Question: An order 5 ordinary differental equation with a single dependent variable y(t) is converted into a first order system of differential equations x =

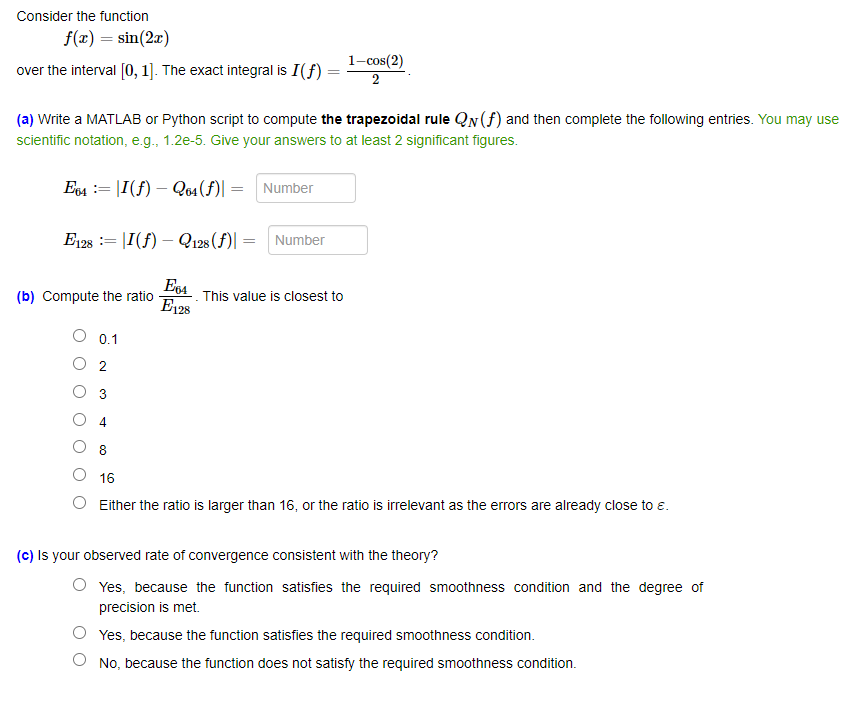
An order 5 ordinary differental equation with a single dependent variable y(t) is converted into a first order system of differential equations x = f(t, x). The number of elements in the vector is 10 7 5 Consider the function f(x) = sin(2x) 1-cos(2) over the interval [0,1]. The exact integral is I(f) 2 (a) Write a MATLAB or Python script to compute the trapezoidal rule QN(f) and then complete the following entries. You may use scientific notation, e.g., 1.2e-5. Give your answers to at least 2 significant figures. E64|I(f)-Q64(f)| = = Number E128= |I(f) - Q128 (f)| = Number E64 (b) Compute the ratio This value is closest to E128 0.1 2 16 Either the ratio is larger than 16, or the ratio is irrelevant as the errors are already close to . (c) Is your observed rate of convergence consistent with the theory? Yes, because the function satisfies the required smoothness condition and the degree of precision is met. Yes, because the function satisfies the required smoothness condition. No, because the function does not satisfy the required smoothness condition.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


