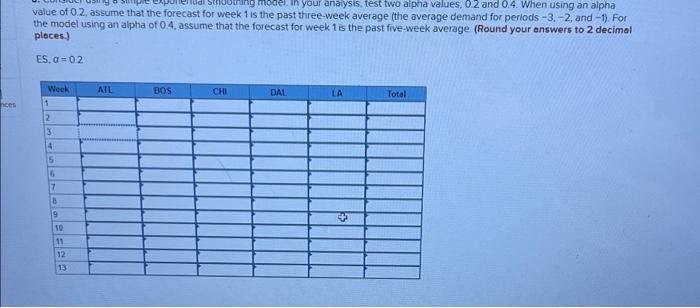
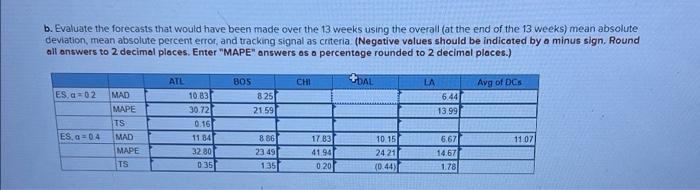
Question: Analytics Exercise 3-02 (Algo) Starbucks has a large global supply chain that must efficiently supply over 17000 stores. Although the stores might appear to be
Analytics Exercise 3-02 (Algo) Starbucks has a large global supply chain that must efficiently supply over 17000 stores. Although the stores might appear to be very Similar, they are actually very different. Depending on the location of the store, its size, and the profile of the customers served, Starbucks management configures the store offerings to take maximum advantage of the space available and customer preferences Starbucks' actual distribution system is much more complex, but for the purpose of our exercise let's focus on a single item that is currently distributed through five distribution centers in the United States. Our item is a logo-branded coffeemaker that is sold at some of the larger retail stores. The coffeemaker has been a steady seller over the years due to its reliability and rugged construction Starbucks does not consider this a seasonal product, but there is some variability in demand Demand for the product over the past 13 weeks is shown in the following table (week-1 is the week before week 1 in the table. -2 is two weeks before week 1, etc.) Management would like you to experiment with some forecasting models to determine what should be used in a new system to be Implemented. The new system is programmed to use one of two forecasting models simple moving average or exponential smoothing 3 36 4 33 WEEK Atlanta Boston Chicago Dallas LA Total 46 59 55 -3 -2 -1 35 32 54 34 26 48 41 33 22 68 42 44 36 38 62 45 41 52 42 37 160 238 241 193 1 33 35 46 26 35 125 46 34 33 28 40 181 25 34 45 153 5 55 28 46 46 42 69 50 62 47 .66 245 271 52 40 45 213 44 247 7 9 10 11 12 13 20 58 45 36 25 55 41 54 24 60 45 32 45 52 65 3a 24 96 35 14 42 68 62 48 42 36 43 42 42 35 39 42 46 53 49 249 209 216 261 174 240 231 Udi Su model in your analysis, test two alpha values, 02 and 0.4 When using an alpha value of 0.2, assume that the forecast for week 1 is the past three week average (the average demand for periods -3.-2, and -1). For the model using an alpha of 0.4 assume that the forecast for week is the past five-week average (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) ES, G=02 Week ATL BOS CHI DAL LA Total nes 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 19 10 11 32 13 b. Evaluate the forecasts that would have been made over the 13 weeks using the overall at the end of the 13 weeks) mean absolute deviation, mean absolute percent error, and tracking signal as criteria (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all answers to 2 decimal places. Enter "MAPE" answers as a percentage rounded to 2 decimal places.) ATL CHI TAL Avg of DCS ES -02 10.83 30.72 BOS 825 21 59 LA 6.44 13.99 0.16 MAD MAPE TS MAD MAPE TS ES a = 04 1107 11 841 32.80 0.35 8.86 23 49 135 1783 4194 0.20 10 15 2421 (0.44) 667 14.67 178 Analytics Exercise 3-02 (Algo) Starbucks has a large global supply chain that must efficiently supply over 17000 stores. Although the stores might appear to be very Similar, they are actually very different. Depending on the location of the store, its size, and the profile of the customers served, Starbucks management configures the store offerings to take maximum advantage of the space available and customer preferences Starbucks' actual distribution system is much more complex, but for the purpose of our exercise let's focus on a single item that is currently distributed through five distribution centers in the United States. Our item is a logo-branded coffeemaker that is sold at some of the larger retail stores. The coffeemaker has been a steady seller over the years due to its reliability and rugged construction Starbucks does not consider this a seasonal product, but there is some variability in demand Demand for the product over the past 13 weeks is shown in the following table (week-1 is the week before week 1 in the table. -2 is two weeks before week 1, etc.) Management would like you to experiment with some forecasting models to determine what should be used in a new system to be Implemented. The new system is programmed to use one of two forecasting models simple moving average or exponential smoothing 3 36 4 33 WEEK Atlanta Boston Chicago Dallas LA Total 46 59 55 -3 -2 -1 35 32 54 34 26 48 41 33 22 68 42 44 36 38 62 45 41 52 42 37 160 238 241 193 1 33 35 46 26 35 125 46 34 33 28 40 181 25 34 45 153 5 55 28 46 46 42 69 50 62 47 .66 245 271 52 40 45 213 44 247 7 9 10 11 12 13 20 58 45 36 25 55 41 54 24 60 45 32 45 52 65 3a 24 96 35 14 42 68 62 48 42 36 43 42 42 35 39 42 46 53 49 249 209 216 261 174 240 231 Udi Su model in your analysis, test two alpha values, 02 and 0.4 When using an alpha value of 0.2, assume that the forecast for week 1 is the past three week average (the average demand for periods -3.-2, and -1). For the model using an alpha of 0.4 assume that the forecast for week is the past five-week average (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) ES, G=02 Week ATL BOS CHI DAL LA Total nes 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 19 10 11 32 13 b. Evaluate the forecasts that would have been made over the 13 weeks using the overall at the end of the 13 weeks) mean absolute deviation, mean absolute percent error, and tracking signal as criteria (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all answers to 2 decimal places. Enter "MAPE" answers as a percentage rounded to 2 decimal places.) ATL CHI TAL Avg of DCS ES -02 10.83 30.72 BOS 825 21 59 LA 6.44 13.99 0.16 MAD MAPE TS MAD MAPE TS ES a = 04 1107 11 841 32.80 0.35 8.86 23 49 135 1783 4194 0.20 10 15 2421 (0.44) 667 14.67 178