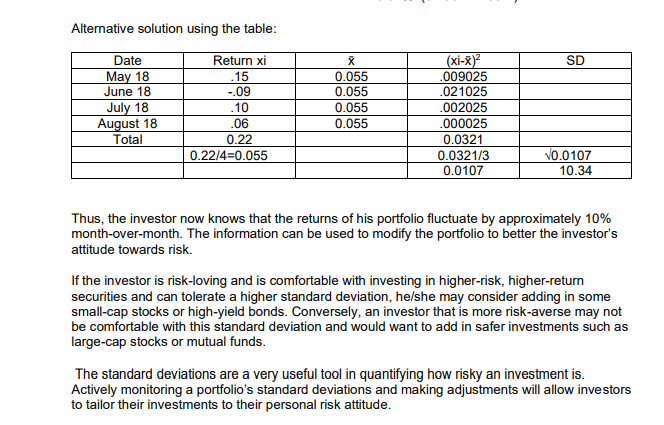
Question: Alternative solution using the table: Date Return xi X (xi-x)2 SD May 18 15 0.055 009025 June 18 -.09 0.055 021025 July 18 10 0.055


Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


