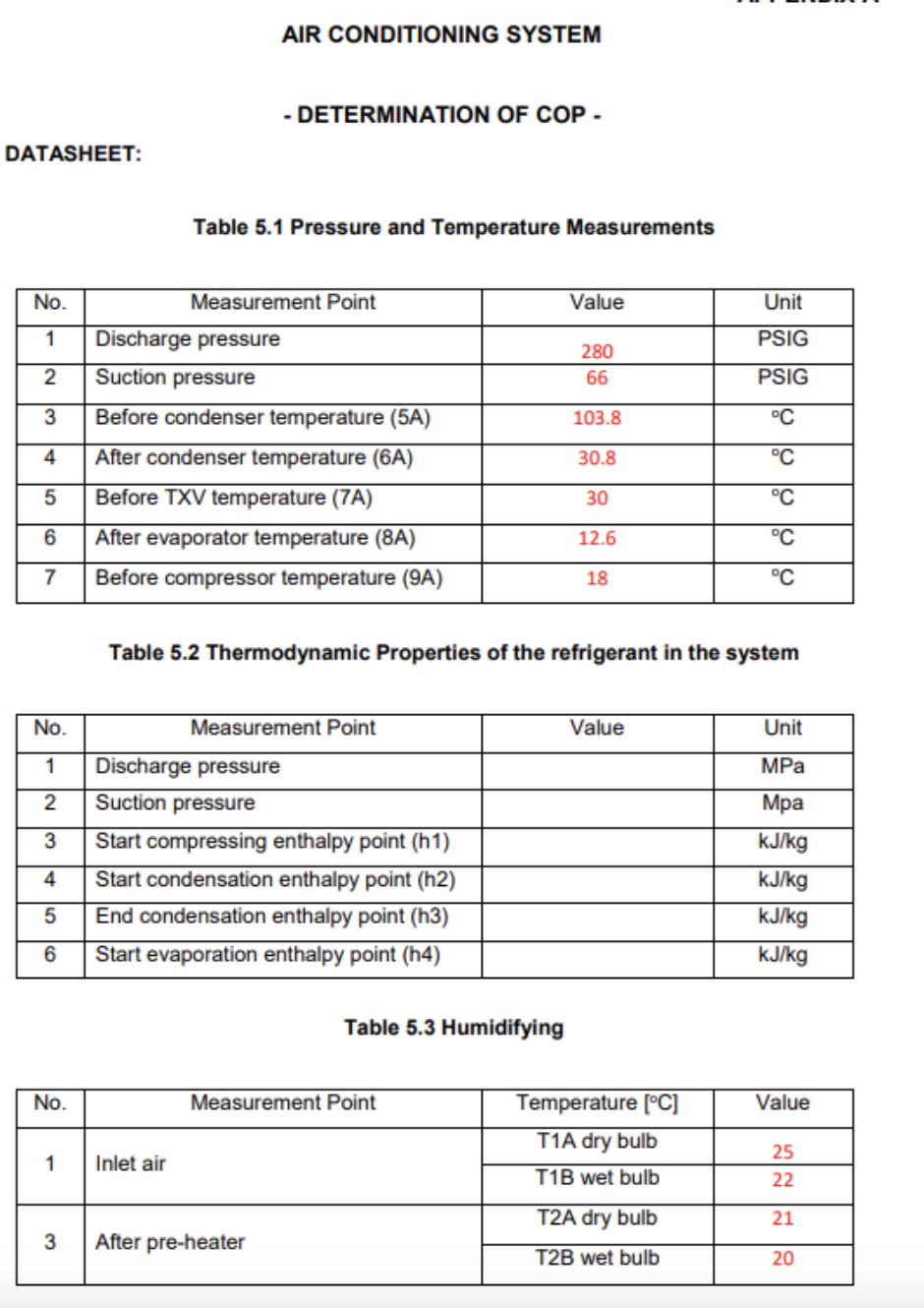
Question: AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM - DETERMINATION OF COP . DATASHEET: Table 5.1 Pressure and Temperature Measurements Table 5.2 Thermodynamic Properties of the refrigerant in the system
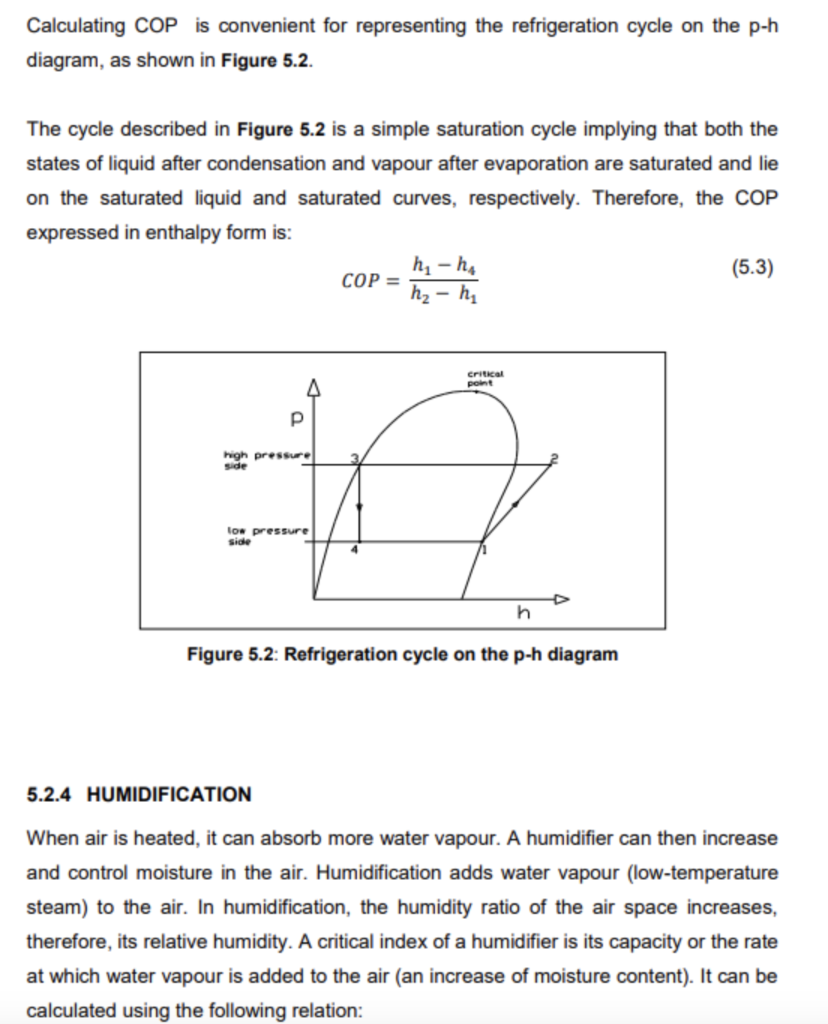


AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM - DETERMINATION OF COP . DATASHEET: Table 5.1 Pressure and Temperature Measurements Table 5.2 Thermodynamic Properties of the refrigerant in the system Table 5.3 Humidifying Calculating COP is convenient for representing the refrigeration cycle on the ph diagram, as shown in Figure 5.2. The cycle described in Figure 5.2 is a simple saturation cycle implying that both the states of liquid after condensation and vapour after evaporation are saturated and lie on the saturated liquid and saturated curves, respectively. Therefore, the COP expressed in enthalpy form is: COP=h2h1h1h4 Figure 5.2: Refrigeration cycle on the ph diagram 5.2.4 HUMIDIFICATION When air is heated, it can absorb more water vapour. A humidifier can then increase and control moisture in the air. Humidification adds water vapour (low-temperature steam) to the air. In humidification, the humidity ratio of the air space increases, therefore, its relative humidity. A critical index of a humidifier is its capacity or the rate at which water vapour is added to the air (an increase of moisture content). It can be calculated using the following relation: m=V(sm) Where: m : Increase of moisture content, [kg/s] V : Supply volume flow rate, [m3/s] : Density of supply air, [kg/m3] s,m: Moisture content of supply and mixture air, respectively The value V can be calculated as follows: V=Au Where: A : Duct cross-section area, [m2] u : Air velocity, [m/s] 5.2.5 AIR FLOW MEASUREMENT The air velocity, u can be calculated using Bernoulli's equation: P1+21u12=P2+22u22 The subscripts 1 and 2 are referred to as the inlet and outlet of the airflow within the duct. Rearranging the equation, it becomes: P1P2=P+22u2221u12 The value p can determine using a water manometer. P=gh Where: : Density of water, [kg/m3] g : Gravity constant, [ m2/s], and h : Velocity pressure in inches of water, [m]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


