Question: Amazons Kindle Fire - Business Model - This case assignment focuses on the trade-offs between different business models and how to do the financial calculations
Amazons Kindle Fire - Business Model - This case assignment focuses on the trade-offs between different business models and how to do the financial calculations in evaluating a business model. (attached ppt. for more details) Additional Tips Do this assignment at the unit economics level, that means on a single device. Don't worry about IRR. Focus on Revenue, Cost, Contribution, and how these grow through time. In the end, you should understand how much money Amazon made out of this in the three years. Need to submit in the attached (screenshot excel format only).










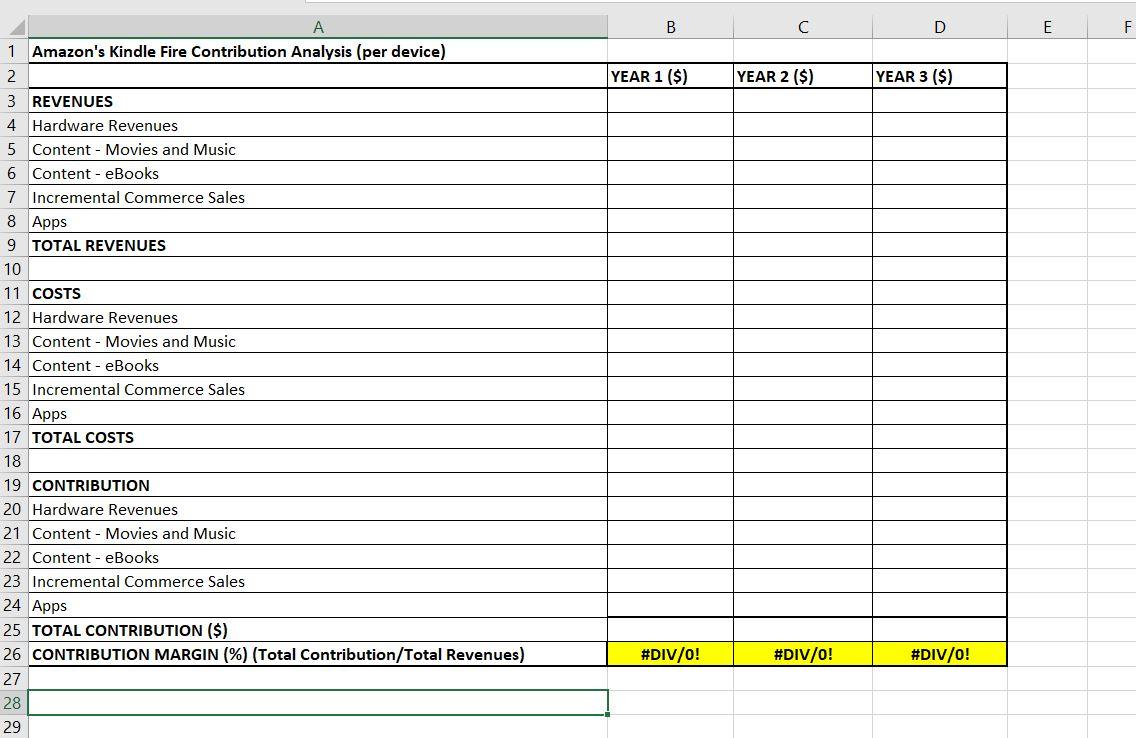
Amazon's Kindle Fire Analyzing the Razor- Razor Blade Business Model This case assignment focuses on the trade-offs between different business models and how to do the financial calculations in evaluating a business model. The case study describes a risky and innovative business model that Amazon created for its low-cost tablet, the Kindle Fire. Amazon introduced the Kindle Fire tablet in 2011 , priced at only $199, well below the price point of Apple's iPad. As opposed to Apple, which made money from selling the hardware, Amazon was betting that it could sell the Kindle Fire hardware close to its cost, but make money through increased content and commerce sales that would result from consumers using the Kindle Fire tablet to buy more stuff and consume more content from the Amazon ecosystem. This is the "Razor-Razor Blade" business model. Was Amazon's bet justified? Would the incremental profits from content and commerce compensate for the massive subsidy that Amazon was offering on the price of the Kindle Fire? It is your job to find out! The Kindle Fire Tablet Amazon launched the Kindle Fire in November 2011 The \$199 tablet featured a 7-inch, color LCD touchscreen with Wi-Fi radio, 8GB of storage and free cloud storage for content purchased from Amazon The tablet leveraged Amazon's cloud-based services, such as the Amazon Silk web browser, which featured cloud-based acceleration to improve performance The Kindle Fire came with thousands of preapproved apps and games available for purchase and download, but it did not work with the Android App store as the operating system was a modified version of Android Amazon also offered its extensive content catalog, including 18 million movies, TV shows, songs and magazines available for streaming or download The Kindle Fire was bundled with a free one-month subscription to Amazon Prime, a gateway to Amazon content, goods and services. Kindle Fire: Target Customer Segments Kids aged 8-12 years who needed a cheap, rugged tablet to play games and watch videos at home Media junkies who watched movies, listened to music and bought a lot of content from Amazon College students looking for an "electronic backpack" to replace their expensive and bulky textbooks Kindle Fire Competitors Kindle Fire Price and Revenue Streams Tablet price: $199 (believed to be at cost) Razor-Razor Blade Business model In this model, the base product (the razor) and dependent goods are sold at varying prices. One product is sold at a discount (razor) while another is sold at a considerable higher price to make up for the loss (razor blades) Amazon has four revenue streams 1. Hardware (tablet sales $199/ tablet) 2. Content Revenues Music \&t Movies eBooks 3. Incremental Commerce Sales 4. Apps sales Content Revenues: Assumptions Movies and Music The average customer will purchase $10 /month in content (including music and movies) These content revenues will increase 10% annually for the next two