Question: Algorithm to implement: Implement the randomized (divide and conquer) selection algorithm described in section 2.4 in the book that returns the k-th smallest value in
 Algorithm to implement:
Algorithm to implement:
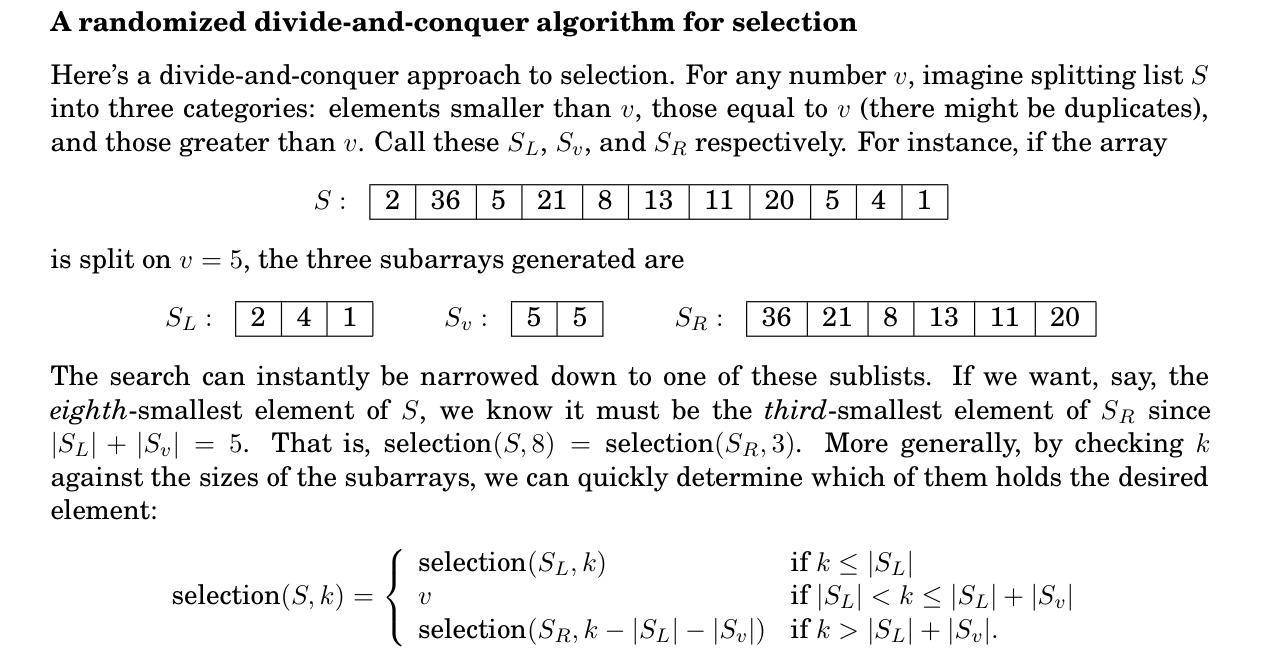
Implement the randomized (divide and conquer) selection algorithm described in section 2.4 in the book that returns the k-th smallest value in an array of n integers. Your code should input n and k as command line parameters. Next generate an array of n random integers in the range [0,n1]. You should generate these n integers independently so that you can have duplicate values in the array. Your code should return the k-th smallest value in the array. Note that k ranges from 1 to n, i.e., k=1 means return the smallest value, k=10 means returns the 10 -th smallest value, and so on. Print out the k-th smallest value in the array, followed by the original array, and the sorted array. For example, on the array [5,8,9,5,0,0,1,7,6,9] the output for k=3 should be: select 1 array [5,8,9,5,0,0,1,7,6,9] sorted array [0,0,1,5,5,6,7,8,9,9] That is, the 3 rd smallest value is 1 , as we can see from the sorted array. Test you code on larger n and k values. Note that for sorting you can use the inbuilt Python sort function. It is just for testing your output. You will find the Python numpy module very useful for this assignment. For example, you can use numpy.random.randint to generate random integers. A randomized divide-and-conquer algorithm for selection Here's a divide-and-conquer approach to selection. For any number v, imagine splitting list S into three categories: elements smaller than v, those equal to v (there might be duplicates), and those greater than v. Call these SL,Sv, and SR respectively. For instance, if the array S is split on v=5, the three subarrays generated are SL:41Sv:55 The search can instantly be narrowed down to one of these sublists. If we want, say, the eighth-smallest element of S, we know it must be the third-smallest element of SR since SL+Sv=5. That is, selection (S,8)=selection(SR,3). More generally, by checking k against the sizes of the subarrays, we can quickly determine which of them holds the desired element: selection(S,k)=selection(SL,k)vselection(SR,kSLSv)ifkSLifSL
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