years Amazon's gross margin on content is 30% E-Books - Average customer will purchase 3 e-books/quarter at $10 /book These e-book revenues will 10% increase annually Amazon's gross margin on e-books is 20% Incremental Commerce Revenues: Assumptions The average Kindle Fire customer will purchase $50/ month in incremental Amazon products/services These commerce revenues will increase by 5% each year Amazon's gross margin on commerce revenues is 20% op Revenues: Assumptions The Amazon Appstore had logged 180 million app downloads in 18 months Of these downloads, 10% were paid apps The average app generated $1.29 in revenue Amazon's share of these app revenues was 30% App revenues would increase by 20% annually 1 million devices were sold in Year 1 Your Assignment 1. Calculate the revenues and profits for the Amazon Kindle Fire by estimating the revenues and gross contribution margin* for: Hardware - Content revenues Commerce revenues App sales 2. Estimate the revenues over a 3-year time frame, assuming that the Kindle Fire has a 3-year life 3. Based on your calculations, what are the most important drivers of revenues for Amazon's Kindle Fire? How about drivers of profit? 4. Do you think Amazon's bet of selling the Kindle Fire at cost will pay off? Justify your position. * Contribution margin calculates per-item profit as opposed to gross margin which calculates the total profit metric for the entire company Steps in the analysis Step 1: Calculate the revenues from each of the revenue streams for three years, making sure you increase the revenues in year 2 and year 3 based on the information in the case. Step 2: Calculate the costs from each of the revenue streams for three years, based on the gross margins for each of the revenue streams. Tip: If the gross margin is 30%, then every $100 in revenues consists of $70 in cost and $30 in margin for Amazon. Step 3: Calculate the contribution from each of the revenue streams by subtracting the costs from the revenues for each revenue stream. Step 4: Calculate the total contribution from the Kindle Fire by adding up the contributions from all the revenue streams. Step 5: Assess the relative importance of the revenue streams by looking at their relative values. their relative values. Amazon's Kindle Fire Analyzing the Razor- Razor Blade Business Model This case assignment focuses on the trade-offs between different business models and how to do the financial calculations in evaluating a business model. The case study describes a risky and innovative business model that Amazon created for its low-cost tablet, the Kindle Fire. Amazon introduced the Kindle Fire tablet in 2011 , priced at only $199, well below the price point of Apple's iPad. As opposed to Apple, which made money from selling the hardware, Amazon was betting that it could sell the Kindle Fire hardware close to its cost, but make money through increased content and commerce sales that would result from consumers using the Kindle Fire tablet to buy more stuff and consume more content from the Amazon ecosystem. This is the "Razor-Razor Blade" business model. Was Amazon's bet justified? Would the incremental profits from content and commerce compensate for the massive subsidy that Amazon was offering on the price of the Kindle Fire? It is your job to find out! The Kindle Fire Tablet Amazon launched the Kindle Fire in November 2011 The \$199 tablet featured a 7-inch, color LCD touchscreen with Wi-Fi radio, 8GB of storage and free cloud storage for content purchased from Amazon The tablet leveraged Amazon's cloud-based services, such as the Amazon Silk web browser, which featured cloud-based acceleration to improve performance The Kindle Fire came with thousands of preapproved apps and games available for purchase and download, but it did not work with the Android App store as the operating system was a modified version of Android Amazon also offered its extensive content catalog, including 18 million movies, TV shows, songs and magazines available for streaming or download The Kindle Fire was bundled with a free one-month subscription to Amazon Prime, a gateway to Amazon content, goods and services. Kindle Fire: Target Customer Segments Kids aged 8-12 years who needed a cheap, rugged tablet to play games and watch videos at home Media junkies who watched movies, listened to music and bought a lot of content from Amazon College students looking for an "electronic backpack" to replace their expensive and bulky textbooks Kindle Fire Competitors Kindle Fire Price and Revenue Streams Tablet price: $199 (believed to be at cost) Razor-Razor Blade Business model In this model, the base product (the razor) and dependent goods are sold at varying prices. One product is sold at a discount (razor) while another is sold at a considerable higher price to make up for the loss (razor blades) Amazon has four revenue streams 1. Hardware (tablet sales $199/ tablet) 2. Content Revenues Music \&t Movies eBooks 3. Incremental Commerce Sales 4. Apps sales Content Revenues: Assumptions Movies and Music The average customer will purchase $10 /month in content (including music and movies) These content revenues will increase 10% annually for the next two years Amazon's gross margin on content is 30% E-Books - Average customer will purchase 3 e-books/quarter at $10 /book These e-book revenues will 10% increase annually Amazon's gross margin on e-books is 20% Incremental Commerce Revenues: Assumptions The average Kindle Fire customer will purchase $50/ month in incremental Amazon products/services These commerce revenues will increase by 5% each year Amazon's gross margin on commerce revenues is 20% op Revenues: Assumptions The Amazon Appstore had logged 180 million app downloads in 18 months Of these downloads, 10% were paid apps The average app generated $1.29 in revenue Amazon's share of these app revenues was 30% App revenues would increase by 20% annually 1 million devices were sold in Year 1 Your Assignment 1. Calculate the revenues and profits for the Amazon Kindle Fire by estimating the revenues and gross contribution margin* for: Hardware - Content revenues Commerce revenues App sales 2. Estimate the revenues over a 3-year time frame, assuming that the Kindle Fire has a 3-year life 3. Based on your calculations, what are the most important drivers of revenues for Amazon's Kindle Fire? How about drivers of profit? 4. Do you think Amazon's bet of selling the Kindle Fire at cost will pay off? Justify your position. * Contribution margin calculates per-item profit as opposed to gross margin which calculates the total profit metric for the entire company Steps in the analysis Step 1: Calculate the revenues from each of the revenue streams for three years, making sure you increase the revenues in year 2 and year 3 based on the information in the case. Step 2: Calculate the costs from each of the revenue streams for three years, based on the gross margins for each of the revenue streams. Tip: If the gross margin is 30%, then every $100 in revenues consists of $70 in cost and $30 in margin for Amazon. Step 3: Calculate the contribution from each of the revenue streams by subtracting the costs from the revenues for each revenue stream. Step 4: Calculate the total contribution from the Kindle Fire by adding up the contributions from all the revenue streams. Step 5: Assess the relative importance of the revenue streams by looking at their relative values. their relative values















